TOPIC: HTML ELEMENT
Rendering Markdown in WordPress without plugins by using Parsedown
4th November 2025Much of what is generated using GenAI as articles is output as Markdown, meaning that you need to convert the content when using it in a WordPress website. Naturally, this kind of thing should be done with care to ensure that you are the creator and that it is not all the work of a machine; orchestration is fine, regurgitation does that add that much. Naturally, fact checking is another need as well.
Writing plain Markdown has secured its own following as well, with WordPress plugins switching over the editor to facilitate such a mode of editing. When I tried Markup Markdown, I found it restrictive when it came to working with images within the text, and it needed a workaround for getting links to open in new browser tabs as well. Thus, I got rid of it to realise that it had not converted any Markdown as I expected, only to provide rendering at post or page display time. Rather than attempting to update the affected text, I decided to see if another solution could be found.
This took me to Parsedown, which proved to be handy for accomplishing what I needed once I had everything set in place. First, that meant cloning its GitHub repo onto the web server. Next, I created a directory called includes under that of my theme. Into there, I copied Parsedown.php to that location. When all was done, I ensured that file and directory ownership were assigned to www-data to avoid execution issues.
Then, I could set to updating the functions.php file. The first line to get added there included the parser file:
require_once get_template_directory() . '/includes/Parsedown.php';
After that, I found that I needed to disable the WordPress rendering machinery because that got in the way of Markdown rendering:
remove_filter('the_content', 'wpautop');
remove_filter('the_content', 'wptexturize');
The last step was to add a filter that parsed the Markdown and passed its output to WordPress rendering to do the rest as usual. This was a simple affair until I needed to deal with code snippets in pre and code tags. Hopefully, the included comments tell you much of what is happening. A possible exception is $matches[0]which itself is an array of entire <pre>...</pre> blocks including the containing tags, with $i => $block doing a $key (not the same variable as in the code, by the way) => $value lookup of the values in the array nesting.
add_filter('the_content', function($content) {
// Prepare a store for placeholders
$placeholders = [];
// 1. Extract pre blocks (including nested code) and replace with safe placeholders
preg_match_all('//si', $content, $pre_matches);
foreach ($pre_matches[0] as $i => $block) {
$key = "§PREBLOCK{$i}§";
$placeholders[$key] = $block;
$content = str_replace($block, $key, $content);
}
// 2. Extract standalone code blocks (not inside pre)
preg_match_all('/).*?<\/code>/si', $content, $code_matches);
foreach ($code_matches[0] as $i => $block) {
$key = "§CODEBLOCK{$i}§";
$placeholders[$key] = $block;
$content = str_replace($block, $key, $content);
}
// 3. Run Parsedown on the remaining content
$Parsedown = new Parsedown();
$content = $Parsedown->text($content);
// 4. Restore both pre and code placeholders
foreach ($placeholders as $key => $block) {
$content = str_replace($key, $block, $content);
}
// 5. Apply paragraph formatting
return wpautop($content);
}, 12); All of this avoided dealing with extra plugins to produce the required result. Handily, I still use the Classic Editor, which makes this work a lot more easily. There still is a Markdown import plugin that I am tempted to remove as well to streamline things. That can wait, though. It best not add any more of them any way, not least avoid clashes between them and what is now in the theme.
Moves to Hugo
30th November 2022What amazes me is how things can become more complicated over time. As long as you knew HTML, CSS and JavaScript, building a website was not as onerous as long as web browsers played ball with it. Since then, things have got easier to use but more complex at the same time. One example is WordPress: in the early days, themes were much simpler than they are now. The web also has got more insecure over time, and that adds to complexity as well. It sometimes feels as if there is a choice to make between ease of use and simplicity.
It is against that background that I reassessed the technology that I was using on my public transport and Irish history websites. The former used WordPress, while the latter used Drupal. The irony was that the simpler website was using the more complex platform, so the act of going simpler probably was not before time. Alternatives to WordPress were being surveyed for the first of the pair, but none had quite the flexibility, pervasiveness and ease of use that WordPress offers.
There is another approach that has been gaining notice recently. One part of this is the use of Markdown for web publishing. This is a simple and distraction-free plain text format that can be transformed into something more readable. It sees usage in blogs hosted on GitHub, but also facilitates the generation of static websites. The clutter is absent for those who have no need of the Gutenberg Editor on WordPress.
With the content written in Markdown, it can be fed to a static website generator like Hugo. Using defined templates and fixed assets like CSS together with images and other static files, it can slot the content into HTML files very speedily since it is written in the Go programming language. Once you get acclimatised, there are no folder structures that cannot be used, so you get full flexibility in how you build out your website. Sitemaps and RSS feeds can be built at the same time, both using the same input as the HTML files.
In a nutshell, it automates what once needed manual effort used a code editor or a visual web page editor. The use of HTML snippets and layouts means that there is no necessity for hand-coding content, like there was at the start of the web. It also helps that Bootstrap can be built in using Node, so that gives a basis for any styling. Then, SCSS can take care of things, giving even more automation.
Given that there is no database involved in any of this, the required information has to be stored somewhere, and neither the Markdown content nor the layout files contain all that is needed. The main site configuration is defined in a single TOML file, and you can have a single one of these for every publishing destination; I have development and production servers, which makes this a very handy feature. Otherwise, every Markdown file needs a YAML header where titles, template references, publishing status and other similar information gets defined. The layouts then are linked to their components, and control logic and other advanced functionality can be added too.
Because static files are being created, it does mean that site searching and commenting, or contact pages cannot work like they would on a dynamic web platform. Often, external services are plugged in using JavaScript. One that I use for contact forms is Forminit. Then, Zapier has had its uses in using the RSS feed to tweet site updates on Twitter when new content gets added. Though I made different choices, Disqus can be used for comments and Algolia for site searching. Generally, though, you can find yourself needing to pay, particularly if you need to remove advertising or gain advanced features.
Some commenting service providers offer open source self-hosted options, but I found these difficult to set up and ended up not offering commenting at all. That was after I tried out Cactus Comments only to find that it was not discriminating between pages, so it showed the same comments everywhere. There are numerous alternatives like Remark42, Hyvor Talk, Commento, FastComments, Utterances, Isso, Mouthful, Muut and HyperComments but trying them all out was too time-consuming for what commenting was worth to me. It also explains why some static websites even send readers to Twitter if they have something to say, though I have not followed this way of working.
For searching, I added a JavaScript/JSON self-hosted component to the transport website, and it works well. However, it adds to the size of what a browser needs to download. That is not a major issue for desktop browsers, but the situation with mobile browsers is such that it has a sizeable effect. Testing with PageSpeed and Lighthouse highlighted this, even if I left things as they are. The solution works well in any case.
One thing that I have yet to work out is how to edit or add content while away from home. Editing files using an SSH connection is as much a possibility as setting up a Hugo publishing setup on a laptop. After that, there is the question of using a tablet or phone, since content management systems make everything web based. These are points that I have yet to explore.
As is natural with a code-based solution, there is a learning curve with Hugo. Reading a book provided some orientation, and looking on the web resolved many conundrums. There is good documentation on the project website, while forum discussions turn up on many a web search. Following any research, there was next to nothing that could not be done in some way.
Migration of content takes some forethought and took quite a bit of time, though there was an opportunity to carry some housekeeping as well. The history website was small, so copying and pasting sufficed. For the transport website, I used Python to convert what was on the database into Markdown files before refining the result. That provided some automation, but left a lot of work to be done afterwards.
The results were satisfactory, and I like the associated simplicity and efficiency. That Hugo works so fast means that it can handle large websites, so it is scalable. The new Markdown method for content production is not problematical so far apart from the need to make it more portable, and it helps that I found a setup that works for me. This also avoids any potential dealbreakers that continued development of publishing platforms like WordPress or Drupal could bring. For the former, I hope to remain with the Classic Editor indefinitely, but now have another option in case things go too far.
Some oddness with table cell display in Opera resolved
14th July 2009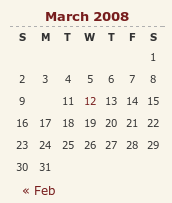
A while back, I reported a baffling problem with Opera managing to miss out an entry in the calendar widget on my hillwalking blog. After a bit of fiddling, I managed to track down the problem: setting position:relative in the CSS for hyperlink tags on my theme. While commenting out CSS declarations may seem a low technology way of finding problems like this, it still retains its place, as this little episode proves. Changing it to position:static for the hyperlinked numbers in the table resolved the issue, while I left the defaults as they were in case they had an adverse impact elsewhere.
If all this sounds rather too empirical in its approach, then I can only agree with you, yet a fix is a fix nonetheless. However, display:block is also set for the table entries, which means that may have a part to play too. Regardless of the trial and error feel to the solution, I could not find the problem documented anywhere, so I am sharing it here to help any others who encounter the same sort of weirdness.
Another way to control line breaks in (X)HTML
22nd October 2008While you can use <br /> tags, there is another way to achieve similar results: the or non-breaking space entity. Put one of them between two words, and you stop them getting separated by a line break; I have been using this in the latest design tweaks that I made to my online photo gallery. Turning this on its head, if you see two words together acting without regard to normal wrapping conventions, then you can suspect that a non-breaking space could be a cause. There might be CSS options too, but their effectiveness in different browsers may limit their usefulness.
Eliminating Peekaboo content display problems in Internet Explorer
1st July 2008Recently, I changed the engine of my online photo gallery to a speedier PHP/MySQL-based affair from its PHP/Perl/XML-powered predecessor. On the server side, all was well, but a peculiar display issue turned up in Internet Explorer (6, 7 & 8 were afflicted by this behaviour) where photo caption text on the thumbnail gallery pages was being displayed erratically.
As far as I can gather, the trigger for the behaviour was that the thumbnail block was placed within a DIV floated using CSS that touched another DIV that cleared the floating behaviour. I use a table to hold the images and their associated captions in place. Furthermore, each caption was also a hyperlink nested within a set of P tags.
The remedy was to set the CSS Display property for the affected XHTML tag to a value of "inline-block". Within a DIV, TABLE, TR, TD, P and A tag hierarchy, finding the right tag where the CSS property in question has the desired effect took some doing. As it happened, it was the tag set, that for the hyperlink, at the bottom of the stack that needed the fix.
Of course, it's all very fine fixing something for one browser, but it's worthless if it breaks the presentation in other browsers. In that vein, I did some testing in Opera, Firefox, Seamonkey and Safari to check if all was well and it was. There may be older browsers, like versions of IE before 6, where things don't appear as intended, yet I get the impression from my visitor statistics that the newer variants hold sway anyway. All in all, it was a useful lesson learnt, and that's never a bad thing.
CSS Control of Text Wrapping
11th September 2007Recently, I spotted a request for a dropdown list like that which you see below. I managed to create it using the CSS, but it only worked for Firefox, so I couldn't suggest it to the requester.
form select, form select option {width: 185px; white-space: normal;}
form select {height: 16px; width: 200px; white-space: normal;}
form {margin: 300px auto 0 auto; width: 300px;}
Here's how it looks in Firefox 2:

And in IE6:

And in Opera 9:

It would be nice if the white-space attribute gave the same result in all three but hey ho... As it happens, the W3C are working up other possible ways of controlling text wrapping in (X)HTML elements, but that's for the future, and I'll be expecting it when I see it.
For menus with wrapped entries, using DHTML menus and DOM scripting seems the best course for now. I suppose that you could always make the entries shorter, which is precisely what I tend to do; I am pragmatic like that. Nevertheless, there's never any harm in attempting to push the boundaries. You just have to come away from the cutting edge at the first sign of bleeding...
Of course, if anyone had other ideas, please let me know.
HennessyBlog theme update
12th February 2007Over the weekend, I have been updating the theme on my other blog, HennessyBlog. It has been a task that projected me onto a learning curve with the WordPress 2.1 codebase. Thus, I have collected what I encountered, so I know that it’s out there on the web for you (and I) to use and peruse. It took some digging to get to know some of what you find below. Since any function used to power WordPress takes some finding, I need to find one place on the web where the code for WordPress is more fully documented. The sites presenting tutorials on how to use WordPress are more often than not geared towards non-techies rather than code cutters like myself. Then again, they might be waiting for someone to do it for them…
The changes made are as follows:
Tweaks to the interface
These are subtle, with the addition of navigation controls to the sidebar and the change in location of the post metadata being the most obvious enhancements. “Decoration” with solid and dashed lines (using CSS border attributes rather than the deprecated hr tagset) and standards compliance links.
Standards compliance
Adding standards compliance links does mean that you’d better check that all is in order; it was then that I discovered that there was work to be done. There is an issue with the WordPress wpautop function (it lives in the formatting.php file) in that it sometimes doesn’t add closing tags. Finding out that it was this function that is implicated took a trip to the WordPress.org website; while a good rummage in the wp-includes folder does a lot, it can’t achieve everything.
Like many things in the WordPress code, the wpautop function isn’t half buried. The the_content function (see template-functions-post.php) used to output blog entries calls the get_content function (also in template-functions-post.php) to extract the data from MySQL. The add_filter function (in plugin.php) associates the wpautop function and others with the get_the_content function to add the p tags to the output.
To return to the non-ideal behaviour that caused me to start out on the above quest, an example is where you have an img tag enclosed by div tags. The required substitution involves the use of regular expressions that work most of the time but get confused here. So adding a hack to the wpautop function was needed to change the code so that the p end tag got inserted. I’ll be keeping an eye out for any more scenarios like this that slip through the net and for any side effects. Otherwise, compliance is just making sure that all those img tags have their alt attributes completed.
Tweaks to navigation code
Most of my time has been spent on tweaking of the PHP code supporting the navigation. Because different functions were being called in different places, I wanted to harmonise things. To accomplish this, I created new functions in the functions.php for my theme and needed to resolve a number of issues along the way. Not least among these were regular expressions used for subsetting with the preg_match function; these were not Perl-compliant to my eyes, as would be implied by the choice of function. Now that I have found that PCRE’s in PHP use a more pragmatic syntax, there appeared to be issues with the expressions that were being used. These seemed to behave OK in their native environment but fell out of favour within the environs of my theme. Being acquainted with Perl, I went for a more familiar expression style and the issue has been resolved.
Along the way, I broke the RSS feed. This was on my off-line test blog so no one, apart from myself, that is, would have noticed. After a bit of searching, I realised that some stray white-space from the end of a PHP file (wp-config.php being a favourite culprit), after the PHP end tag in the script file as it happens, was finding its way into the feed and causing things to fall over. Feed readers don’t take too kindly to the idea of the XML declaration not making an appearance on the first line of the file. Some confusion was caused by the refusal of Firefox to refresh things as it should before I realised that a forced refresh of the feed display was needed. Sometimes, it takes a while for an addled brain to think of these kinds of things.