TOPIC: SAS INSTITUTE
Using ODS Graphics to Create Plots Using PROC LIFETEST
3rd September 2010One of the nice things about SAS 9.2 is that creation of statistical graphics is enhanced using the Output Delivery System (ODS). One of the beneficiaries of this is PROC LIFETEST, a procedure that gained a lot when data sets could be created from it using ODS OUTPUT statements. Before that, it was a matter of creating text output and converting it to a SAS data set using Data Step, and that was a nuisance on a system that attached special significance to output destinations set up using PROC PRINTTO. What you’ll find below is a sample of the type of code for creating a Kaplan-Meier survival plot for time to adverse events resulting in discontinuation of study treatment, with actual and censored times. The IMAGENAME parameter on the ODS GRAPHICS statement line controls the name of the file, and it is possible to change the type using the IMAGEFMT parameter too.
ods graphics on / imagename=”fig5″;
proc lifetest data=km3 method=km plots=survival;
time timetoae*cens_ae(0);
run;
ods graphics off;ERROR 22-322: Syntax error, expecting one of the following: a name, *.
14th June 2010This is one of the classic SAS errors that you can get from PROC SQL, and it can be thrown by a number of things. Missing out a comma in a list of variables in a SELECT statement is one situation that will do it, as will be having an extraneous one. As I discovered recently, an ill-defined SAS function nesting like LEFT(TRIM(PERIOD,BEST.)) will have the same effect; notice the missing PUT function in the example. The latter surprised me because I might have expected something more descriptive for this, as would be the case in data step code. In the event, it took some looking before the problem hit me because it's remarkable how blind you can become to things that are staring you in the face. Familiarity really can make you pay less attention.
ERROR: Invalid value for width specified - width out of range
8th June 2010This could be the beginning of a series of error messages from PROC SQL that may appear unclear to a programmer more familiar with Data Step. The cause of my getting the message that heads this posting is that there was a numeric variable with a length less than the default of 8, not the best of situations. Sadly, the message doesn't pinpoint the affected variable, so it took some commenting out of pieces of code before I found the cause of the problem. That's never to say that PROC SQL does not have debugging functionality in the form of FEEDBACK, NOEXEC, _METHOD and _TREE options on the PROC SQL line itself or the validation statement, but neither of these seemed to help in this instance. Still, they're worth keeping in mind for the future, as is SAS Institute's own page on SQL query debugging. Of course, now that I know what might be the cause, a simple PROC SQL report using the dictionary tables should help. The following code should do the needful:
proc sql;
select memname, name, type, length
from dictionary.columns
where libname="DATA" and type="num" and length ne 8;
quit;Reading data into SAS using the EXCEL and PCFILES library engines
4th March 2010Recently, I had the opportunity to have a look at the Excel library engine again because I need to read Excel data into SAS. You need SAS Access for PC Files licensed for it to work, but it does simplify the process of getting data from spreadsheets into SAS. It all revolves around setting up a library pointing at the Excel file using the Excel engine. The result is that every worksheet in the file is treated like a SAS dataset, even if their names contain characters that SAS considers invalid for dataset names. The way around that is to enclose the worksheet name in single quotes with the letter n straight after the closing quote, much in the same way as you'd read in text strings as SAS date values ('04MAR2010'd, for example). To make all of this clearer, I have added some example code below.
libname testxl excel 'c:\test.xls';
data test;
set testxl.'sheet1$'n;
run;All of the above does apply to SAS on Windows (I have used it successfully in 9.1.3 and 9.2) but there appears to be a way of using the same type of thing on UNIX too. Again, SAS Access for PC Files is needed as well as a SAS PC Files server on an available Windows machine, and it is the PCFILES engine that is specified. While I cannot say that I have had the chance to see it working in practice but seeing it described in SAS Online Documentation corrected my previous misimpressions about the UNIX variant of SAS and its ability to read in Excel or Access data. Well, you learn something new every day.
Working with the ODS templates and styles when batch processing
8th December 2008I ran into some trouble with creating new templates and styles while running a SAS job in batch mode. The cause was the user of the RSASUSER switch on the SAS command. This sets the SASUSER library to be read-only, and that is what is used to store new templates and styles by default. The fix is to switch these to another library to which there is write-access, WORK, for example. Here's the line of code that achieves the manoeuvre:
ODS PATH work.templat(update) sasuser.templat(read) sashelp.tmplmst(read);
Apparently, the same change might be needed for stored processes too, so it's one to keep in mind.
SAS Macro and Dataline/Cards Statements in Data Step
28th October 2008Recently, I tried code like this in a SAS macro:
data sections;
infile datalines dlm=",";
input graph_table_number $15. text_line @1 @;
datalines;
"11.1 ,Section 11.1",
"11.2 ,Section 11.2",
"11.3 ,Section 11.3"
;
run;While it works in its own right, including it as part of a macro yielded this type of result:
ERROR: The macro X generated CARDS (data lines) for the DATA step, which could cause incorrect results. The DATA step and the macro will stop executing.
A bit of googling landed me on SAS-L where I spotted a solution like this one that didn't involve throwing everything out:
filename temp temp;
data _null_;
file temp;
put;
run;data sections;
length graph_table_number $15 text_line $100;
infile temp dlm=",";
input @;
do _infile_=
"11.1 ,Section 11.1",
"11.2 ,Section 11.2",
"11.3 ,Section 11.3"
;
input graph_table_number $15. text_line @1 @;
output;
end;
run;filename temp clear;
The filename statement and ensuing data step creates a dummy file in the SAS work area that gets cleared at the end of every session. That seems to fool the macro engine into thinking that input is from a file and not the CARDS/DATALINES method, to which it takes grave exception. The trailing @'s hold an input record for the execution of the next INPUT statement within the same iteration of the DATA step so that the automatic variable _infile_ can be fed as part of the input process in a do block with the output statement ensure that all records from the input buffer reach the data set being created.
While this method does work, I would like to know the underlying reason as to why SAS Macro won't play well with included data entry using DATALINES or CARDS statements in a data step, particularly when it allows other methods that using either SQL insert statements or standard variable assignment in data step. I find it such a curious behaviour that I remain on the lookout for the explanation why it is like this.
Transferring data between SAS and R
5th June 2008A question regarding the ability to transfer of data between SAS and R set me off on a spot of investigation a while back, and I have always planned to share the results of my labours. Once I managed to locate the required documentation, things became clearer with further inspection. Functions from the foreign package seem to offer the most from the data import and export point of view, so they're what I'll be featuring in this posting.
Here, I am starting with importing, and using the read.ssd function makes life so much easier for getting SAS data into R. When I discovered that the foreign package may not be loaded by default, that could be determined easily using the following command:
search()
If package:foreign isn't in the list, then you need to issue the following function call:
library(foreign)
Of course, if the foreign package isn't installed, none of this will work. It should live in the library sub-folder of the main R installation directory, but if it isn't there, then downloading the relevant binary package from CRAN is in order. Assuming that all is installed, then a command like the following will perform the needful:
read.ssd("c:/data","data1",sascmd="C:/Program Files/SAS Institute/SAS/V8/sas.exe")
This creates a temporary SAS program that converts the SAS data set into a transport file for reading by another R function that is called in the background, read.xport. From my experience, it all seems to work fairly seamlessly.
To get data out of R and into SAS is a multi-stage process, even with the foreign package. While there are other ways, using the write.foreign seems more useful than most. Here is an example function call:
write.foreign(data1,"C:/test.txt","C:/test.sas",package="SAS",dataname="data1",validvarname="V7")
While no SAS data sets are created at this stage, a text file is generated along with a SAS program for converting it into a data set. Running the SAS program is a separate step that follows the creation of the two files. Even if it is less streamlined than read.ssd, write.foreign does make it easier to transfer data into SAS than having to write a program from scratch to read in write.table output.
In summary, R can neither read nor write SAS data sets by itself, so you need SAS installed to really make things happen. SAS gets called by read.ssd and I feel that it would be better if was called by write.foreign also rather than a SAS program generated for execution later on. Even so, it is good to see some custom functionality being provided that makes life easier. There's also the hmisc package, but my experiences while working with that on S-Plus have been such that it compares less favourably with foreign on the reliability front. Saying that, things may have changed since I last tried it.
New version of SAS on the way
16th January 2008This is something of a newsflash posting, but this morning's issue of the SAS Tech Report newsletter has said at last when SAS 9.2 is expected to be released. Though SAS has been talking a bit about 9.2, dates were elusive and, to a point, they still are. Nevertheless, hearing the Q1 of this year is the time slot for the unveiling is better than knowing nothing at all. Am I alone in wondering if it is coming later than was planned?
Controlling what the wpgm command calls in Windows SAS
30th November 2007Recently, I was setting up a key mapping in SAS 8.1 such that the log and output windows are cleared and a SAS program run in the most recently used program editor window. The idea was that debugging would be easier, and the command was what you see below:
log; clear; output; clear; wpgm; submit
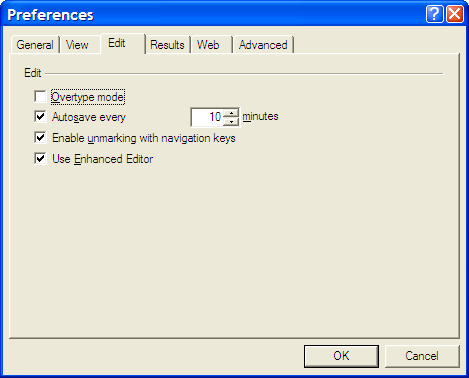
However, I was having trouble getting SAS to pick up the most recently used Enhanced Editor window, and it was opening up an old style Program Editor window in its place. If I had wanted to use that, I would have used pgm and not wpgm. What was conspiring against me was a pesky system option. Pottering over to Tools > Options > Preferences and navigating to the Edit tab brought me to the cause of the problem: the Use Enhanced Editor check box was in the clear, and fixing that set me on my way. SAS 9 could also be afflicted by the same irritation and that is where I got the screenshot that you see below where everything is hunky-dory.
Using SAS FILE statements with the MOD option to append output to plain text files
25th November 2007SAS can generate many types of output: plain text, XML, PDF, RTF, Excel, etc. With all of these and the SAS procedures like PROC REPORT, PROC TABULATE and so on, it might seem surprising for me to say that I have been generating output with data step PUT and FILE statements. There was, of course, a reason for this: creating text files for loading into a new database-driven software application. At one stage, I also did some data interleaving at the output stage and that's when I discovered that the default behaviour for SAS FILE statements is to completely overwrite a file unless the MOD option was specified. Adding that switches on APPEND behaviour. The code below adds a header in one step, while adding data below it in another. While I know that there are better ways to achieve this, like setting up your data as you want it or using _N_ to ensure that something only appears once, here's another way. As per the Perl, there's often more than one way to do something with SAS.
data _null_;
file ds_data;
put "fieldtype;datasetname;datasetlabel;datasetlayout;datasetclass;datasetstandardversion";
run;data _null_;
set ds_ispec;
file ds_data mod;
line="datasetstandard;"||trim(memname)||";"||trim(memlabel)||";;;"||trim(memver);
put line;
run;