TOPIC: SAS INSTITUTE
Porting SAS files to other platforms and versions
1st October 2007SAS uses its transport file format to port files between operating and, where the need arises, different software versions. As with many things, there is more than one method to create these transport files: PROC CPORT/CIMPORT and PROC COPY with the XPORT engine. The former method is for within version transfer of SAS files between different operating systems (UNIX to Windows, for instance) and the latter is for cross-version transfer (SAS9 to SAS 8, for example). SAS Institute has a page devoted to this subject which may share more details.
SAS Institute enters the blogosphere
19th September 2007To get to the blogs hosted by SAS Institute, all you need to do is go here. I have to say that there is quite a spread of subject matter ranging from the high-level business strategy offerings through to detailed snippets for SAS programmers. There appears to be a lot here for anyone interested in SAS and business intelligence. I must take a longer look.
Update: I have since discovered a central listing of SAS Institute RSS feeds. The list is well worth your perusal.
SAS9 SQL Constraints
23rd July 2007With SAS 9, SAS Institute has introduced the sort of integrity constraints that have been bread and butter for relational database SQL programs, but some SAS programmers may find them more restrictive than they might like. The main one that comes to my mind is the following:
proc sql noprint;
create table a as select a.*,b.var from a left join b on a.index=b.index;
quit;Before SAS 9, that worked merrily with nary a comment, only for you now to see a warning like this:
WARNING: This CREATE TABLE statement recursively references the target table. A consequence of this is a possible data integrity problem.
In the data step, the following still runs without a complaint:
data a;
merge a b(keep=index var);
by index;
run;On the surface of it, this does look inconsistent. From a database programmer's point of view having to use different source and target datasets is no hardship but seems a little surplus to requirements for a SAS programmer trained to keep down the number of temporary datasets to reduce I/O and keep things tidy, an academic concept perhaps in these days of high processing power and large disks. While adding UNDO_POLICY=NONE to the PROC SQL line does make everything consistent again, I see this as being anathema to a database programming type. Though I do admit to indulging in the override for personal quick and dirty purposes, abiding by the constraint is how I do things for formal purposes like inclusion in an application to a regulatory authority like FDA.
WARNING: The quoted string currently being processed has become more than 262 characters long…
20th June 2007This is a SAS error that can be seen from time to time:
WARNING: The quoted string currently being processed has become more than 262 characters long. You may have unbalanced quotation marks.
In the days before SAS version 8, this was something that needed to be immediately corrected. In these days of SAS character variables extending beyond 200 characters in length, it becomes a potential millstone around a SAS programmer's neck. If you run a piece of code like this:
data _null_;
x="aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa";
run;What you get back is the warning message at the heart of the matter. While the code is legitimate and works fine, the spurious error is returned because SAS hasn't found a closing quote by the required position and the 262-character limit is a hard constraint that cannot be extended. There is another way, though: the new QUOTELENMAX option in SAS9. Setting it as follows removes the messages in most situations (yes, I did find one where it didn't play ball):
options noquotelenmax;
This does, however, beg the question as to how you check for unbalanced quotes in SAS logs these days; clearly, looking for a closing quote is an outmoded approach. Thanks to code highlighting, it is far easier to pick them out before the code gets submitted. The other question that arises is why you would cause this to happen anyway, but there are occasions where you assign the value of a macro variable to a data set one and the string is longer than the limit set by SAS. Here's some example code:
data _null_;
length y $400;
y=repeat("f",400);
call symput("y",y)
run;data _null_;
x="&y";
run;My own weakness is where I use PROC SQL to combine strings into a macro variable, a lazy man's method of combining all distinct values for a variable into a delimited list like this:
proc sql noprint;
select distinct compress(string_var) into :vals separated by " " from dataset;
quit;Of course, creating a long delimited string using the CATX (new to SAS9) function avoids the whole situation and there are other means, but there may be occasions, like the use of system macro variables, where it is unavoidable and NOQUOTELENMAX makes a much better impression when these arise.
A peculiarity with PROC EXPORT
10th June 2007I have just encountered an issue with PROC EXPORT that I did not expect to see: it needs to run in a windowing environment. The way that I found this was that I was running a SAS macro as part of a batch job in a headless UNIX session and my program stopped dead with the job needing to be killed; that returned a message containing something about SAS/FSP and SAS/AF which does explain things. Still, this was not something that I would have expected with an export to a CSV file; the behaviour sounds more what you see with the likes of PROC GPLOT or PROC REPORT. As it happened, adding the -noterminal option to the batch command line sorted things out.
Using alternative editors for SAS programming
5th June 2007When it comes to writing SAS programs, most use the tools that SAS gives us, be it Enterprise Guide, the Enhanced Editor or the Program Editor. While Enterprise Guide can work with UNIX SAS as the processing engine, it is very much a Windows tool and the Enhanced Editor functionality is provided through Windows-only programming (ActiveX, I seem to recall). However, that means that creature comforts are left behind you if you turn to writing SAS code using UNIX SAS; you have only got the good old-fashioned Program Editor supplied by SAS itself. However, there is a trick that you can use to make life more comfortable: SAS does allow you to submit the contents of your paste buffer (or clipboard) using the command SUBMIT BUFFER=DEFAULT and this can be assigned to a function key for ease of use (I use the same key to clear the log and output screens at the same time). In the Windows, you may need to explicitly copy the code to do this but, in UNIX, merely highlighting a section of code with an editor like NEdit will do the trick and, given that NEdit is reasonably pleasant tool for code cutting (the ability to define its macros with a spot of scripting is a definite plus point), this makes life more comfortable again.
Selecting SAS code in the Program Editor on UNIX
5th June 2007Here's a possible bugbear with programming using the SAS Display Manager in UNIX, selecting sections of code and running them. In the installations that I have encountered, the mouse selection is not retained, so the code selection cannot be run. There is a fix for this that is not the most obvious. Going to the Preferences dialogue box (Tools > Options > Preferences... from the menu bar) and selecting the Editing tab brings up the screen below:
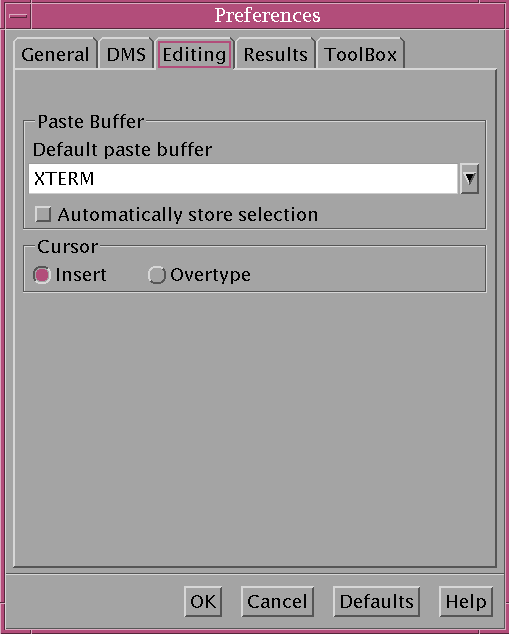
Ensuring that "Automatically store selection" is switched off, as shown above, will allow one to select and submit sections of code from a SAS program like what is normal practice with Windows SAS. Though it isn't an obvious solution, it does the trick for me.
Finding the number of observations in a SAS dataset
16th May 2007There are a number of ways of finding out the number of observations (also known as records or rows) in a SAS data set and, while they are documented in a number of different places, I have decided to collect them together in one place. At the very least, it means that I can find them again.
First up is the most basic and least efficient method: read the whole data set and increment a counter to pick up its last value. The END option allows you to find the last value of count without recourse to FIRST.x/LAST.x logic.
data _null_;
set test end=eof;
count+1;
if eof then call symput(”nobs”,count);
run;The next option is a more succinct SQL variation on the same idea. The colon prefix denotes a macro variable whose value is to be assigned in the SELECT statement; there should be no surprise as to what the COUNT(*) does…
proc sql noprint;
select count(*) into :nobs from test;
quit;Continuing the SQL theme, accessing the dictionary tables is another route to the same end and has the advantage of needing to access the actual data set in question. You may have an efficiency saving when you are testing large datasets, but you are still reading some data here.
proc sql noprint;
select nobs into :nobs from dictionary.tables where libname=”WORK” and memname=”TEST”;
quit;The most efficient way to do the trick is just to access the data set header. Here’s the data step way to do it:
data _null_;
if 0 then set test nobs=nobs;
call symputx(”nobs”,nobs);
stop;
run;The IF/STOP logic stops the data set read in its tracks so that only the header is accessed, saving the time otherwise used to read the data from the data set. Using the SYMPUTX routine avoids the need to explicitly code a numeric to character transformation; it’s a SAS 9 feature, though.
To finish, here is the most succinct and efficient way of all: the use of macro and SCL functions. It’s my preferred option, and you don’t need a SAS/AF licence to do it, either.
%let dsid=%sysfunc(open(work.test,in));
%let nobs=%sysfunc(attrn(&dsid,nobs));
%if &dsid > 0 %then %let rc=%sysfunc(close(&dsid));
The first line opens the data set, and the last one closes it; this is needed because you are not using data step or SCL and could leave a data set open, causing problems later. The second line is what captures the number of observations from the header of the data set using the SCL ATTRN function called by %SYSFUNC.