TOPIC: VMWARE
Trying out a new way to upgrade Linux Mint in situ while going from 17.3 to 18.1
19th March 2017There was a time when the only recommended way to upgrade Linux Mint from one version to another was to do a fresh installation with back-ups of data and a list of the installed applications created from a special tool.
Even so, it never stopped me doing my own style of in situ upgrade, though some might see that as a risky option. More often than not, that actually worked without causing major problems in a time when Linux Mint releases were more tightly tied to Ubuntu's own six-monthly cycle.
Linux Mint releases now align with Ubuntu's Long Term Support (LTS) editions. This means major changes occur only every two years, with minor releases in between. These minor updates are delivered through Linux Mint's Update Manager, making the process simple. Upgrades are not forced, so you can decide when to upgrade, as all main and interim versions receive the same extended support. The recommendation is to avoid upgrading unless something is broken on your installation.
For a number of reasons, I stuck with that advice by sticking on my main machine with Linux Mint 17.3 instead of upgrading to Linux Mint 18. The fact that I broke things on another machine using an older method of upgrading provided even more encouragement.
However, I subsequently discovered another means of upgrading between major versions of Linux Mint that had some endorsement from the project. There still are warnings about testing a live DVD version of Linux Mint on your PC first and backing up your data beforehand. Another task is ensuring that you are upgraded from a fully up-to-date Linux Mint 17.3 installation.
When you are ready, you can install mintupgrade using the following command:
sudo apt-get install mintupgrade
When that is installed, there is a sequence of tasks that you need to do. The first of these is to simulate an upgrade to test for the appearance of untoward messages and resolve them. Repeating any checking, until all is well, gets a recommendation. The command is as follows:
mintupgrade check
Once you are happy that the system is ready, the next step is to download the updated packages so they are on your machine ahead of their installation. Only then should you begin the upgrade process. The two commands that you need to execute are below:
mintupgrade download
mintupgrade upgrade
After these complete, restart your system. In my case, the process worked well, with only my PHP installation requiring attention. I resolved a clash between different versions of the scripting interpreter by removing the older one, as PHP 7 is best kept for testing. Apart from reinstalling VMware Player and upgrading from version 18 to 18.1, I had almost nothing else to do and experienced minimal disruption. This is fortunate as I rely heavily on my main PC. The alternative of a full installation would have left me sorting things out for several days afterwards because I use a customised selection of software.
Migrating a virtual machine from VirtualBox to VMware Player on Linux
1st February 2015The progress of Windows 10 is something that I have been watching. Early signs have been promising, and the most recent live event certainly contained its share of excitement. The subsequent build that was released was another step in the journey, though the new Start Menu appears more of a work in progress than it did in previous builds. Keeping up with these advances sometimes steps ahead of VirtualBox support for them, and I discovered that again in the last few days. VMware Player seems unaffected, so I thought that I'd try a migration of the VirtualBox VM with Windows 10 onto there. In the past, I did something similar with a 32-bit instance of Windows 7 that subsequently got upgraded all the way up to 8.1, but that may not have been as slick as the latest effort, so I thought that I would share it here.
The first step was to export the virtual machine as an OVF appliance, and I used File > Export Appliance... only to make a foolish choice regarding the version of OVF. The one that I picked was 2.0 only to subsequently discover that 1.0 was the better option. The equivalent command line would look like the following (there are two dashes before the ovf10 option below):
VboxManage export [name of VM] -o [name of file].ova --ovf10
VMware has a tool for extracting virtual machines from OVF files that will generate a set of files that will work with Player and other similar products of theirs. It goes under the unsurprising name of OVF Tool and usefully works from a command line session. When I first tried it with an OVF 2.0 files, I got the following error, and it stopped doing anything as a result:
Line 2: Incorrect namespace http://schemas.dmtf.org/ovf/envelope/2 found.
The only solution was to create a version 1.0 file and use a command like the following:
ovftool --lax [name of file].ova [directory location of VM files]/[name of file].vmx
The --lax option is needed to ensure successful execution, even with an OVF 1.0 file as the input. Once I had done this on my Ubuntu GNOME system, the virtual machine could be opened up on VMware Player and I could use the latest build of Windows 10 at full screen, something that was not possible with VirtualBox. This may be how I survey the various builds of the operating that appear before its final edition is launched later this year.
Initial impressions of Windows 10
31st October 2014Being ever curious on the technology front, the release of the first build of a Technical Preview of Windows 10 was enough to get me having a look at what was on offer. The furore regarding Windows 8.x added to the interest, so I went to the download page to get a 64-bit installation ISO image.
That got installed into a fresh VirtualBox virtual machine and the process worked smoothly to give something not so far removed from Windows 8.1. However, it took until release 4.3.18 of VirtualBox before the Guest additions had caught up with the Windows prototype, so I signed up for the Windows Insider program and got a 64-bit ISO image to install the Enterprise preview of Windows 10 into a VMware virtual machine since and that supported full screen display of the preview while VirtualBox caught up with it.
Of course, the most obvious development was the return of the Start Menu, and it works exactly as expected too. Initially, the apparent lack of an easy way to disable App panels had me going to Classic Shell for an acceptable Start Menu. It was only later that it dawned on me that unpinning these panels would deliver to me the undistracting result that I wanted.
Another feature that attracted my interest is the new virtual desktop functionality. Here I was expecting something like what I have used on Linux and UNIX. There, each workspace is a distinct desktop, with only the applications open in a given workspace showing on a panel in there. Windows does not work that way with all applications visible on the taskbar regardless of what workspace they occupy, which causes clutter. Another deficiency is not having a desktop indicator on the taskbar instead of the Task View button. On Windows 7 and 8.x, I have been a user of VirtuaWin and this still works largely in the way that I expect of it too, except for any application windows that have some persistence associated with them; the Task Manager is an example and I include some security software in the same category too.
Even so, here are some keyboard shortcuts for anyone who wants to take advantage of the Windows 10 virtual desktop feature:
- Create a new desktop: Windows key + Ctrl + D
- Switch to previous desktop: Windows key + Ctrl + Left arrow
- Switch to next desktop: Windows key + Ctrl + Right arrow
Otherwise, stability is excellent for a preview of a version of Windows that is early on its road to final release. An upgrade to a whole new build went smoothly when initiated following a prompt from the operating system itself. All installed applications were retained, and a new taskbar button for notifications made its appearance alongside the existing Action Centre icon. So far, I am unsure what this does and whether the Action Centre button will be replaced in the fullness of time, yet I am happy to await where things go with this.
All is polished up to now, and there is nothing to suggest that Windows 10 will not be to 8.x what 7 was to Vista. The Start Screen has been dispatched after what has proved to be a misadventure for Microsoft. Regardless of what was hyped a few years ago, the PC still is with us; touchscreen devices like tablets are augmenting it instead of replacing it for any tasks involving some sort of creation. If anything, we have seen the PC evolve with laptops perhaps becoming more like the Surface Pro, at least when it comes to hybrid devices. However, we are not as happy to smudge our PC screens quite like those on phones and tablets, so a return to a more keyboard and mouse centred approach for some devices is welcome.
What I have here are just a few observations; there are more elsewhere, including a useful article by Ed Bott on ZDNet. All in all, we are early in the process for Windows 10 and, though it looks favourable so far, I will continue to keep an eye on how it progresses. The need to be less experimental than Windows 8.x is being fulfilled: so far, it certainly is less schizophrenic and should not be a major jump for users of Windows 7.
A reappraisal of Windows 8 and 8.1 licensing
15th November 2013With the release of Windows 8 around this time last year, I thought that the full retail version that some of us got for fresh installations on PC's, real or virtual, had become a thing of the past. In fact, it did seem that every respecting technology news website and magazine was saying just that. The release that you would buy from Microsoft or from mainstream computer stores was labelled as an upgrade. That made it look as if you needed the OEM or System Builder edition for those PC's that needed a new Windows installation, and that the licence that you bought was then attached to the machine from when it got installed on there.
As is usual with Microsoft, the situation is less clear-cut than that. For instance, there was some back-pedalling to allow OEM editions of Windows to be licensed for personal use on real or virtual PC's. With Windows 7 and its predecessors, it even was possible to be able to install afresh on a PC without Windows by first installing on inactivated copy on there and then upgrading that as if it were a previous version of Windows. Of course, an actual licence was of the previous version of Windows was needed for full compliance, if not the actual installation. At times, Microsoft muddies waters to keep its support costs down.
Even with Microsoft's track record in mind, it still surprised me when I noticed that Amazon was selling what appeared to be full versions of both Windows 8.1 and Windows 8.1 Pro. Having set up a 64-bit VirtualBox virtual machine for Windows 8.1, I got to discover the same for software purchased from the Microsoft website. However, unlike the DVD versions, you do need an active Windows installation if you fancy a same day installation of the downloaded software. For those without Windows on a machine, this can be as simple as downloading either the 32-bit or the 64-bit 90-day evaluation editions of Windows 8.1 Enterprise and using that as a springboard for the next steps. Though this not only be an actual in-situ installation, there are options to create an ISO or USB image of the installation disk for later installation.
In my case, I created a 64-bit ISO image and used that to reboot the virtual machine that had Windows 8.1 Enterprise on there before continuing with the installation. By all appearances, there seemed to be little need for a pre-existing Windows instance for it to work, so it looks as if upgrades have fallen by the wayside and only full editions of Windows 8.1 are available now. The OEM version saves money so long as you are happy to stick with just one machine, and most users probably will do that. As for the portability of the full retail version, that is not something that I have tested, so I am unsure that I will go beyond what I have done already.
My main machine has seen a change of motherboard, CPU and memory, so it could have deactivated a pre-existing Windows licence. However, I run Linux as my main operating system and, apart possibly from one surmountable hiccup, this proves surprisingly resilient in the face of such major system changes. For running Windows, I turn to virtual machines and there were no messages about licence activation during the changeover either. Microsoft is anything but confiding when it comes to declaring what hardware changes inactivate a licence. Changing a virtual machine from VirtualBox to VMware or vice versa definitely does it, so I tend to avoid doing that. One item that is fundamental to either a virtual or a real PC is the motherboard, and I have seen suggestions that this is the critical component for Windows licence activation, which would make sense if that was the case.
However, this rule is not hard and fast either, since there appears to be room for manoeuvre should your PC break. It might be worth calling Microsoft after a motherboard replacement to see if they can help you, and I have noticed that it is. All in all, Microsoft often makes what appear to be simple rules only to override them when faced with what happens in the real world. Is that why they can be unclear about some matters at times? Do they still hanker after how they want things to be, even when they are impossible to keep like that?
Sorting out hogging of the Super (or Windows) Key by GNOME Shell
12th November 2013Most of the time, GNOME Shell's use of the Super (or Windows) key on a standard keyboard to open up its dash area is no issue and is a handy counterpart to what you might do in Windows, especially in its latest incarnations. However, it does cause trouble if you are using a VirtualBox virtual machine with Windows installed in there. While VMware Player is immune to this problem, I thought that I would see if there was a workaround for it.
Though the issue might arise from VirtualBox's non-grabbing of the Super key like others, a solution can be found in GNOME itself. Opening up dconf-editor and navigating to org > gnome > mutter. In there, you will find a setting called overlay-key and this can be changed. One option is to delete the SUPER_L value and leave it that way. My own preference was to set it to a different key and, to accomplish that, I needed to know what the various key identifiers were. To get these, I ran the following command (just replace any quotes with alternatives in the shell before executing this):
xev | grep -A2 --line-buffered '^KeyRelease' | sed -n '/keycode /s/^.*keycode \([0-9]*\).* (.*, \(.*\)).*$/\1 \2/p'
This opened up an Event Tester window that will need to be closed when testing is complete. More importantly, the aliases for any keys that were pressed are issued to the terminal session so you can see what's what. Initially, the one for the Alt Gr key appealed to me, and I set "ISO_Level3_Shift" as the value of the overlay-key property in dconf-editor. When that didn't work, I set the value to "Menu" and it behaved as expected. While this will mean that context menus will have to be accessed by right-clicking in a Windows session, that is what I do anyway, so there will not be much of a loss in what I have done. Though a function key might have been another option, I reckon that the context menu key will do me.
A look at Windows 8.1
4th July 2013Last week, Microsoft released a preview of Windows 8.1 and some hailed the return of the Start button, yet the reality is not as simple as that. Being a Linux user, I am left wondering if ideas have been borrowed from GNOME Shell instead of putting back the Start Menu like it was in Windows 7. What we have got is a smoothing of the interface that is there for those who like to tweak settings and not available by default. GNOME Shell has been controversial too, so borrowing from it is not an uncontentious move, even if there are people like me who are at home with that kind of interface.
What you get now is more configuration options to go with the new Start button. While right-clicking on the latter does get you a menu, this is no Start Menu like we had before. Instead, we get a settings menu with a "Shut down" entry. That's better than before, which might be saying something about what was done in Windows 8, and it produces a sub-menu with options of shutting down or restarting your PC as well as putting it to sleep. Otherwise, it is a place for accessing system configuration items and not your more usual software, not a bad thing, but it's best to be clear about these things. Holding down the Windows key and pressing X will pop up the same menu if you prefer keyboard shortcuts, and I have a soft spot for them too.
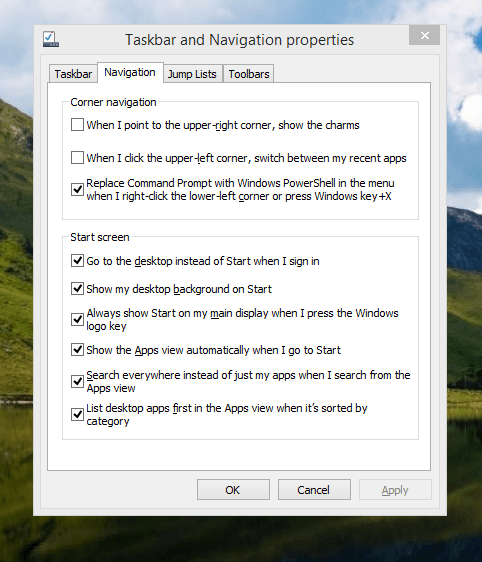
The real power is to be discovered when you right-click on the task bar and select Properties from the pop-up menu. Within the dialogue box that appears, there is the Navigation tab that contains a whole plethora of interesting options. Corner navigation can be scaled back to remove the options of switching between applications in the upper-left corner or getting what is called the Charms menu from the upper-right corner. Things get interesting in the Start Screen section. This where you tell Windows to boot to the desktop instead of the Start Screen and adjust what the Start button gives you. For instance, you can make it use your desktop background and display the Start Screen Apps View. Both of these make the new Start interface less intrusive and make the Apps View feel not unlike the way GNOME Shell overlays your screen when you hit the Activities button or hover over the upper-left corner of the desktop.
It all seems rather more like a series of little concessions, and not the restoration that some (many?) would prefer. Classic Shell still works for all those seeking an actual Start Menu and even replaces the restored Microsoft Start button too. So, if the new improvements aren't enough for you, you still can take matters into your own hands until you start to take advantage of what's new in 8.1.
Apart from the refusal to give us back a Windows 7 style desktop experience, we now have a touchscreen keyboard button added to the taskbar. So far, it always appears there even when I try turning it off. For me, that's a bug, so it's something that I'd like to see fixed before the final release.
All in all, Windows 8.1 feels more polished than Windows 8 was and will be a free update when the production version is released. My explorations have taken place within a separate VMware virtual machine because updating a Windows 8 installation to the 8.1 preview is forcing a complete re-installation on yourself later on. Though there are talks about Windows 9 now, I am left wondering if going for point releases like 8.2, 8.3, etc. might be a better strategy for Microsoft. It still looks as if Windows 8 could do with continual polishing before it gets more acceptable to users. 8.1 is a step forward, and more like it may be needed yet.
A need to update graphics hardware
16th June 2013As someone who doesn't play computer games, I rarely prioritise graphics card upgrades. Yet, I recently upgraded graphics cards in two of my PCs despite nothing being broken. My backup machine, built nearly four years ago, has run multiple Linux distributions. It uses an ASRock K10N78 motherboard from MicroDirect with an integrated NVIDIA graphics chip that performs adequately, if not exceptionally. The only issue was slightly poor text rendering in web browsers, but this alone wasn't enough to justify adding a dedicated graphics card.
More recently, I ran into trouble with Sabayon 13.04 with only the 2D variant of the Cinnamon desktop environment working on it and things getting totally non-functional when a full re-installation of the GNOME edition was attempted. Everything went fine until I added the latest updates to the system, when a reboot revealed that it was impossible to boot into a desktop environment. Some will relish this as a challenge, but I need to admit that I am not one of those. In fact, I tried out two Arch-based distros on the same PC and got the same results following a system update on each. So, my explorations of Antergos and Manjaro have to continue in virtual machines instead.
When I tried Linux Mint 15 Cinnamon, it worked perfectly. However, newer distributions with systemd didn't work with my onboard NVIDIA graphics. Since systemd will likely come to Linux Mint eventually, I decided to add a dedicated graphics card. Based on good past experiences with Radeon, I chose an AMD Radeon HD 6450 from PC World, confirming it had Linux driver support. Installation was simple: power off, insert card, close case, power on. Later, I configured the BIOS to prioritise PCI Express graphics, though this step wasn't necessary. I then used Linux Mint's Additional Driver applet to install the proprietary driver and restarted. To improve web browser font rendering, I selected full RGBA hinting in the Fonts applet. The improvement was obvious, though still not as good as on my main machine. Overall, the upgrade improved performance and future-proofed my system.
After upgrading my standby machine, I examined my main PC. It has both onboard Radeon graphics and an added Radeon 4650 card. Ubuntu GNOME 12.10 and 13.04 weren't providing 3D support to VMware Player, which complained when virtual machines were configured for 3D. Installing the latest fglrx driver only made things worse, leaving me with just a command line instead of a graphical interface. The only fix was to run one of the following commands and reboot:
sudo apt-get remove fglrx
sudo apt-get remove fglrx-updates
Looking at the AMD website revealed that they no longer support 2000, 3000 or 4000 series Radeon cards with their latest Catalyst driver, the last version that did not install on my machine since it was built for version 3.4.x of the Linux kernel. A new graphics card then was in order if I wanted 3D graphics in VMware VM's and both GNOME and Cinnamon appear to need this capability. Another ASUS card, a Radeon HD 6670, duly was acquired and installed in a manner similar to the Radeon HD 6450 on the standby PC. Apart from not needing to alter the font rendering (there is a Font tab on the Gnome Tweak Tool where this can be set), the only real exception was to add the Jockey software to my main PC for installation of the proprietary Radeon driver. The following command does this:
sudo apt-get install jockey-kde
After completing installation, I ran the jockey-kde command and selected the first driver option. Upon restart, the system worked properly except for an AMD message in the bottom-right corner warning about unrecognised hardware. Since there were two identical entries in the Jockey list, I tried the second option. After restarting, the incompatibility message disappeared and everything functioned correctly. VMware even ran virtual machines with 3D support without any errors, confirming the upgrade had solved my problem.
Hearing of someone doing two PC graphics card upgrades during a single weekend may make you see them as an enthusiast, but my disinterest in computer gaming belies this. Maybe it highlights that Linux operating systems need 3D more than might be expected. The Cinnamon desktop environment now issues messages if it is operating in 2D mode with software 3D rendering and GNOME always had the tendency to fall back to classic mode, as it had been doing when Sabayon was installed on my standby PC. However, there remain cases where Linux can rejuvenate older hardware and I installed Lubuntu onto a machine with 10-year-old technology on there (an 1100 MHz Athlon CPU, 1GB of RAM and 60GB of hard drive space in a case dating from 1998) and it works surprisingly well too.
It appears that having fancier desktop environments like GNOME Shell and Cinnamon means having the hardware on which it could run. For a while, I have been tempted by the possibility of a new PC, since even my main machine is not far from four years old either. However, I also spied a CPU, motherboard and RAM bundle featuring an Intel Core i5-4670 CPU, 8GB of Corsair Vengeance Pro Blue memory and a Gigabyte Z87-HD3 ATX motherboard included as part of a pre-built bundle (with a heat sink and fan for the CPU) for around £420. Even for someone who has used AMD CPU's since 1998, that does look tempting, but I'll hold off before making any such upgrade decisions. Apart from exercising sensible spending restraint, waiting for Linux UEFI support to mature a little more may be no bad idea either.
Update 2013-06-23: The new graphics card in my main machine works well and has reduced system error messages; Ubuntu GNOME 13.04 likely had issues with my old card. On my standby machine, I found and removed a rogue .fonts.conf file in my home directory, which dramatically improved font display. If you find this file on your system, consider removing or renaming it to see if it helps. Alternatively, adjusting font rendering settings can improve display quality, even on older systems like Debian 6 with GNOME 2. I may test these improvements on Debian 7.1 in the future.
Upgrading from Windows 7 to Windows 8 within a VMWare Virtual Machine
1st November 2012Though my main home PC runs Linux Mint, I do like to have the facility to use Windows software occasionally, and virtualisation has allowed me to continue doing that. For a good while, it was a Windows 7 guest within a VirtualBox virtual machine and, before that, one running Windows XP fulfilled the same role. However, it did feel as if things were running slower in VirtualBox than once might have been the case, so I jumped ship to VMware Player. While it may be proprietary and closed source, it is free of charge and has been doing what was needed. A subsequent recent upgrade of a video driver on the host operating system allowed the enabling of a better graphical environment in the Windows 7 guest.
Instability
However, there were issues with stability and I lost the ability to flit from the VM window to the Linux desktop at will, with the system freezing on me and needing a reboot. Working in Windows 7 using full-screen mode avoided this, yet it did feel as I was constrained to working on a Windows-only machine whenever I did so. The graphics performance was imperfect too, with screening refreshing being very blocky with some momentary scrambling whenever I opened the Start menu. Others would not have been as patient with that as I was, though there was the matter of an expensive Photoshop licence to be guarded too.
In hindsight, a bit of pruning could have helped. An example would have been driver housekeeping in the form of removing VirtualBox Guest Additions because they could have been conflicting with their VMware counterparts. For some reason, those thoughts entered my mind to make me consider another, more expensive option instead.
Considering NAS & Windows/Linux Networking
That would have taken the form of setting aside a PC for running Windows 7 and having a NAS for sharing files between it and my Linux system. In fact, I did get to exploring what a four bay QNAP TS-412 would offer me and realised that you cannot put normal desktop hard drives into devices like that. For a while, it looked as if it would be a matter of getting drives bundled with the device or acquiring enterprise grade disks to main the required continuity of operation. The final edition of PC Plus highlighted another one, though: the Western Digital Red Pro range. These are part way been desktop and enterprise classifications and have been developed in association with NAS makers too.
While looking at the NAS option certainly became an education, it has exited any sort of wish list that I have. After all, it is the cost of such a setup that gets me asking if I really need such a thing. While the purchase of a Netgear FS 605 Ethernet switch would have helped incorporate it, there has been no trouble sorting alternative uses for that device since it bumps up the number of networked devices that I can have, never a bad capability to have. As I was to find, there was a less expensive alternative that would become sufficient for my needs.
In-situ Windows 8 Upgrade
Microsoft has been making available evaluation copies of Windows 8 Enterprise that last for 90 days before expiring. One is in my hands has been running faultlessly in a VMware virtual machine for the past few weeks. That made me wonder if upgrading from Windows 7 to Windows 8 help with my main Windows VM problems. Being a curious risk-taking type I decided to answer the question for myself using the £24.99 Windows Pro upgrade offer that Microsoft have been running for those not needing a disk up front; they need to pay £49.99 while you can get one afterwards for an extra £12.99 and £3.49 postage if you wish, a slightly cheaper option. Though there also was a time cost in that it occupied a lot of a weekend for me, it seems to have done what was needed, so it was worth the outlay.
Given the element of risk, Photoshop was deactivated to be on the safe side. That wasn't the only pre-upgrade action that was needed because the Windows 8 Pro 32-bit upgrade needs at least 16 GB before it will proceed. Of course, there was the matter of downloading the installer from the Microsoft website too. This took care of system evaluation and paying for the software, as well as the actual upgrade itself.
The installation took a few hours, with virtual machine reboots along the way. Naturally, the licence key was needed too, as well as the selection of a few options, though there weren't many of these. Being able to carry over settings from the pre-existing Windows 7 instance certainly helped with this and with making the process smoother too. No software needed reinstatement, and it doesn't feel as if the system has forgotten very much at all, a successful outcome.
Post-upgrade Actions
Just because I had a working Windows 8 instance didn't mean that there wasn't more to be done. In fact, it was the post-upgrade sorting that took up more time than the actual installation. For one thing, my digital mapping software wouldn't work without .Net Framework 3.5 and turning on the operating system feature from the Control Panel fell over at the point where it was being downloaded from the Microsoft Update website. Even removing Avira Internet Security after updating it to the latest version had no effect, and that was a finding during the Windows 8 system evaluation process. The solution was to mount the Windows 8 Enterprise ISO installation image that I had and issue the following command from a command prompt running with administrative privileges:
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:NetFX3 /Source:d:\sources\sxs /LimitAccess
For sake of assurance regarding compatibility, Avira has been replaced with Trend Micro Titanium Internet Security. The Avira licence won't go to waste, since I have another home in mind for it. Removing Avira without crashing Windows 8 proved impossible, though, and necessitating booting Windows 8 into Safe Mode. Because of much faster startup times, that cannot be achieved with a key press at the appropriate moment because the time window is too short now. One solution is to set the Safe Boot tick box in the Boot tab of MSCONFIG (or System Configuration, as it otherwise calls itself) before the machine is restarted. While there may be others, this was the one that I used. With Avira removed, clearing the same setting and rebooting restored normal service.
Dealing with a Dual Personality
One observer has stated that Windows 8 gives you two operating systems for the price of one: the one on the Start screen and the one on the desktop. Having got to wanting to work with one at a time, I decided to make some adjustments. Adding Classic Shell got me back a Start menu, and I omitted the Windows Explorer (or File Explorer as it is known in Windows 8) and Internet Explorer components. Though Classic Shell will present a desktop like what we have been getting from Windows 7 by sweeping the Start screen out of the way for you, I found that this wasn't quick enough for my liking, so I added Skip Metro Suite to speed up things. Though the tool does more than sweeping the Start screen out of the way, I have switched off these functions. Classic Shell has been configured too, so the Start screen can be accessed with a press of the Windows key. It has updated too so that boot into the desktop should be faster now. As for me, I'll leave things as they are for now. Even the possibility of using Windows' own functionality to go directly to the traditional desktop will be left untested while things are left to settle. Tinkering can need a break.
Outcome
After all that effort, I now have a seemingly more stable Windows virtual machine running Windows 8. Flitting between it and other Linux desktop applications has not caused a system freeze so far, and that was the result that I wanted. There now is no need to consider having separate Windows and Linux PC's with a NAS for sharing files between them, so that option is well off my wish-list. There are better uses for my money.
Not everyone has had my experience, though, because I saw a report that one user failed to update a physical machine to Windows 8 and installed Ubuntu instead; they were a Linux user anyway, even if they used Fedora more than Ubuntu. It is possible to roll back from Windows 8 to the previous version of Windows because there is a windows.old directory left primarily for that purpose. However, that may not help you if you have a partially operating system that doesn't allow you to do just that. In time, I'll remove it using the Disk Clean-up utility by asking it to remove previous Windows installations or running File Explorer with administrator privileges. Somehow, the former approach sounds the safer.
What About Installing Afresh?
While there was a time when I went solely for upgrades when moving from one version of Windows to the next, the annoyance of the process got to me. If I had known that installing the upgrade twice onto a computer with a clean disk would suffice, it would have saved me a lot. Staring from Windows 95 (from the days when you got a full installation disk with a PC and not the rescue media that we get now) and moving through a sequence of successors not only was time-consuming, but it also revealed the limitations of the first in the series when it came to supporting more recent hardware. It was enough to have me buying the full retailed editions of Windows XP and Windows 7 when they were released; the latter got downloaded directly from Microsoft. While these were retail versions that you could move from one computer to another, Windows 8 will not be like that. In fact, you will need to get its System Builder edition from a reseller and that can only be used on one machine. It is the merging of the former retail and OEM product offerings.
What I have been reading is that the market for full retail versions of Windows was not a big one anyway. However, it was how I used to work as you have read above, and it does give you a fresh system. Most probably get Windows with a new PC and don't go building them from scratch like I have done for more than a decade. Maybe the System Builder version would apply to me anyway, and it appears to be intended for virtual machine use as well as on physical ones. More care will be needed with those licences by the looks of things, and I wonder what needs not to be changed so as not to invalidate a licence. After all, making a mistake might cost between £75 and £120 depending on the edition.
Final Thoughts
So far, Windows 8 is treating me well, and I have managed to bend it to my will too, always a good thing to be able to say. In time, it might be that a System Builder copy could need buying yet, but I'll leave well alone for now. Though I needed new security software, the upgrade still saved me money over a hardware solution to my home computing needs and I have a backup disk on order from Microsoft too. That I have had to spend some time settling things was a means of learning new things for me but others may not be so patient and, with Windows 7 working well enough for most, you have to ask if it's only curious folk like me who are taking the plunge. Still, the dramatic change has re-energised the PC world in an era when smartphones and tablets have made so much of the running recently. That too is no bad thing because an unchanging technology is one that dies and there are times when significant changes are needed, as much as they upset some folk. For Microsoft, this looks like one of them, and it'll be interesting to see where things go from here for PC technology.
Migrating a Windows 7 Virtual Machine from VirtualBox to VMware Player
14th October 2012Seeing how well Windows 8 was running in a VMware Player virtual machine and that was without installing VMware Tools in the guest operating system, I was reminded about how sluggish my Windows 7 VirtualBox VM had become. Therefore, I decided to try a migration of the VM from VirtualBox to VMware. My hope was this: it would be as easy as exporting to an OVA file (File > Export Appliance... in VirtualBox) and importing that into VMware (File > Open a VM in Player). However, even selecting OVF compatibility was insufficient for achieving this, and the size of the virtual disks meant that the export took a while to run as well. The solution was to create a new VM in VirtualBox from the OVA file and use the newly created VMDK files with VMware. That worked successfully to give me a speedier, more responsive Windows 7 VM for my pains.
Access to host directories needed reinstatement using a combination of the VMware Shared Folders feature and updating drive mappings in Windows 7 itself to use what appeared to it as network drives in the Shared Folders directory on the \\vmware-host domain. For that to work, VMware Tools needed to be installed in the guest OS (go to Virtual Machine > Install VMware Tools to make available a virtual CD from which the installation can be done) as I discovered when trying the same thing with my Windows 8 VM, where I dare not instate VMware Tools due to their causing trouble when I last attempted it.
Moving virtual machine software brought about its side effects, though. Software like Windows 7 detects that it's on different hardware, so reactivation can be needed. While Windows 7 reactivation was a painless online affair, it wasn't the same for Photoshop CS5. That meant that I needed help from Adobe's technical support people top get past the number of PC's for which the software already had been activated. In hindsight, deactivation should have been done before the move, but that's a lesson that I know well now. Technical support sorted my predicament politely and efficiently while reinforcing the aforementioned learning point. Moving virtual machine platform is very like moving from one PC to the next, and it hadn't clicked with me quite how real those virtual machines can be when it comes to software licensing.
Apart from that and figuring out how to do it, the move went smoothly. An upgrade to the graphics driver on the host system and getting Windows 7 to recheck the capabilities of the virtual machine even gained me a fuller Aero experience than I had before then. Full-screen operation is quite reasonable too (the CTRL + ALT + ENTER activates and deactivates it) and photo editing now feels less boxed in too.
Removing VMware Player from Linux Mint Debian Edition
4th August 2012A whole slew of updates has appeared for my Linux Mint Debian Edition PC. However, to instate them, I needed to remove VMware Player and this is the command to do so:
sudo vmware-installer -u vmware-player
It worked in my case, and my system updates are in progress as I write this. The same command should work for other Linux distros where VMware Player was installed using the *.bundle installer. VMware Player remains in place on my main PC though, so I am not ditching it just yet, even if I have to be careful when running it on Linux Mint 13 so as not to freeze the system on myself.