Enlarging a VirtualBox VDI virtual disk
20th December 2018It is amazing how the Windows folder manages to grow on your C drive and on in a Windows 7 installation was the cause of my needing to expand the VirtualBox virtual machine VDI disk on which it was installed. After trying various ways to cut down the size, an enlargement could not be avoided. In all of this, it was handy that I had a recent backup for restoration after any damage.
The same thing meant that I could resort to enlarging the VDI file with more peace of mind than otherwise might have been the case. This needed use of the command line once the VM was shut down. The form of the command that I used was the following:
VBoxManage modifyhd <filepath/filename>.vdi --resize 102400
It appears that this also would work on a Windows host but mine was Linux and it did what I needed. The next step was to attach it to an Ubuntu VM and use GParted to expand the main partition to fill the newly available space. That does not mean that it takes up 100 GiB on my system just yet because these things can be left to grow over time and there is a way to shrink them too if you ever need to do just that. As ever, having a backup made before any such operation may have its uses if anything goes awry.
Sorting out sluggish start-up and shutdown times in Linux Mint 19
9th August 2018The Linux Mint team never pushes anyone into upgrading to the latest version of their distribution but curiosity often is strong enough an impulse to make me do just that. When it brings me across some rough edges, then the wisdom of leaving things alone is evident. Nevertheless, doing so also brings its share of learning and that is what I am sharing in this post. It also also me to collect a number of titbits that may be of use to others.
Again, I went with the in-situ upgrade option though the addition of the Timeshift backup tool means that it is less frowned upon than once would have been the case. It worked well too part from slow start-up and shutdown times so I set about track down the causes on the two machines that I have running Linux Mint. As it happens, the cause was different on each machine.
On one PC, it was networking that holding up things. The cause was my specifying a fixed IP address in /etc/network/interfaces instead of using the Network Settings GUI tool. Resetting the configuration file back to its defaults and using the Cinnamon settings interface took away the delays. It was inspecting /var/log/boot.log that highlighted problem so that is worth checking if I ever encounter slow start times again.
As I mentioned earlier, the second PC had a very different problem though it also involved a configuration file. What had happened was that /etc/initramfs-tools/conf.d/resume contained the wrong UUID for my system’s swap drive so I was seeing messages like the following:
W: initramfs-tools configuration sets RESUME=UUID=<specified UUID for swap partition>
W: but no matching swap device is available.
I: The initramfs will attempt to resume from <specified file system location>
I: (UUID=<specified UUID for swap partition>)
I: Set the RESUME variable to override this.
Correcting the file and executing the following command fixed the issue by updating the affected initramfs image for all installed kernels and speeded up PC start-up times:
sudo update-initramfs -u -k all
Though it was not a cause of system sluggishness, I also sorted another message that I kept seeing during kernel updates and removals on both machines. This has been there for a while and causes warning messages about my system locale not being recognised. The problem has been described elsewhere as follows: /usr/share/initramfs-tools/hooks/root_locale is expecting to see individual locale directories in /usr/lib/locale but locale-gen is configured to generate an archive file by default. Issuing the following command sorted that:
sudo locale-gen --purge --no-archive
Following these, my new Linux Mint 19 installations have stabilised with more speedy start-up and shutdown times. That allows me to look at what is on Flathub to see what applications and if they get updated to the latest version on an ongoing basis. That may be a topic for another entry on here but the applications that I have tried work well so far.
Restoring GRUB for dual booting of Linux and Windows
11th April 2015Once you end up with Windows overwriting your master boot record (MBR), you have lost the ability to use GRUB. Therefore, it would be handy to get it back if you want to start up Linux again. Though the loss of GRUB from the MBR was a deliberate act of mine, I knew that I’d have to restore GRUB to get Linux working again.So, I have been addressing the situation with a Live DVD for the likes of Ubuntu or Linux Mint. Once one of those had loaded its copy of the distribution, issuing the following command in a terminal session gets things back again:
sudo grub-install --root-directory=/media/0d104aff-ec8c-44c8-b811-92b993823444 /dev/sda
When there were error messages, I tried this one to see if I could get more information:
sudo grub-install --root-directory=/media/0d104aff-ec8c-44c8-b811-92b993823444 /dev/sda --recheck
Also, it is possible to mount a partition on the boot drive and use that in the command to restore GRUB. Here is the required combination:
sudo mount /dev/sda1 /mnt
sudo grub-install --root-directory=/mnt /dev/sda
Either of these will get GRUB working without a hitch and they are far more snappy than downloading Boot-Repair and using that; I was doing that for a while until a feature on triple booting appeared in an issue of Linux User & Developer that reminded me of the more readily available option. Once, there was a need to manually add an entry for Windows 7 to the GRUB menu too and, with that instated, I was able to dual-boot Ubuntu and Windows using GRUB to select which one was to start for me. Since then, I have been able to dual boot Linux Mint and Windows 8.1 with GRUB finding the latter all by itself so your experiences too may show this variation so it’s worth bearing in mind.
Do we need to pay for disk partitioning tools anymore?
29th November 2010My early explorations of dual-booting of Windows and Linux led me into the world of disk partitioning. It also served a another use since any Windows 9x installations (that dates things a bit…) that I had didn’t have a tendency to last longer than six months at one point; putting the data on another partition meant that a fresh Windows installation didn’t jeopardise any data that I had should a mishap occur.
Then, Partition Magic was the favoured tool and it wasn’t free of charge, though it wasn’t extortionately priced either. For those operations that couldn’t be done with Windows running, you could create bootable floppy disks to get the system going in order to perform those. Thinking about it now, it all worked well enough and the usual caveats about taking care with your data applied as much then as they do now.
For the last few years, many Linux distributions have coming in the form of CD’s or DVD’s from which you can boot into a full operating system session, complete with near enough the same GUI that an installed version. When a PC is poorly, this is a godsend and makes me wonder how we managed without; having that visual way of saving data sounds all too necessary now. For me, the answer to that is that I misspent too many hours blundering blindly using the very limited Windows command line to get myself out of a crux. Looking back on it now, it all feels very dark compared to today.
Another good aspect to these Live Distribution Disks is that they come with hard disk partitioning tools such as the effective GParted. They are needed to configure hard drives during the actual installation process but they serve another process too: they can be used in place of the old proprietary software disks that were in use not so long ago. Being able to deal with the hard disk sizes available today is a very good thing as is coping with NTFS partitions along with the usual Linux options. The operations may be time consuming but they have seemed reliable so far and I hope that it stays that way in spite of any warning that get issued but you make any changes. Last weekend, I got to see a lot of what that means and I setting up my Toshiba Equium laptop for Windows/Ubuntu dual booting.
With the capability that is available both free of charge and free of limitations, you cannot justify paying for disk partitioning software nowadays and that’s handy when you consider the state of the economy. It also shows how things have changed over the last decade. Being able to load up a complete operating system from a DVD also serves to calm any nerves when a system goes down on you, especially when you surf the web to find a solution for the malady that’s causing the downtime.
Restoring the MBR for Windows 7
25th November 2010During my explorations of dual-booting of Windows 7 and Ubuntu 10.10, I ended up restoring the master boot record (MBR) so that Windows 7 could load again or to find out if it wouldn’t start for me. The first hint that came to me when I went searching was the bootsect command but this only updates the master boot code on the partition so it did nothing for me. What got things going again was the bootrec command.
To use either of these, I needed to boot from a Windows 7 installation DVD. With my Toshiba Equium laptop, I needed to hold down the F12 key until I was presented with a menu that allowed me to choose from what drive I wanted to boot the machine, the DVD drive in this case. Then, the disk started and gave me a screen where I selected my location and moved to the next one where I selected the Repair option. After that, I got a screen where my Windows 7 installation was located. Once that was selected, I moved on to another screen from I started a command line session. Then, I could issue the commands that I needed.
bootsect /nt60 C:
This would repair the boot sector on the C: drive in a way that is compatible with BOOTMGR. This wasn’t enough for me but was something worth trying anyway in case there was some corruption.
bootrec /fixmbr
bootrec /fixboot
The first of these restores the MBR and the second sorts out the boot sector on the system drive (where the Windows directory resides on your system. In the event, I ran both of these and Windows restarted again, proving that it had come through disk partition changes without a glitch, though CHKDISK did run in the process but that’s understandable. There’s another option for those wanting to get back a boot menu and here it is:
bootrec /rebuildbcd
Though I didn’t need to do so, I ran that too but later used EasyBCD to remove the boot menu from the start-up process because it was surplus to my requirements. That’s a graphical tool that has gained something of a reputation since Microsoft dispensed with the boot.ini file that came with Windows XP for later versions of the operating system.
Manually adding an entry for Windows 7 to an Ubuntu GRUB2 menu
21st November 2010A recent endeavour of mine has been to set up a dual-booting arrangement on my Toshiba Equium laptop with Ubuntu 10.10 and Windows 7 side by side on there. However, unlike the same attempt with my Asus Eee PC where Windows XP coexists with Ubuntu, there was no menu entry on the GRUB (I understand that Ubuntu has had version 2 of this since 9.04 though the internal version is of the form 1.9x; you can issue grub-install -v at the command line to find out what version you have on your system) menu afterwards. Thankfully, I eventually figured out how to do this and the process is shared here in a more coherent order than the one in which I discovered all the steps.
The first step is to edit /etc/grub.d/40_custom (using SUDO) and add the following lines to the bottom of the file:
menuentry 'Windows 7' {
set root='(hd0,msdos2)'
chainloader +1
}
Since the location of the Windows installation can differ widely, I need to explain the “set root” line because (hd0,msdos2) refers to /dev/sda2 on my machine. More generally, hd0 (or /dev/sda elsewhere) refers to the first hard disk installed in any PC with hd1 (or /dev/sdb elsewhere) being the second and so on. While I was expecting to see entries like (hd0,6) in /boot/grub/grub.cfg, what I saw were ones like (hd0,msdos6) instead with the number in the text after the comma being the partition identifier; 1 is the first (sda1), 2 (sda2) is the second and so on. The next line (staring with chainloader) tells GRUB to load the first sector of the Windows drive so that it can boot. After all that decoding, my final remark on what’s above is a simple one: the text “Windows 7” is what will appear in the GRUB menu so you can change this as you see fit.
After saving 40_custom, the next step is to issue the following command to update grub.cfg:
sudo update-grub2
Once that has done its business, then you can look into /boot/grub/grub.cfg to check that the text added into 40_custom has found its way in there. That is important because this is the file read by GRUB2 when it builds the menu that appears at start-up time. A system reboot will prove conclusively that the new entry has been added successfully. Then, there’s the matter of selectively to see if Windows loads properly like it did for me, once I chose the correct disk partition for the menu entry, that is!
An introduction to Wubi
14th July 2008
The Toshiba laptop that I acquired at the start of the year is a Windows Vista box and it isn’t something with which I want to play too roughly because the OS came pre-installed on it. I still want to continue to see how Vista goes at close quarters so removing it to put Ubuntu or some other Linux distribution on there wasn’t ever going to be an option that I was willing to take either. Neither was the option of setting up a dual booting arrangement using disk partitioning; I have plenty of experience of doing that to set up dual booting machines over the years and I don’t needed any more than what I already have. So, I was happy to leave it as a Windows box and only as a Windows box.
That situation has changed and the cause was Canonical’s decision to go for something novel when it brought out Ubuntu 8.04. The premise is as follows: a Windows style installation that popped an entry in the Windows boot menu that allowed you to fire up Ubuntu without ever having to do disk partitioning or other similar rough play. For those who are less than enamoured with the Linux option, it’s even easy to remove too, as easy any other Windows program in fact. Removal of Linux is very definitely not what I’d do and that’s even without the pain and upheaval of more more customary means for setting dual booting machines. In these days of virtualisation and hypervisor technology, I have my ideas as to what has been used to give us that easy way in.
Being an Ubuntu user anyway, the possibility of having Ubuntu on the laptop and the interesting opportunity that Wubi offered for getting it on there was too tempting for me to give it a miss. A small download from the Wubi website is all that is needed to set things off. You get a number of options up front like where to put the (large) file to be used to house the Ubuntu world and how large you might want it. Setting a user name and password for the thing gets included among other items. The next stage is to download the files to be used to perform the installation. Once that is completed and it took me a few goes to get the whole lot (thankfully, it stores things up to the point where the downloading operation cuts out so you didn’t start from scratch each time; even so, it’s still annoying and could put some off), it is time to restart the computer and boot into Ubuntu to complete the set up of the operating system itself; it is at this point that the familiar very much returns. A reboot later and you are into a world that does its level best to fool you into thinking that Windows is another universe and never existed on that machine at all.
So, a machine that seemed destined only ever run Windows can run Linux now as well. Wubi comes across as a neat and clever way to get a dual booting computer and I hope to leave mine as I now have it. No feathers were ruffled on the Windows side and I saw no sign of any destruction. That makes Ubuntu’s way of doing things a much better option than other distributions that make you go down more invasive routes when creating a dual booting PC. A question remains in my mind. Could this approach take off?
Hard drive partitioning
22nd January 2007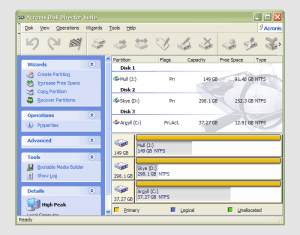 It has to be said that hard drive partitioning isn’t something that most people do very often, if at all in these days of cheap storage and system virtualisation. I must admit to having several disks in my main machine and can vouch for the virtues of virtualisation: VMware allows me to run multiple operating systems on the same machine, a very useful asset so long as enough memory is available. We can expect to hear more about virtualisation with the likes of Intel and AMD looking at hypervisor solutions for this.
It has to be said that hard drive partitioning isn’t something that most people do very often, if at all in these days of cheap storage and system virtualisation. I must admit to having several disks in my main machine and can vouch for the virtues of virtualisation: VMware allows me to run multiple operating systems on the same machine, a very useful asset so long as enough memory is available. We can expect to hear more about virtualisation with the likes of Intel and AMD looking at hypervisor solutions for this.
Partitioning does give you what appear to be multiple drives from just the one and that is very useful when you only have a single hard drive in your PC. This was very much the case in my early computing days when catastrophic Windows 9x crashes (some self-inflicted…) often resulted in the pain of a complete re-installation of everything that had been on there. The independence offered by partitions certainly offered me peace of mind back then but 100MB Iomega Zip disks were a very useful defence in depth.
Without partitioning, my curiosity regarding the world of Linux would not have been sated though an approach involving multiple hard drives certainly came into play later on. Having been a Sun Solaris user at university, Linux certainly aroused much interest in me and I have to say that it has come a long, long way since my first ventures into its world.
While the Windows tool FDISK could partition hard drives for you, it wasn’t non-destructive: you had be prepared to restore all of your files from a backup and do a complete software re-installation following its use. It was designed for setting things up at the outset and not changing them later and that thinking seems to have pervaded the design of the Disk Management console found in XP.
For more flexible and non-destructive partitioning, Powerquest’s Partition Magic became the tool of choice, though I did have a dalliance with a package called Partition It before taking the plunge. Partition Magic is now in the Symantec stable and not a lot seems to be heard of it. Version 7, the last from Powerquest before its takeover, has been my staple but 983 errors have been thrown by the application at times and one partitioning operation went awry, forcing me to depend on my backups. Version 8 still throws 983 errors so I started to look beyond Partition Magic altogether. In my search, I happened on version 10 of Acronis Disk Director Suite. It got a strong recommendation from reviewer Davey Winder in PC Pro magazine (backup software True Image 10 from the same company also got a thumbs up from a different PC Pro reviewer) which gave some reassurance and I have to say that I agree. An operation refused by Partition Magic was completed successfully and safely so I know where my vote goes.
Adding a new hard drive
21st January 2007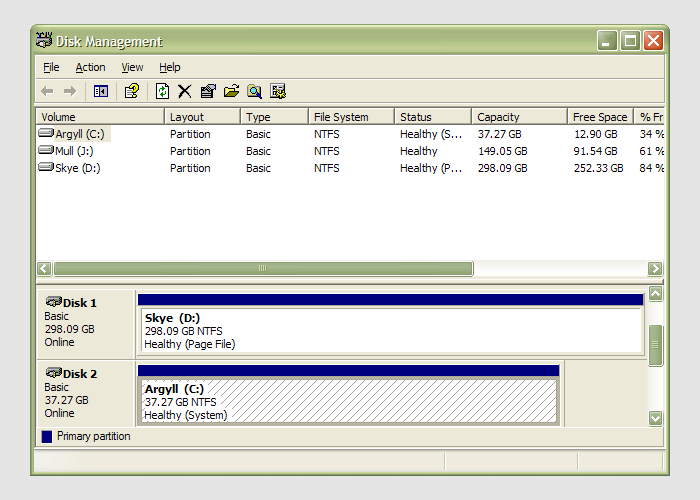
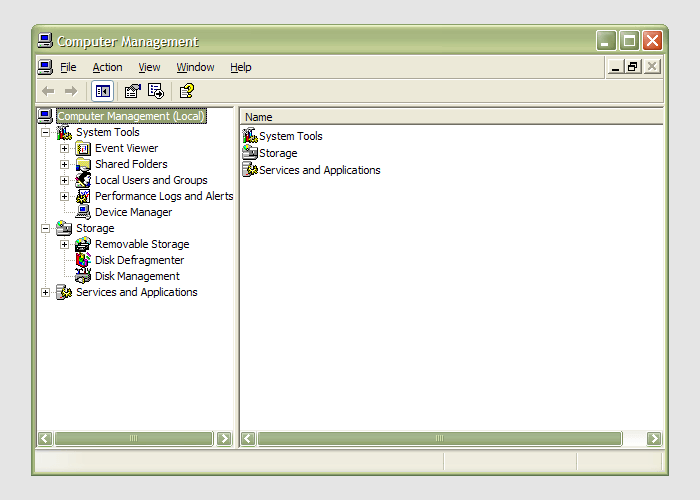 Having during the week obtained a new 320 GB hard drive, today I am adding it to my system after yesterdays scare with a PSU. As with any such item, you need to format and configure it to work with your operating system, be it Windows, Linux or whatever. Good old Partition Magic can help with this (I have version 7 from the Powerquest days) but Windows XP (Professional, anyway) does offer its own tool for the job: the Disk Management console. Unfortunately, it’s a bit hard to find. The easiest way to get to it is to type diskmgmt.msc into the Run command box. Otherwise, it is a matter of setting your Start Menu to show the Administrative Tools group (Taskbar and Start Menu properties> Start Menu tab > Customise > Advanced tab) and accessing through the computer Management console for which there is a shortcut in this group. Of course, you need to have administrator access to your PC in order to to do any of this.
Having during the week obtained a new 320 GB hard drive, today I am adding it to my system after yesterdays scare with a PSU. As with any such item, you need to format and configure it to work with your operating system, be it Windows, Linux or whatever. Good old Partition Magic can help with this (I have version 7 from the Powerquest days) but Windows XP (Professional, anyway) does offer its own tool for the job: the Disk Management console. Unfortunately, it’s a bit hard to find. The easiest way to get to it is to type diskmgmt.msc into the Run command box. Otherwise, it is a matter of setting your Start Menu to show the Administrative Tools group (Taskbar and Start Menu properties> Start Menu tab > Customise > Advanced tab) and accessing through the computer Management console for which there is a shortcut in this group. Of course, you need to have administrator access to your PC in order to to do any of this.