TOPIC: LINUX
Taking the sudo command beyond Ubuntu
27th October 2010Though some may call it introducing a security risk, being able to execute administrator commands on Ubuntu using sudo and gksu by default is handy. It's not the only Linux distribution with the facility, though, since the /etc/sudoers file is found in Debian and I plan to have a look into Fedora. The thing that needs to be done is to add the following line to the aforementioned file (you will need to do this as root):
[your user name] ALL=(ALL) ALL
One that is done, you are all set. Just make sure that you're using a secure password, though, and removing the sudo/gksu permissions is as simple as reversing the change.
Update on 2011-12-03: The very same can be done for both Arch Linux and Fedora, The same file locations apply too.
A look at Emacs
10th August 2010It's remarkable what work can bring your way in terms of technology. For me, (GNU) Emacs Has proved to be such a thing recently. It may have been around since 1975, long before my adventures in computing ever started, in fact, but I am asking myself why I never really have used it much. There are vague recollections of my being aware of its existence in the early days of my using UNIX over a decade ago. Was it a shortcut card with loads of seemingly esoteric keyboard shortcuts and commands that put me off it back then? The truth may have been that I got bedazzled with the world of Microsoft Windows instead, and so began a distraction that lingered until very recently. As unlikely as it looks now, Word and Office would have been part of the allure of what some consider as the dark side these days. O how OpenOffice.org and their ilk have changed that state of affairs...
The unfortunate part of the Emacs story might be that its innovations were never taken up as conventions by mainstream computing. If its counterparts elsewhere used the same keyboard shortcuts, it would feel like learning such an unfamiliar tool. Still, it's not as if there isn't logic behind it because it will work both in a terminal session (where I may have met it for the first time) and a desktop application GUI. The latter is the easier to learn, and the menus list equivalent keyboard shortcuts for many of their entries, too. For a fuller experience though, I can recommend the online manual, and you can buy it in paper form too if you prefer.
One thing that I discovered recently is that external factors can sour the impressions of a piece of software. For instance, I was using a UNIX session where the keyboard mapping wasn't optimal. There's nothing like an unfamiliar behaviour for throwing you off track because you feel that your usual habits are being obstructed. For instance, finding that a Backspace key is behaving like a Delete one is such an obstruction. It wasn't the fault of Emacs, and I have found that using Ctrl+K (C-k in the documentation) to delete whole lines is invaluable.
Apart from keyboard mapping niggles, Emacs has to be respected as a powerful piece of software in its own right. It may not have the syntax highlighting capabilities of some, like gedit or NEdit for instance, but I have a hunch that a spot of Lisp programming would address that need. What you get instead is support for version control systems like RCS or CVS, along with integration with GDB for debugging programs written in a number of languages. Then, there are features like file management, email handling, newsgroup browsing, a calendar and a calculator that make you wonder if they tried to turn a text editor into something like an operating system. With Google trying to use Chrome as the basis of one, it almost feels as is Emacs was ahead of its time, though that may have been more due to its needing to work within a UNIX shell in those far-off pre-GUI days. It really is saying something that it has stood the test of time when so much has fallen by the wayside. Like Vi, it looks as if the esteemable piece of software is showing no signs of going away just yet. Maybe it was well-designed in the beginning, and the thing certainly seems more than a text editor with its extras. Well, it has to offer a good reason for making its way into Linux too...
A look at Slackware 13.0
5th June 2010Some curiosity has come upon me and I have been giving a few Linux distros a spin in VirtualBox virtual machines. One was Slackware, which reminds me of a fellow university student using it in the mid/late 1990's. Since then, my exploration took me into Red Hat, SuSE, Mandrake and eventually to Ubuntu, Debian and Fedora. Since all of that bypassed Slackware, it was to give the thing a look.
While the current version is 13.1, it was 13.0 that I had to hand, so I had a go with that. In many ways, the installation was a flashback to the 1990's and I can see it looking intimidating to many computer users with its now old-fashioned installation GUI. If you can see through that, though, the reality is that it isn't too difficult to install.
After all, the DVD was bootable. However, it did leave you at a command prompt and I can see that throwing many. The next step is to use cfdisk to create partitions (at least two are needed, swap and normal). Once that is done, it is time to issue the command setup and things look more graphical again. I picked the item for setting the locale of the keyboard and everything followed from there, but there is a help option too for those who need it. If you have installed Linux before, you'll recognise a lot of what you see. It'll finish off the set-up of disk partitions for you and supports ext4 too; it's best not to let antique impressions fool you. For most of the time, I stuck with the defaults and left it to perform a full installation with KDE as the desktop environment. If there is any real criticism, it is the absence of an overall progress bar to see where it is with package installation.
Once the installation was complete, it was time to restart the virtual machine, and I found myself left at the command prompt. Only the root user was set up during installation, so I needed to add a normal user too. Issuing startx was enough to get me into KDE (along with included alternatives like XFCE, there is a community build using GNOME too) for that, but I wanted to have that loading automatically. To fix that, you need to edit /etc/inittab to change the default run level from 3 to 4 (hint: look for a line with id:3:initdefault: in it near the top of the file and change that; the file is well commented so you can find your way around it easily without having to look for specific esoteric test strings).
After all this, I ended up with a usable Slackware 130.0 installation. Login screens have a pleasing dark theme by default, while the desktop is very blue. There may be no OpenOffice but KOffice is there in its place and Seamonkey is an unusual inclusion along with Firefox. Though it looks as if it'll take a little more time to get to know Slackware, it looks good so far; I may even go about getting 13.1 to see how things might have changed and report my impressions accordingly. Some will complain about the rough edges that I describe here but remarks about using Slackware to learn about Linux persist. Maybe, Linux distributions are like camera film; some are right for you and some aren't. Personally, I wouldn't thrust Slackware upon a new Linux user if they have to install it themselves, but it's not at all bad for that.
Relocating the Apache web server document root directory in Fedora 12
9th April 2010So as not to deface anything that is available online on the web, I have a tendency to set up an offline Apache server on a home PC to do any tinkering away from the eyes of the unsuspecting public. Though Ubuntu is my mainstay for home computing, I do have a PC with Fedora installed, and I have been trying to get an Apache instance to start automatically on there unsuccessfully for a few months. While I can start it by running the following command as root, I'd rather not have more manual steps than is necessary.
httpd -k start
The command used by the system when it starts is different and, even when manually run as root, it failed with messages saying that it couldn't find the directory while the web server files are stored. Here it is:
service httpd start
The default document root location on any Linux distribution that I have seen is /var/www and all is very well with this, but it isn't a safe place to leave things if ever a re-installation is needed. Having needed to wipe /var after having it on a separate disk or partition for the sake of one installation, it doesn't look so persistent to me. In contrast, you can safeguard /home by having it on another disk or in a dedicated partition, which means that it can be retained even when you change the distro that you're using. Thus, I have got into the habit of having the root of the web server document root folder in my home area, and that is where I have been seeing the problem.
Because of the access message, I tried using chmod and chgrp, but to no avail. The remedy has to do with reassigning the security contexts used by SELinux. In Fedora, Apache will not work with the context user_home_t that is usually associated with home directories, but needs httpd_sys_content_t instead. To find out what contexts are associated with particular folders, issue the following command:
ls -Z
The final solution was to create a user account whose home directory hosts the root of the web server file system, called www in my case. Then, I executed the following command as root to get things going:
chcon -R -h -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/www
It appears that even the root of the home directory has to have an appropriate security context (/home has home_root_t so that might do the needful too). Without that, nothing will work, even if all is well at the next level down. The switches for chcon command translate as follows:
-R : recursive; applies changes to all files and folders within a directory.
-h : changes apply only to symbolic links and not to where they refer in the file system.
-t : alters context type.
It took a while for all of this stuff about SELinux security contexts to percolate through to the point where I was able to solve the problem. A spot of further inspiration was needed too and even guided my search for the information that I needed. It's well worth trying Linux Home Networking if you need further details. Though there are references to an earlier release of Fedora, the content still applies to later versions of Fedora to the current release, if my experience is typical.
Command Line Software Management
2nd December 2009One of the nice things about a Debian-based Linux distribution is that it is easy to pull a piece of software onto your system from a repository using either apt-get or aptitude. While some may prefer a GUI, but I find that the command line offers a certain extra transparency that stops the "what's it doing?" type of question. That's never to say that the GUI-based approach hasn't a place, and I only go using it when seeking out a piece of software without knowing its aptitude-ready name. Interestingly, there are signs that Canonical may be playing with the idea of making Ubuntu's Software Centre a full application management tool with updates and upgrades getting added to the current searching, installation and removal facilities. That well may be, but it's going to take a lot of effort to get me away from the command line altogether.
Fedora and openSUSE have their software management commands too in the shape of yum and zypper, respectively. The recent flurry of new operating system releases has had me experimenting with both of those distros on a real test machine. As might be expected, the usual battery of installation, removal and update activities are well served, and I have been playing with software searching using yum too.
One thing that has yet to mature is in-situ distribution upgrading, à la Ubuntu. In principle, it is possible, but I got a black screen when I tried moving from openSUSE 11.1 to 11.2 within VirtualBox using instructions on the openSUSE website. Not wanting to wait, I reached for a Live CD instead, and that worked a treat on both virtual and real machines.
Being in an experimental turn of mind, I attempted the same to get from Fedora 11 to the beta release of its version 12. A spot of repository trouble got me using a Live CD in its place. You can perform an in-situ upgrade from a full Fedora DVD, but the only option is system replacement when you have a Live CD.
Once installation is out of the way, YAST can be ignored in favour of zypper and yum is good enough that Fedora's GUI-using alternative can be ignored. It's nice to see good transparent ideas taking hold elsewhere and may make migration between distros much easier too.
Making Nautilus work like it does in Ubuntu for any other GNOME-using distro
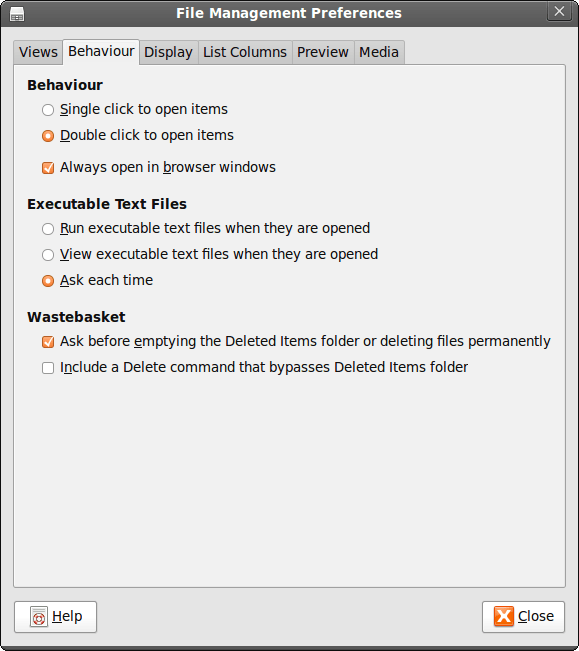
26th July 2009While It's a personal preference, I like the way that Nautilus (GNOME's default file manager if you need to know) is set to work on Ubuntu by default. For some tastes, it might look too similar to Windows Explorer, but having all the action happening in the same window is a convenience that users of other GNOME using distributions may not realise is there at all. By default, Debian and Fedora use what is called spatial mode, with each double-clicking action on a folder icon firing up a new window. Personally, I think that clutters the desktop without good cause, yet it's easy to change. All that's needed is to go to Edit>Preferences in a Nautilus window, proceed to the Behaviour tab and toggle the Always open in browser windows tick box as shown below. Quite why this is not the default in all GNOME using distributions is beyond me, but others may prefer what I dislike and Linux is all about choice, after all. Well, you can decide to use Gnome Commander instead and there are times when I do the same along with being a command line user too.
Getting Fedora working in VirtualBox
12th May 2009After a hiatus induced by disk errors seen on start up, I have gone having a go with Fedora again. In the world of real PC's, its place has been taken by Debian, so virtualisation was brought into play for my most recent explorations. I could have gone with 10, the current stable version, but curiosity got the better of me and I downloaded a pre-release version of 11 instead.
On my way to getting that instated, I encountered two issues. The first of these was boot failure with the message like this:
FATAL: INT18: BOOT FAILURE
As it turned out, that was easily sorted. I was performing the installation from a DVD image mounted as if it were a real DVD, and laziness or some other similar reason had me rebooting with it still mounted. Though there is an option to load the hard disk variant, it wasn't happening, resulting in the message that's above. A complete shutdown and replacement of the virtual DVD with a real one set matters to rights.
The next trick was to get Guest Additions added, but Fedora's 2.6.29 was not what VirtualBox was expecting, and it demanded the same ransom as Debian: gcc, make and kernel header files. Unfamiliarity had me firing up Fedora's software installation software, only to find that Synaptic seems to beat it hands down in the search department. Turning to Google dredged up the following command to be executed, which got me further:
yum install binutils gcc make patch libgomp glibc-headers glibc-devel kernel-headers kernel-devel
However, the installed kernel headers didn't match the kernel, but a reboot fixed that once the kernel was updated. Then, the Guest Additions installed themselves as intended, with necessary compilations to match the installed kernel.
The procedures that I have described here would, it seems, work for Fedora 10; well, they certainly have bequeathed me a working system. I have had a little poke and a beta of Firefox 3.5 is included, and I saw sign of OpenOffice 3.1 too. So, it looks very cutting edge, easily so in comparison with Ubuntu and Debian. Apart from one or niggles, it seems to run smoothly too. Firstly, don't use the command shutdown -h now to close the thing down, or you'll cause VirtualBox to choke. Using the usual means ensures that all goes well, though. The other irritation is that it doesn't connect to the network without a poke from me. Whether SELinux is to blame for this or not, I cannot tell, but it might be something for consideration by the powers than be. That these are the sorts of things that I have noticed should be telling you that I have no major cause for complaint. While I have mulled over a move to Fedora in the past and that option remains as strong as ever, Ubuntu is not forcing me to look at an alternative and the fact that I know how to achieve what I need is resulting in inertia anyway.
On keyboards
17th April 2009While there cannot be too many Linux users who go out and partner a Microsoft keyboard with their system, my recent cable-induced mishap has resulted in exactly that outcome. Keyboards are such standard items that it is not so possible to generate any excitement about them, apart from RSI-related concerns. While I wasn't about to go for something cheap and nasty that would do me an injury, going for something too elaborate wasn't part of the plan either, even if examples of that ilk from Microsoft and Logitech were sorely tempting.
Shopping in a bricks and mortar store, like I was, has its pluses and its minuses. The main plus points are that you see and feel what you are buying, with the main drawback being that the selection on offer isn't likely to be as extensive as you'd find on the web, even if I was in a superstore. Despite the latter, there was still a good deal available. Though there were PS/2 keyboards for anyone needing them, USB ones seemed to be the main offer, with wireless examples showcased too. Strangely, the latter were only available as kits with mice included, further adding to the cost of an already none too cheap item. The result was that I wasn't lured away from the wired option.
While I didn't emerge with what would have been my first choice because that was out of stock, that's not to say that what I have doesn't do the job for me. The key action is soft and cushioned, which is a change from that to which I am accustomed; some keyboards feel like they belong on a laptop, but not this one. There are other bells and whistles too, with a surprising number of them working. The calculator and email buttons number among these along with the play/pause, back and forward ones for a media player; I am not so convinced about the volume controls though an on-screen indicator does pop up. You'd expect a Microsoft item to be more Windows specific than others, yet mine works as well as anything else in the Ubuntu world and I have no reason to suspect that other Linux distros would spurn it either. Keyboards tend to be one of those "buy-it-and-forget-it" items, and the new arrival should be no different.
Some things that I'd miss on moving from Linux to Windows
17th January 2009The latest buzz surrounding Windows 7 has caused one observer to suggest that it's about to blast Linux from the desktop. While my experiences might be positive, there are still things that I like about Linux that make me reluctant to consider switching back. Here are a few in no particular order:
Virtual Desktops (or Workspaces)
I find these very handy for keeping things organised when I have a few applications open at the same time. While I think that someone has come with a way of adding the same functionality to Windows, I'd need to go looking for that. Having everything cluttering up a single taskbar would feel a bit limiting.
Symbolic Links
If you have not come across these before, they are a little difficult to explain, but it's great to have the ability to make the contents of a folder appear in more than one place at a time without filling up your hard drive. While it's true to say that Windows 7 gets Libraries, I have a soft spot for the way that Linux does it so simply.
Lack of (intrusive) fidgeting
One of Windows' biggest problems is that it's such a massive target for attacks by the less desirable elements of the web community. The result is a multitude of security software vendors wanting to get their wares onto your PC; it's when they get there that all the fidgeting starts. The cause is the constant need for system monitoring that eats up resources that could be used for other things. Though I know some packages are less intrusive than others, I do like the idea of feeling as if I am in full control of my PC rather someone else taking decisions for me (unavoidable in the world of work, I know). An example of this is Norton's not allowing me to shut it down when it goes rogue, even when acting as Administrator. While I can see the reason for this in that it's trying to hamper the attentions of nefarious malware, it ends up making me feel less than empowered and I also like to feel trusted too. Another thing that I like is the idea of something awaiting my input rather than going away and trying to guess what I need and getting it wrong, an experience that seems typical of Microsoft software.
Command Line
Though this is less of a miss than it used to be, there is now a learning curve with PowerShell's inclusion with Windows 7, and it's not something that I want to foist on myself without my having the time to learn its ins and outs. Though it's not a bad skill to have listed on the proverbial CV, I now know my way around bash and its ilk while knowing where to look when I intend to take things further.
After these, there are other personal reasons for my sticking with Linux, like memories of bad experiences with Windows XP and the way that Linux just seems to get on with the job. Its being free of charge is another bonus, and the freedom to have things as you want makes you feel that you have a safer haven in this ever-changing digital world. While I am not sure if I'd acquire the final version of Windows 7, I am certain that it will not be replacing Linux as my main home computing platform, something that should come as no surprise given what I have said above.
No disruption here
12th November 2008It was just over a year ago that I gave Linux a go after Windows XP gave me a torrid time of it. Since then, I have been able to work more than happily with it and have picked a few new and useful tricks along the way too. All in all, it has been a good experience and I have been able to resolve most of the issues that I have seen. The various Ubuntu upgrades along the way have been taken in their stride, too. Version 7.04 was the first one, with version 7.10 coming immediately afterwards. 8.04 went in equally seamlessly as did 8.10. Some may decry what they might perceive as the glacial nature of any changes, but the flip-side is that change can cause disruption, so my vote is for the more gradual approach, whatever others might think. In line with this, I haven't noticed too many changes in Ubuntu's latest release, and any that I have seen have been of the pleasant kind. Saying that, it's so much better than the contortions surrounding Windows upgrades. All in all, Linux is being kind to me and I hope that it stays that way.