TOPIC: LINUX DISTRIBUTIONS
Ubuntu 10.10 and Citrix
15th January 2011Many of us with the opportunity to work from home will have met up with logging via a Citrix server. With that in mind, I set to getting an ICA client going on my main Ubuntu box at home. There is information scattered about the web in the form of a question on the Ubuntu forum and a step-by-step guide by Liberian Geek. To summarise the process that I followed here, you have to download a copy of the Citrix Receiver installer for Linux from the company's website. There, you'll see DEB and RPM packages, along with a tarball for other systems. The latter needs a bit more work, so I got the x86 DEB package and installed that in the usual way, using Ubuntu's Software Centre to do the installation following the download. Needing to start the Citrix connection via a browser session meant that a browser restart was needed too. That wasn't the end of the leg work because Thawte certificate errors were to stop me in my tracks until I downloaded their root certificates from their website. Once the zip file was on my PC, I extracted it and copied the required certificate (Thawte Server CA.cer from the thawte Server CA directory) to /usr/lib/ICAClient/keystore/cacerts on my system; it helped that the error message had told me which was the one I needed from the collection in the zip file. With that matter addressed, the connection happened without a glitch, and I was able to get to working without recourse to a Windows virtual machine. For once, Linux wasn't to be excluded from one of the ways of using computers that has been getting more prevalent these days.
Update 2012-04-14: On an equivalent installation on Linux Mint Debian Edition, I found that the installation location for the certificate had moved to /opt/Citrix/ICAClient/keystore/cacerts. This was for the 64-bit edition.
Update 2012-12-17: The above applied to an installation of version 12.10 on 32-bit Ubuntu GNOME Remix too.
A lot of work ahead
6th December 2010Recently, I tested Ubuntu 11.04's first alpha release on both a VirtualBox VM and a spare PC. As expected with alpha software, it had issues. The new Unity desktop environment didn't work properly on either system: no top or side panels appeared, and applications lacked menu bars. Others appear to have had better experiences, possibly because they did fresh installations rather than upgrades like I did. I might try a clean install or wait for the next alpha release. The final version will include Firefox 4 along with the desktop changes. Overall, Natty Narwhal promises to be an unusually significant Ubuntu update. I'll monitor its development before deciding whether to upgrade. There's still plenty of time, as the release is months away.
On upgrading from Fedora 13 to Fedora 14
7th November 2010My Fedora box recently got upgraded to the latest version of the distribution (14) and I stuck to a method that I have used successfully before and one that isn't that common with variants of Linux either. What I did was to go to the Fedora website and download a full DVD image, burn it to a disk and boot from that. Then, I chose the upgrade option from the menus and all went smoothly with only commonplace options needing selection from the menus and no data got lost either. Apparently, this way of going about things is only offered by the DVD option because the equivalent Live CD versions only do full installations.
However, there was another option that I fancied trying, but was stymied by messages about a troublesome Dropbox repository. As I later discovered, that would have been easily sorted, only for my opting for a tried and tested method instead. This was a pity because only two commands would have needed to be issued when logged in as root, and it would have been good to have had a go with them:
yum update yum
yum --releasever=14 update --skip-broken
These may have done what I habitually do with Ubuntu upgrades but trying them out either will have to await the release of the next version or my getting around to setting up a Fedora virtual machine to see what happens. The latter course of action might be sensible anyway to see if all works without any problems before doing it for a real PC installation.
Ridding Fedora of Unwanted Software Repositories
4th November 2010Like other Linux distributions, Fedora has the software repository scheme of things for software installation and updating. However, it could do with having the ability to remove unwanted repositories through a GUI, only it doesn't. What you need to do instead is switch to root in a terminal using the command su - and enter your root user password before navigating to /etc/yum.repos.d/ to delete the troublesome [file name].repo file. Recently, I needed to do this after upgrading to Fedora 14 or yum wouldn't work from the command line, which is the way that I tend to update Fedora (yum -y update is the command that I use because it automatically does all installations unattended until it is finished doing what's needed). The offending repository, or "Software Source" as these things are called in the GUI, belonged to Dropbox and even disabling it didn't make yum operate from the command like it should, so it had to go. Maybe Dropbox hasn't caught up with the latest release of Fedora, but that can be resolved another day.
Taking the sudo command beyond Ubuntu
27th October 2010Though some may call it introducing a security risk, being able to execute administrator commands on Ubuntu using sudo and gksu by default is handy. It's not the only Linux distribution with the facility, though, since the /etc/sudoers file is found in Debian and I plan to have a look into Fedora. The thing that needs to be done is to add the following line to the aforementioned file (you will need to do this as root):
[your user name] ALL=(ALL) ALL
One that is done, you are all set. Just make sure that you're using a secure password, though, and removing the sudo/gksu permissions is as simple as reversing the change.
Update on 2011-12-03: The very same can be done for both Arch Linux and Fedora, The same file locations apply too.
Exploring the option of mobile broadband
20th September 2010Last week, I decided to buy and experiment with a Vodafone PAYG mobile broadband dongle (the actual device is a ZTE K3570-Z) partly as a backup for my usual broadband (it has had its moments recently) and partly to allow me to stay more connected while on the move. Thoughts of blogging and checking up on email or the real-time web while travelling to and from different places must have swayed me.
Hearing that the use of Windows or OS X with the device had me attempting to hook up the device to Windows 7 running within a VirtualBox virtual machine on my main home computer. When that proved too big a request from the software setup, I went googling out of curiosity and found that there was a way to get the thing going with Linux. While I am not so sure that it works with Ubuntu without any further adjustments, my downloading of a copy of the Sakis3G script was enough to do the needful, and I was online from my main OS after all. So much for what is said on the box...
More success was had with Windows 7 as loaded on my Toshiba Equium notebook, with setting up and connections being as near to being effortless as these things can be. Ubuntu is available on there too, courtesy of Wubi, and the Sakis3G trick didn't fail for that either.
That's not to say that mobile broadband doesn't have its limitations, as I found. For instance, Subversion protocols and Wubi installations aren't supported, but that may be a result of non-support of IPv6 than anything else. Nevertheless, connection speeds are good as far as I can see, though I yet have to test out the persistence of Vodafone's network while constantly on the move. Having seen how flaky T-Mobile's network can be in the U.K. as I travel around using my BlackBerry, that is something that needs doing, yet all seems painless enough so far. However, the fact that Vodafone uses the more usual mobile phone frequency may be a help.
A look at Slackware 13.0
5th June 2010Some curiosity has come upon me and I have been giving a few Linux distros a spin in VirtualBox virtual machines. One was Slackware, which reminds me of a fellow university student using it in the mid/late 1990's. Since then, my exploration took me into Red Hat, SuSE, Mandrake and eventually to Ubuntu, Debian and Fedora. Since all of that bypassed Slackware, it was to give the thing a look.
While the current version is 13.1, it was 13.0 that I had to hand, so I had a go with that. In many ways, the installation was a flashback to the 1990's and I can see it looking intimidating to many computer users with its now old-fashioned installation GUI. If you can see through that, though, the reality is that it isn't too difficult to install.
After all, the DVD was bootable. However, it did leave you at a command prompt and I can see that throwing many. The next step is to use cfdisk to create partitions (at least two are needed, swap and normal). Once that is done, it is time to issue the command setup and things look more graphical again. I picked the item for setting the locale of the keyboard and everything followed from there, but there is a help option too for those who need it. If you have installed Linux before, you'll recognise a lot of what you see. It'll finish off the set-up of disk partitions for you and supports ext4 too; it's best not to let antique impressions fool you. For most of the time, I stuck with the defaults and left it to perform a full installation with KDE as the desktop environment. If there is any real criticism, it is the absence of an overall progress bar to see where it is with package installation.
Once the installation was complete, it was time to restart the virtual machine, and I found myself left at the command prompt. Only the root user was set up during installation, so I needed to add a normal user too. Issuing startx was enough to get me into KDE (along with included alternatives like XFCE, there is a community build using GNOME too) for that, but I wanted to have that loading automatically. To fix that, you need to edit /etc/inittab to change the default run level from 3 to 4 (hint: look for a line with id:3:initdefault: in it near the top of the file and change that; the file is well commented so you can find your way around it easily without having to look for specific esoteric test strings).
After all this, I ended up with a usable Slackware 130.0 installation. Login screens have a pleasing dark theme by default, while the desktop is very blue. There may be no OpenOffice but KOffice is there in its place and Seamonkey is an unusual inclusion along with Firefox. Though it looks as if it'll take a little more time to get to know Slackware, it looks good so far; I may even go about getting 13.1 to see how things might have changed and report my impressions accordingly. Some will complain about the rough edges that I describe here but remarks about using Slackware to learn about Linux persist. Maybe, Linux distributions are like camera film; some are right for you and some aren't. Personally, I wouldn't thrust Slackware upon a new Linux user if they have to install it themselves, but it's not at all bad for that.
If all else fails...
3rd June 2010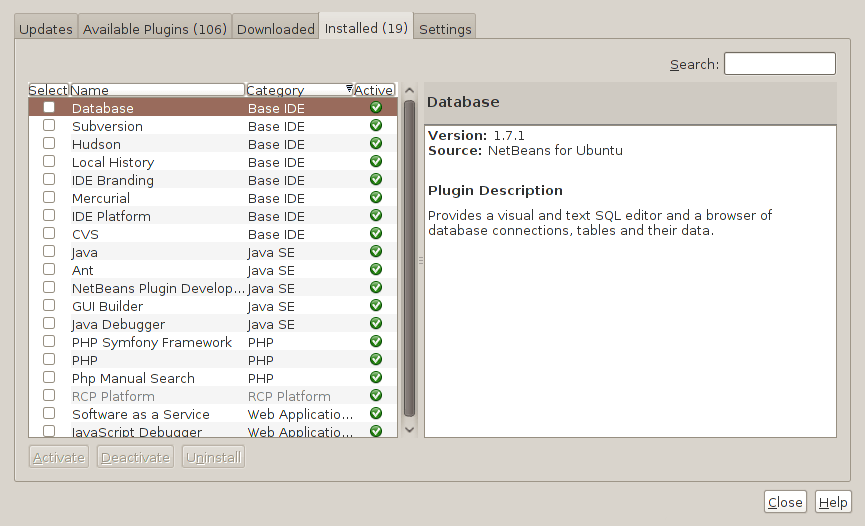
Two problems have come my way that were resolved by removing configuration files and going again. Both affected Linux installations that I have. The Ubuntu installation on my main PC is working well, but I ran into trouble starting up NetBeans 6.8. No GUI would ever appear but taking away the .netbeans folder from my home area allowed a fresh start with the IDE starting up as it should. To date, not all the various projects that I have are restored, but that can be done as I go along. Plugins for PHP development needing reinstatement, but that was another easy thing to achieve; just go to Tools > Plugins on the menus and work with the dialogue box that appears to download and install the needful.
The inspiration for taking the configuration folder from the home area came from needing to address a misadventure with a Debian VM. Perhaps foolishly, I went using gconf-editor on there and messed up the appearance of the terminal window with whatever change I made. Getting rid of the .gconf folder restored order with its recreation by the system. Next time, remembering what changes have been made and reversing them might be the best course of action...
Upgrading to Fedora 13
1st June 2010After having a spin of Fedora's latest in a VirtualBox virtual machine on my main home PC, I decided to upgrade my Fedora box. First, I needed to battle imperfect Internet speeds to get an ISO image that I could burn to a DVD. Once that was in place, I rebooted the Fedora machine using the DVD and chose the upgrade option to avoid bringing a major upheaval upon myself. You need the full DVD for this because only a full installation is available from Live ISO images and CD's.
Since all was graphical easiness, I got back into Fedora again without a hitch. Along with other bits and pieces, MySQL, PHP and Apache are working as before. If there was any glitch, it was with NetBeans 6.8 because the upgrade from the previous version didn't seem as complete as hoped. However, it was nothing that an update of the open source variant of Java and NetBeans itself couldn't resolve. There may have been untidy poking around before the solution was found, but all has been well since then.
Solving an upgrade hitch en route to Ubuntu 10.04
4th May 2010After waiting until after a weekend in the Isle of Man, I got to upgrade my main home PC to Ubuntu 10.04. Before the weekend away, I had been updating a 10.04 installation on an old spare PC and that worked fine, so the prospects were good for a similar changeover on the main box. That may have been so, but breaking a computer hardly is the perfect complement to a getaway.
To keep the level of disruption to a minimum, I opted for an in-situ upgrade. The download was left to complete in its own good time, and I returned to attend to installation messages asking me if I wished to retain old logs files for the likes of Apache. When the system asked for reboot at the end of the sequence of package downloading, installation and removal, I was ready to leave it do the needful.
However, I met with a hitch when the machine restarted: it couldn't find the root drive. Live CD's were pressed into service to shed light on what had happened. First up was an old disc for 9.10 before one for 10.04 Beta 1 was used. That identified a difference between the two that was to prove to be the cause of what I was seeing. 10.04 uses /dev/hd*# (/dev/hda1 is an example) nomenclature for everything, including software RAID arrays ("fakeraid"). 9.10 used the /dev/mapper/sil_**************# convention for two of my drives, and I get the impression that the names differ according to the chipset that is used.
During the upgrade process, the one thing that was missed was the changeover from /dev/mapper/sil_**************# to /dev/hd*# in the appropriate places in /boot/grub/menu.lst; look for the lines starting with the word kernel. When I did what the operating system forgot, I was greeted by a screen telling of the progress of checks on one of the system's disks. While that process took a while, a login screen followed, and I had my desktop much as before. The only other thing that I had to do was run gconf-editor from the terminal to send the title bar buttons to the right, where I am accustomed to having them. Since then, I have been working away as before.
Some may decry the lack of change (ImageMagick and UFRaw could do with working together much faster, though) but I'm not complaining; the rough of 9.10 drilled that into me. Nevertheless, I am left wondering how many are getting tripped up by what I encountered, even if it means that Palimpsest (what Ubuntu calls Disk Utility) looks much tidier than it did. Could the same thing be affecting /etc/fstab too? The reason that I don't know the answer to that question is that I changed all hard disk drive references to UUID a while ago, but it's another place to look if the GRUB change isn't fixing things for you. If my memory isn't failing me, I seem to remember seeing /dev/mapper/sil_**************# drive names in there too.