TOPIC: OPENAI
Advance your Data Science, AI and Computer Science skills using these online learning opportunities
25th July 2025The landscape of online education has transformed dramatically over the past decade, creating unprecedented access to high-quality learning resources across multiple disciplines. This comprehensive examination explores the diverse array of courses available for aspiring data scientists, analysts, and computer science professionals, spanning from foundational programming concepts to cutting-edge artificial intelligence applications.
Data Analysis with R Programming
R programming has established itself as a cornerstone language for statistical analysis and data visualisation, making it an essential skill for modern data professionals. DataCamp's Data Analyst with R programme represents a comprehensive 77-hour journey through the fundamentals of data analysis, encompassing 21 distinct courses that progressively build expertise. Students begin with core programming concepts including data structures, conditional statements, and loops before advancing to sophisticated data manipulation techniques using tools such as dplyr and ggplot2. The curriculum extends beyond basic programming to include R Markdown for reproducible research, data manipulation with data.table, and essential database skills through SQL integration.
For those seeking more advanced statistical expertise, DataCamp's Statistician with R career track provides an extensive 108-hour programme spanning 27 courses. This comprehensive pathway develops essential skills for professional statistician roles, progressing from fundamental concepts of data collection and analysis to advanced statistical methodology. Students explore random variables, distributions, and conditioning through practical examples before advancing to linear and logistic regression techniques. The curriculum encompasses sophisticated topics including binomial and Poisson regression models, sampling methodologies, hypothesis testing, experimental design, and A/B testing frameworks. Advanced modules cover missing data handling, survey design principles, survival analysis, Bayesian data analysis, and factor analysis, making this track particularly suitable for those with existing R programming knowledge who seek to specialise in statistical practice.
The Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate programme, developed by Google and hosted on Coursera with US and UK versions, offers a structured six-month pathway for those seeking industry-recognised credentials. Students progress through eight carefully designed courses, beginning with foundational concepts in "Foundations: Data, Data, Everywhere" and culminating in a practical capstone project. The curriculum emphasises real-world applications, teaching students to formulate data-driven questions, prepare datasets for analysis, and communicate findings effectively to stakeholders.
Udacity's Data Analysis with R course presents a unique proposition as a completely free resource spanning two months of study. This programme focuses intensively on exploratory data analysis techniques, providing students with hands-on experience using RStudio and essential R packages. The course structure emphasises practical application through projects, including an in-depth exploration of diamond pricing data that demonstrates predictive modelling techniques.
Advanced Statistical Learning and Specialised Applications
Duke University's Statistics with R Specialisation elevates statistical understanding through a comprehensive seven-month programme that has earned a 4.6-star rating from participants. This five-course sequence delves deep into statistical theory and application, beginning with probability and data fundamentals before progressing through inferential statistics, linear regression, and Bayesian analysis. The programme distinguishes itself by emphasising both theoretical understanding and practical implementation, making it particularly valuable for those seeking to master statistical concepts rather than merely apply them.
The R Programming: Advanced Analytics course on Udemy, led by instructor Kirill, provides focused training in advanced R techniques within a compact six-hour format. This course addresses specific challenges that working analysts face, including data preparation workflows, handling missing data through median imputation, and working with complex date-time formats. The curriculum emphasises efficiency techniques such as using apply functions instead of traditional loops, making it particularly valuable for professionals seeking to optimise their analytical workflows.
Complementing this practical approach, the Applied Statistical Modelling for Data Analysis in R course on Udemy offers a more comprehensive 9.5-hour exploration of statistical methodology. The curriculum covers linear modelling implementation, advanced regression analysis techniques, and multivariate analysis methods. With its emphasis on statistical theory and application, this course serves those who already possess foundational R and RStudio knowledge but seek to deepen their understanding of statistical modelling approaches.
Imperial College London's Statistical Analysis with R for Public Health Specialisation brings academic rigour to practical health applications through a four-month programme. This specialisation addresses real-world public health challenges, using datasets that examine fruit and vegetable consumption patterns, diabetes risk factors, and cardiac outcomes. Students develop expertise in linear and logistic regression while gaining exposure to survival analysis techniques, making this programme particularly relevant for those interested in healthcare analytics.
Visualisation and Data Communication
Johns Hopkins University's Data Visualisation & Dashboarding with R Specialisation represents the pinnacle of visual analytics education, achieving an exceptional 4.9-star rating across its four-month curriculum. This five-course programme begins with fundamental visualisation principles before progressing through advanced ggplot2 techniques and interactive dashboard development. Students learn to create compelling visual narratives using Shiny applications and flexdashboard frameworks, skills that are increasingly essential in today's data-driven business environment.
The programme's emphasis on publication-ready visualisations and interactive dashboards addresses the growing demand for data professionals who can not only analyse data but also communicate insights effectively to diverse audiences. The curriculum balances technical skill development with design principles, ensuring graduates can create both statistically accurate and visually compelling presentations.
Professional Certification Pathways
DataCamp's certification programmes offer accelerated pathways to professional recognition, with each certification designed to be completed within 30 days. The Data Analyst Certification combines timed examinations with practical assessments to evaluate real-world competency. Candidates must demonstrate proficiency in data extraction, quality assessment, cleaning procedures, and metric calculation, reflecting the core responsibilities of working data analysts.
The Data Scientist Certification expands these requirements to include machine learning and artificial intelligence applications, requiring candidates to collect and interpret large datasets whilst effectively communicating results to business stakeholders. Similarly, the Data Engineer Certification focuses on data infrastructure and preprocessing capabilities, essential skills as organisations increasingly rely on automated data pipelines and real-time analytics.
The SQL Associate Certification addresses the universal need for database querying skills across all data roles. This certification validates both theoretical knowledge through timed examinations and practical application through hands-on database challenges, ensuring graduates can confidently extract and manipulate data from various database systems.
Emerging Technologies and Artificial Intelligence
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence has created new educational opportunities that bridge traditional data science with cutting-edge generative technologies. DataCamp's Understanding Artificial Intelligence course provides a foundation for those new to AI concepts, requiring no programming background whilst covering machine learning, deep learning, and generative model fundamentals. This accessibility makes it valuable for business professionals seeking to understand AI's implications without becoming technical practitioners.
The Generative AI Concepts course builds upon this foundation to explore the specific technologies driving current AI innovation. Students examine how large language models function, consider ethical implications of AI deployment, and learn to maximise the effectiveness of AI tools in professional contexts. This programme addresses the growing need for AI literacy across various industries and roles.
DataCamp's Large Language Model Concepts course provides intermediate-level exploration of the technologies underlying systems like ChatGPT. The curriculum covers natural language processing fundamentals, fine-tuning techniques, and various learning approaches including zero-shot and few-shot learning. This technical depth makes it particularly valuable for professionals seeking to implement or customise language models within their organisations.
The ChatGPT Prompt Engineering for Developers course addresses the developing field of prompt engineering, a skill that has gained significant commercial value. Students learn to craft effective prompts that consistently produce desired outputs from language models, a capability that combines technical understanding with creative problem-solving. This expertise has become increasingly valuable as organisations integrate AI tools into their workflows.
Working with OpenAI API provides practical implementation skills for those seeking to build AI-powered applications. The course covers text generation, sentiment analysis, and chatbot development, giving students hands-on experience with the tools that are reshaping how businesses interact with customers and process information.
Computer Science Foundations
Stanford University's Computer Science 101 offers an accessible introduction to computing concepts without requiring prior programming experience. This course addresses fundamental questions about computational capabilities and limitations whilst exploring hardware architecture, software development, and internet infrastructure. The curriculum includes essential topics such as computer security, making it valuable for anyone seeking to understand the digital systems that underpin modern society.
The University of Leeds' Introduction to Logic for Computer Science provides focused training in logical reasoning, a skill that underlies algorithm design and problem-solving approaches. This compact course covers propositional logic and logical modelling techniques that form the foundation for more advanced computer science concepts.
Harvard's CS50 course, taught by Professor David Malan, has gained worldwide recognition for its engaging approach to computer science education. The programme combines theoretical concepts with practical projects, teaching algorithmic thinking alongside multiple programming languages including Python, SQL, HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. This breadth of coverage makes it particularly valuable for those seeking a comprehensive introduction to software development.
MIT's Introduction to Computer Science and Programming Using Python focuses specifically on computational thinking and Python programming. The curriculum emphasises problem-solving methodologies, testing and debugging strategies, and algorithmic complexity analysis. This foundation proves essential for those planning to specialise in data science or software development.
MIT's The Missing Semester course addresses practical tools that traditional computer science curricula often overlook. Students learn command-line environments, version control with Git, debugging techniques, and security practices. These skills prove essential for professional software development but are rarely taught systematically in traditional academic settings.
Accessible Learning Resources and Community Support
The democratisation of education extends beyond formal courses to include diverse learning resources that support different learning styles and schedules. YouTube channels such as Programming with Mosh, freeCodeCamp, Alex the Analyst, Tina Huang, and Ken Lee provide free, high-quality content that complements formal education programmes. These resources offer everything from comprehensive programming tutorials to career guidance and project-based learning opportunities.
The 365 Data Science platform contributes to this ecosystem through flashcard decks that reinforce learning of essential terminology and concepts across Excel, SQL, Python, and emerging technologies like ChatGPT. Their statistics calculators provide interactive tools that help students understand the mechanics behind statistical calculations, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application.
Udemy's marketplace model supports this diversity by hosting over 100,000 courses, including many free options that allow instructors to share expertise with global audiences. The platform's filtering capabilities enable learners to identify resources that match their specific needs and learning preferences.
Industry Integration and Career Development
Major technology companies have recognised the value of contributing to global education initiatives, with Google, Microsoft and Amazon offering professional-grade courses at no cost. Google's Data Analytics Professional Certificate exemplifies this trend, providing industry-recognised credentials that directly align with employment requirements at leading technology firms.
These industry partnerships ensure that course content remains current with rapidly evolving technological landscapes, whilst providing students with credentials that carry weight in hiring decisions. The integration of real-world projects and case studies helps bridge the gap between academic learning and professional application.
The comprehensive nature of these educational opportunities reflects the complex requirements of modern data and technology roles. Successful professionals must combine technical proficiency with communication skills, statistical understanding with programming capability, and theoretical knowledge with practical application. The diversity of available courses enables learners to develop these multifaceted skill sets according to their career goals and learning preferences.
As technology continues to reshape industries and create new professional opportunities, access to high-quality education becomes increasingly critical. These courses represent more than mere skill development; they provide pathways for career transformation and professional advancement that transcend traditional educational barriers. Whether pursuing data analysis, software development, or artificial intelligence applications, learners can now access world-class education that was previously available only through expensive university programmes or exclusive corporate training initiatives.
The future of professional development lies in this combination of accessibility, quality, and relevance that characterises the modern online education landscape. These resources enable individuals to build expertise that matches industry demands, also maintaining the flexibility to learn at their own pace and according to their specific circumstances and goals.
Resolving a glitch in the ChatGPT interface on Firefox using Tampermonkey
19th July 2025It may be caused either by a new version of Firefox or an update on the OpenAI side, but the ChatGPT prompt box lost its ability to show a cursor while I am entering text. The Ask anything text also disappeared. In Brave, all looked well, and it still persisted in clean Firefox sessions with no extensions loaded. Thus, it was a case of moving browser or getting a fix in Firefox.
The latter has not been needed because I found a fix of sorts. For that, I needed to install the Tampermonkey extension. Then, I could add a new script to override the behaviour that I was seeing:
// ==UserScript==
// @name ChatGPT Prompt Box Fix (Firefox)
// @namespace http://tampermonkey.net/
// @version 1.0
// @description Forces the ChatGPT prompt box textarea to remain visible in Firefox
// @author You
// @match https://chatgpt.com/*
// @grant none
// ==/UserScript==
(function () {
'use strict';
const waitForTextarea = () => {
const textarea = document.querySelector('textarea');
if (textarea) {
textarea.style.display = 'block';
const observer = new MutationObserver(() => {
if (textarea.style.display === 'none') {
console.log('Textarea display:none overridden');
textarea.style.display = 'block';
}
});
observer.observe(textarea, { attributes: true, attributeFilter: ['style'] });
} else {
setTimeout(waitForTextarea, 300); // Keep retrying until textarea appears
}
};
waitForTextarea();
})();In short, this deals with a rogue display: none; line in the CSS, which equally well could have been inserted by JavaScript from somewhere that I cannot track down. The extra code is executed within a self-contained function to prevent interference with other elements and is restricted to the ChatGPT domain, which avoids unwanted impacts on the display of other websites.
The first step is to search for the relevant element on the page, retrying at intervals if necessary. Once located, the element's visibility is ensured by explicitly setting its display property to block. Continued monitoring of the element thwarts any dynamic attempts to hide it by changing its style. When such an action is detected, the script automatically overrides such changes to maintain its visibility, thereby ensuring consistent accessibility.
However, challenges with finding the affected element mean that I get the advisory text duplicated. Thus, I see two instances of Ask anything. However, that is a small price to pay for having a flashing cursor telling me where I am in the interface. Such is the nature of modern web coding that its complexity hinders debugging, thus posing the question as to why we are making such things so complicated in the first place.
What SAS Innovate 2025 revealed about the future of enterprise analytics
21st June 2025SAS Innovate 2025 comprised a global event in Orlando (6th-9th May) followed by regional editions on tour. This document provides observations from both the global event and the London stop (3rd-4th June), covering technical content, platform developments and thematic emphasis across the two occasions. The global event featured extensive recorded content covering platform capabilities, migration approaches and practical applications, whilst the London event incorporated these themes with additional local perspectives and a particular focus on governance and life sciences applications.

Global Event
Platform Expansion and New Capabilities
The global SAS Innovate 2025 event included content on SAS Clinical Acceleration, positioned as a SAS Viya equivalent to SAS LSAF. Whilst much appeared familiar from the predecessor platform, performance improvements and additional capabilities represented meaningful enhancements.
Two presentations, likely restricted to in-person attendees based on their absence from certain schedules, covered AI-powered SAS code generation. Shionogi presented on using AI for clinical studies and real-world evidence generation, with the significant detail that the AI capability existed within SAS Viya rather than depending on external large language models. Another session addressed interrogating and generating study protocols using SAS Viya, including functionality intended to support study planning in ways that could improve success probability.
These sessions collectively indicated a directional shift. The scope extends beyond conventional expectations of "SAS in clinical" contexts, moving into upstream and adjacent activities, including protocol development and more integrated automation.
Architectural Approaches and Data Movement
A significant theme across multiple sessions addressed fundamental shifts in data architecture. The traditional approach of moving massive datasets from various sources into a single centralised analytics engine is being challenged by a new paradigm: bringing analytics to the data. The integration of SAS Viya with SingleStore exemplifies this approach, where analytics processing occurs directly within the source database rather than requiring data extraction and loading. This architectural change can reduce infrastructure requirements for specific workloads by as much as 50 per cent, whilst eliminating the complexity and cost associated with constant data movement and duplication.
Trustworthy AI and Organisational Reflection
Keynote presentations addressed the relationship between AI systems and organisational practices. SAS Vice President of Data Ethics Practice Reggie Townsend articulated a perspective that reframes common concerns about AI bias. When AI produces biased results, the issue is not primarily technical failure, but rather a reflection of biases already embedded within cultural and organisational practices. This view positions AI as a diagnostic tool that surfaces systemic issues requiring organisational attention rather than merely technical remediation.
The focus on trustworthy AI extended beyond bias to encompass governance frameworks, transparency requirements and the persistent challenge that poor data quality leads to ineffective AI regardless of model sophistication. These considerations hold particular significance in probabilistic AI contexts, especially where SAS aims to incorporate deterministic elements into aspects of its AI offering.
Natural Language Interfaces and Accessibility
Content addressing SAS Viya Copilot demonstrated the platform's natural language capabilities, enabling users to interact with analytics through conversational queries rather than requiring technical syntax. This approach aims to democratise data access by allowing users with limited technical knowledge to directly engage with complex datasets. The Copilot functionality, built on Microsoft Azure OpenAI Service, supports code generation, model development assistance and natural language explanations of analytical outputs.
Cloud Migration and Infrastructure Considerations
A presentation on transforming clinical programming using SAS Clinical Acceleration was scheduled but not accessible at the global event. The closing session featured the CIO of Parexel discussing their transition to SAS managed cloud services. Characterised as a modernisation initiative, reported outcomes included reduced outage frequency. This aligns with observations from other multi-tenant systems, where maintaining stability and availability represents a fundamental requirement that often proves more complex than external perspectives might suggest.
Content addressing cloud-native strategies emphasised a fundamental psychological shift in resource management. Rather than the traditional capital expenditure mindset where physical servers run continuously, cloud environments enable strategic use of the capability to create and destroy computing resources on demand. Approaches include spinning up analytics environments at the start of the working day and shutting them down at the end, with more sophisticated implementations that automatically save and shut down environments after periods of inactivity. This dynamic approach ensures organisations pay only for actively used resources.
Presentations on organisational change management accompanying technical migrations emphasised that successful technology projects require attention to human factors alongside technical implementation. Strategies discussed included formal launch events to mark transitions, structured support mechanisms such as office hours for technical questions and community-building activities designed to foster relationships and maintain engagement during periods of change.
Platform Integration and Practical Applications
Content on SAS Viya Workbench covered availability through Azure and AWS, Python integration, R compatibility and interfacing with SAS Enterprise Guide, with demonstrations of several features. As SAS expands support for open-source languages, the presentation illustrated how these capabilities can provide a unified platform for different technical communities.
A presentation on retrieval augmented generation with unstructured data (such as system manuals), combined with agentic AI for diagnosing manufacturing system problems, offered a concrete use case. Given the tendency for these subjects to become abstract, the connected example provided practical insight into how components can function together in operational settings.
Digital Twins and Immersive Simulation
A notable announcement at the global event involved the partnership between SAS and Epic Games to create enhanced digital twins using Unreal Engine. This collaboration applies the same photorealistic 3D rendering technology used in Fortnite to industrial applications. Georgia-Pacific piloted this technology at its Savannah River Mill, which manufactures napkins, paper towels and toilet tissue. The facility was captured using RealityScan, Epic's mobile application, to create photorealistic renderings imported into Unreal Engine.
The application focused on optimising automated guided vehicle deployment and routing strategies. Rather than testing scenarios in the physical environment with associated costs and safety risks, the digital twin enables simulation of complex factory floor operations including AGV navigation, proximity alerts, obstacles and rare adverse events. SAS CTO Bryan Harris emphasised that digital twins should not only function like the real world but also look like it, enabling more accessible decision-making for frontline workers, engineers and machine operators beyond traditional data scientist roles.
The collaboration extends beyond visual fidelity. SAS developed a plugin connecting Unreal Engine to SAS Viya, enabling real-time data from simulated environments to fuel AI models that analyse, optimise and test industrial operations. This approach allows organisations to explore "what-if" scenarios virtually before implementing changes in physical facilities, potentially delivering cost savings whilst improving safety and operational efficiency.
Marketing Intelligence and Customer Respect
Content on SAS Customer Intelligence 360 addressed the platform's marketing decisioning capabilities, including next-best-offer functionality and real-time personalisation across channels. A notable emphasis concerned contact policies and rules that enable marketers to limit communication frequency, reflecting a strategic choice to respect customer attention rather than maximise message volume. This approach recognises that in environments characterised by notification saturation, demonstrating restraint can build trust and ensure greater engagement when communications do occur.
Financial Crime and Integrated Analytics
Presentations on financial crime addressed the value of integrated platforms that connect traditionally siloed functions such as fraud detection, anti-money laundering and sanctions screening. Network analytics capabilities enable identification of patterns and relationships across these domains that might otherwise remain hidden. Examples illustrated how seemingly routine alerts, when analysed within a comprehensive view of connected data, can reveal connections to significant criminal networks, transforming tactical operational issues into sources of strategic intelligence.
Data Lineage and Transformation Planning
Content on data lineage reframed this capability from a purely technical concern to a strategic tool for transformation planning. For large-scale modernisation initiatives, comprehensive mapping of data flows, transformations and dependencies provides the foundation for accurate effort estimation, budgetary planning and risk assessment. This visibility enables organisations to proceed with complex changes whilst maintaining confidence that critical downstream processes will not be inadvertently affected.
Development Practices and Migration Approaches
Sessions included content on using Bitbucket with SAS Viya to support continuous integration and continuous deployment pipelines for SAS code. Git formed the foundation of the approach, with supporting tools such as JQ. Given the current state of manual validation processes, this content addressed a genuine need for more robust validation methods for SAS macros used across clinical portfolios, where these activities can require several weeks and efficiency improvements would represent substantial value.
Another session provided detailed coverage of migrating from SAS 9 to SAS Viya, focusing on assessment methods for determining what requires migration and techniques for locating existing assets. The content reflected the reality that the discovery phase often constitutes the primary work effort rather than a preliminary step.
A presentation on implementing SAS Viya on-premises under restrictive security requirements described a solution requiring sustained collaboration with SAS over multiple years to achieve necessary modifications. This illustrated how certain deployments are defined primarily by governance, controls and assurance requirements rather than by product features.
Technical Fundamentals and Persistent Challenges
A hands-on session on data-driven output programming with SAS macros provided practical content with life sciences examples. Control tables and CALL EXECUTE represented familiar approaches, whilst the data step RESOLVE function offered new functionality worth exploring, particularly given its capability to work with macro expressions rather than being limited to macro variables in the manner of SYMGET.
A recurring theme across multiple contexts emphasised that poor data quality leads to ineffective AI and consequently to flawed decision-making. The technological environment evolves, but fundamental challenges persist. This consideration holds particular significance in probabilistic AI contexts, especially where SAS aims to incorporate deterministic elements into aspects of its AI offering.
London Event
Overview and Core Themes
The London edition of SAS Innovate 2025 on Tour demonstrated the pervasive influence of AI across the programme. The event concluded with Michael Wooldridge from the University of Oxford providing an overview of different categories of AI, offering conceptual grounding for a day when terminology and ambition frequently extended beyond current practical adoption.
The opening session presented SAS' recent offerings, maintaining consistency with content from the global event in Orlando whilst incorporating local perspectives. Trustworthiness, responsibility and governance emerged as prominent themes, particularly relevant given the current industry emphasis on innovation. A panel discussion included a brief exchange regarding the term "digital workforce", reflecting an awareness of the human implications that can be absent from wider industry discussion.
Life Sciences Stream Content
The Life Sciences stream focused heavily on AI, with presentations from AWS, AstraZeneca and IQVIA addressing the subject, followed by a panel discussion continuing this direction. The scale of technological change represents a tangible shift affecting all parts of the ecosystem. A presentation from a healthcare professional provided context regarding the operational environment within which pharmaceutical companies function. SAS CTO Bryan Harris expressed appreciation for pharmaceutical research and development work, an acknowledgement that appeared both substantive and appropriate to the setting.
The critical differences between Generative AI, AI Agents, and Agentic Systems
9th April 2025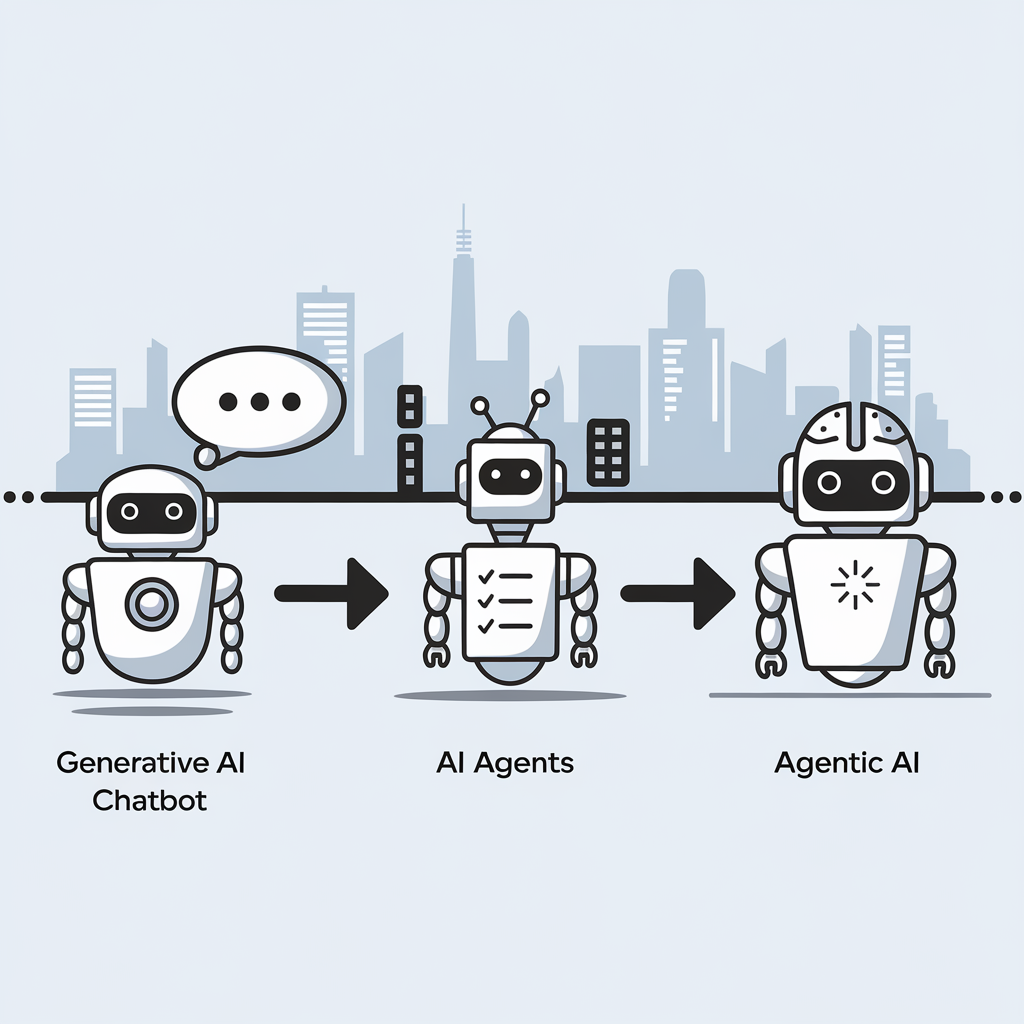
The distinction between three key artificial intelligence concepts can be explained without technical jargon. Here then are the descriptions:
- Generative AI functions as a responsive assistant that creates content when prompted but lacks initiative, memory or goals. Examples include ChatGPT, Claude and GitHub Copilot.
- AI Agents represent a step forward, actively completing tasks by planning, using tools, interacting with APIs and working through processes independently with minimal supervision, similar to a junior colleague.
- Agentic AI represents the most sophisticated approach, possessing goals and memory while adapting to changing circumstances; it operates as a thinking system rather than a simple chatbot, capable of collaboration, self-improvement and autonomous operation.
This evolution marks a significant shift from building applications to designing autonomous workflows, with various frameworks currently being developed in this rapidly advancing field.
Little helpers
22nd September 2024This could have been a piece that appeared on my outdoors blog until I got second thoughts. One reason why I might have done so is that I am making more use of Perplexity for searching the web and gaining more value from its output. However, that is proving more useful in writing what you find on here. Knowing the sources for a dynamically generated article adds more confidence when fact checking, and it is remarkable what comes up that you would find quickly with Google. There is added value with this one.
A better candidate would have been Anthropic's Claude. That has come in handy when writing trip reports. Being able to use a stub to prototype a blog entry really has its uses. The reality is that everything gets rewritten before anything gets published; these tools are never so good as to feature everything that you want to mention, even if they do a good job of mimicking your writing tone and style. Nevertheless, being able to work with the content beyond doing a brain dump from one's memory is an undeniable advance.
Sometimes, there are occasions when using Bing's access to OpenAI through Copilot helps with production of images. In reality, I do have an extensive personal library of images, so they possibly should suffice in many ways. However, curiosity about the technology overrides the effort that photo processing requires.
While there may be some level of controversy surrounding the use of AI tools in content creation, using such tooling for proofing content should not raise too much ire. Grammarly comes up a lot, though it is LanguageTool that I use to avoid excessive butting into my writing style. That has changed to comply with rules that had passed me without my noticing, but there are other things that need to be turned off. Configuring the proof tools in other ways might be better, so that is something to explore, or we could end up with too much standardisation of writing; there needs to be room for human creativity at all times.
All of these are just a sample of what is available. Just checking in with The Rundown AI will reveal that there is an onslaught of innovation right now. Hype also is a problem, yet we need to learn to use these tools. The changeover is equivalent to the explosive increase in availability of personal computing a generation ago. That brought its own share of challenges (some were on the curve while others were not) until everything settled down, and it will be the same with what is happening now.
Observations from selected sessions of SAS Innovate 2024
21st June 2024SAS Innovate 2024 provided insight into evolving approaches to analytics modernisation, platform development and applied data science across multiple industries. This document captures observations from sessions addressing strategic platform migrations, unified analytics environments, enterprise integration patterns and practical applications in regulated sectors. The content reflects a discipline transitioning from experimental implementations to production-grade, business-critical infrastructure.

Strategic Platform Modernisation
A presentation from DNB Bank detailed the organisation's migration from SAS 9.4 to SAS Viya on Microsoft Azure. The strategic approach proved counter-intuitive: whilst SAS Viya supports both SAS and Python code seamlessly, DNB deliberately chose to rewrite their legacy SAS code library into Python. The rationale combined two business objectives. First, expanding the addressable talent market by tapping into the global Python developer pool. Second, creating a viable exit strategy from their primary analytics vendor, ensuring compliance with financial regulatory requirements to demonstrate realistic vendor transition options within 30 to 90 days.
This decision represents a fundamental shift in enterprise software value propositions. Competitive advantage no longer derives from creating vendor lock-in, but from providing powerful, stable and governed environments that fully embrace open-source tools. The winning strategy involves convincing customers to remain because the platform delivers undeniable value, not because departure presents insurmountable difficulty. This is something that signals the maturing of a market, where value flows through partnership rather than proprietary constraints.
Unified Analytics Environments
A healthcare analytics presentation addressed the persistent debate between low-code/no-code interfaces for business users and professional coding environments for data scientists. Two analysts tackled identical problems (predicting diabetes risk factors using a public CDC dataset) using different approaches within the same platform.
The low-code user employed SAS Viya's Model Studio, a visual interface. This analyst assessed the model for statistical bias against variables such as age and gender by selecting a configuration option, whereupon the platform automatically generated fairness statistics and visualisations.
The professional coder used SAS Viya Workbench, a code-first environment similar to Visual Studio Code. This analyst manually wrote code to perform identical bias assessments. However, direct code access enabled fine-tuning of variable interactions (such as age and cholesterol), ultimately producing a logistic regression model with marginally superior performance compared to the low-code approach.
The demonstration illustrated that the debate presents a false dichotomy. The actual value resides in unified platforms, enabling both personas to achieve exceptional productivity. Citizen data scientists can rapidly build and validate baseline models, whilst expert coders can refine those same models with advanced techniques and deploy them, all within a single ecosystem. This unified approach characterises disciplinary development, where focus shifts from tribal tool debates to collective problem-solving.
Analytics as Enterprise Infrastructure
Multiple architectural demonstrations illustrated analytics platforms evolving beyond sophisticated workbenches for specialists into the central nervous system of enterprise operations. Three distinct patterns emerged:
The AI Assistant Architecture: A demonstration featured a customer-facing AI assistant built with Azure OpenAI. When users interacted with the chatbot regarding credit risk, requests routed through Azure Logic App not to the large language model for decisions but to a SAS Intelligent Decisioning engine. The SAS engine functioned as the trusted decision core, executing business rules and models to generate real-time risk assessments, which returned to the chatbot for customer delivery. SAS provided not the interface but the automated decision engine.
The Digital Twin Pattern: A pharmaceutical use case described using historical data from penicillin manufacturing batches to train machine learning models. These models became digital twins of physical bioreactors. Rather than conducting costly and time-consuming physical experiments, researchers executed thousands of in silico simulated experiments, adjusting parameters in the model to discover the optimal recipe for maximising yield (the "Golden Batch").
The Microsoft 365 Automation Hub: A workflow demonstration showed SAS programmes functioning as critical nodes in Microsoft 365 ecosystems. The automated process involved SAS code accessing SharePoint folders, retrieving Excel files, executing analyses, generating new reports as Excel files and delivering those reports directly into Microsoft Teams channels for business users.
These patterns mark profound evolution. Analytics platforms are moving beyond sophisticated calculators for experts, becoming foundational infrastructure: the connective tissue enabling intelligent automation and integrating disparate systems such as cloud office suites, AI interfaces and industrial hardware into cohesive business processes. This evolution from specialised tool to core infrastructure clearly indicates analytics' growing maturity within enterprise contexts.
Applied Data Science in High-Stakes Environments
Whilst much data science narrative focuses on e-commerce recommendations or marketing optimisation, compelling applications tackle intensely human, high-stakes operational challenges. Heather Hallett, a former ICU nurse and healthcare industry consultant at SAS, presented on improving hospital efficiency.
She described the challenge of staffing intensive care units, where having appropriate nurse numbers with correct skills proves critical. Staffing decisions constitute "life and death decisions". Her team uses forecasting models (such as ARIMA) to predict patient demand and optimisation algorithms (including mixed-integer programming) to create optimal nurse schedules. The optimisation addresses more than headcount; it matches nurses' specific skills, such as certifications for complex assistive devices like intra-aortic balloon pumps, to forecasted needs of the sickest patients.
A second use case applied identical operational rigour to community care. Using the classic "travelling salesman solver" from optimisation theory, the team planned efficient daily routes for mobile care vans serving maximum numbers of patients in their homes, delivering essential services to those unable to reach hospitals easily.
These applications ground abstract concepts of forecasting and optimisation in deeply tangible human contexts. They demonstrate that beyond driving revenue or reducing costs, the ultimate purpose of data science and operational analytics can be directly improving and even saving human lives. This application of sophisticated mathematics to life preservation marks data science evolution from commercial tool to critical component of human-centred operations.
Transparency as Competitive Advantage
In highly regulated industries such as pharmaceuticals, generating trustworthy research proves paramount. A presentation from Japanese pharmaceutical company Shionogi detailed how they transform the transparency challenge in Real-World Evidence (RWE) into competitive advantage.
The core problem with RWE studies, which analyse data from sources such as electronic health records and insurance claims, involves their historical lack of standardisation and transparency compared to randomised clinical trials, leading regulators and peers to question validity. Shionogi's solution is an internal system called "AI SAS for RWE", addressing the challenge through two approaches:
Standardisation: The system transforms disparate Real-World Data from various vendors into a Shionogi-defined common data model based on OMOP principles, ensuring consistency where direct conversion of Japanese RWD proves challenging.
Semi-Automation: It semi-automates the entire analysis workflow, from defining research concepts to generating final tables, figures and reports.
The most innovative aspect involves its foundation in radical transparency. The system automatically records every research process step: from the initial concept suite where analysis is defined, through specification documents, final analysis programmes and resulting reports, directly into Git. This creates a complete, immutable and auditable history of exactly how evidence was generated.
This represents more than a clever technical solution; it constitutes profound strategic positioning. By building transparent, reproducible and efficient systems for generating RWE, Shionogi directly addresses core industry challenges. They work to increase research quality and trustworthiness, effectively transforming regulatory burden into competitive edge built on integrity. This move toward provable, auditable results hallmarks a discipline transitioning from experimental art to industrial-grade science.
User Experience as Productivity Multiplier
In complex data tool contexts, user experience (UX) has evolved beyond "nice-to-have" aesthetic features into a central product strategy pillar, directly tied to user productivity and talent acquisition. A detailed examination of the upcoming complete rewrite of SAS Studio illustrated this point.
The motivation for the massive undertaking proved straightforward: the old architecture was slow and becoming a drag on user productivity. The primary goal for the new version involved making a web-based application "feel like a desktop application" regarding speed and responsiveness. To achieve this, the team focused on improvements directly boosting productivity for coders and analysts:
A Modern Editor: Integrating the Monaco editor used in the widely popular Visual Studio Code, providing familiar and powerful coding experiences.
Smarter Assistance: Improving code completion and syntax help to reduce errors and time spent consulting documentation.
Better Navigation: Adding features such as code "mini-maps" enabling programmers to navigate thousands of lines of code instantly.
For modern technical software, UX has become a fundamental competitive differentiator. Faster, more intuitive and less frustrating tools do not merely improve existing user satisfaction; they enhance productivity. In competitive markets for top data science and engineering talent, providing a best-in-class user experience represents a key strategy for attracting and retaining exceptional people. The next leap in team productivity might derive not from new algorithms but from superior interfaces.
Conclusion
These observations from SAS Innovate 2024 illustrate a discipline maturing. Data science is moving beyond isolated experiments and "science projects", becoming pragmatic, integrated, transparent and deeply human business functionality. Focus shifts from algorithmic novelty to real-world application value (whether enabling better user experiences, building regulatory trust or making life-or-death decisions on ICU floors).
As analytics becomes more integrated and accessible, the challenge involves identifying where it might unexpectedly transform core processes within organisations, moving from specialist concern to foundational infrastructure enabling intelligent, automated and human-centred operations.
Automating writing using R and Claude
16th April 2024Automation of writing using AI has become prominent recently, especially since GPT came to everyone's notice. It is more than automation of proofreading but of producing the content itself, as Mark Hinkle and Luke Matthews can testify. Figuring out how to use Generative AI needs more than one line prompts, so knowing what multi-line ones will work is what is earning six digit annual salaries for some.
Recently, I gave this a go when writing a post that used content from a Reddit post thread. The first step was to extract the content from the thread, and I found that I could use R to do this. That meant installing the RedditExtractoR package using the following command:
install.packages("RedditExtractoR")
Then, I created a short script containing the following lines of code with placeholders added in place of the actual locations:
library("RedditExtractoR")
write.csv(get_thread_content("<URL for Reddit post thread>"), "<location of text file>")
The first line above calls the RedditExtractoR package for use so that its get_thread_content function could be used to scape the thread's textual content. This was then fed to write.csv for writing out a text file with content.
Once I had the text file, I could upload it to Anthropic's Claude for the next steps. Firstly, I got it to give me a summary of the thread discussion before I asked it to give me the suggested solutions to the issue. Impressively, it capably provided me with the latter.
Now armed with these answers, I set to crafting the post from them. Claude did not do all the work for me, but it certainly helped with the writing. This is something that I fancy exploring further, especially given how business computing is likely to proceed in the next few years.
OWASP Top 10 for Large Language Model Applications
21st January 2024OWASP stands for Open Web Application Security Project, and it is an online community dedicated to web application security. They are well known for their Top 10 Web Application Security Risks and late last year, they added a Top 10 for
Large Language Model (LLM) Applications.
Given that large language models made quite a splash last year, this was not before time. ChatGPT gained a lot of attention (OpenAI also has had DALL-E for generation of images for quite a while now), there are many others with Anthropic Claude and Perplexity also being mentioned more widely.
Figuring out what to do with any of these is not as easy as one might think. For someone more used to working with computer code, using natural language requests is quite a shift when you no longer have documentation that tells what can and what cannot be done. It is little wonder that prompt engineering has emerged as a way to deal with this.
Others have been plugging in LLM capability into chatbots and other applications, so security concerns have come to light, so far, I have not heard anything about a major security incident, but some are thinking already about how to deal with AI-suggested code that others already are using more and more.
Given all that, here is OWASP's summary of their Top 10 for LLM Applications. This is a subject that is sure to draw more and more interest with the increasing presence of artificial intelligence in our everyday working and no-working lives.
LLM01: Prompt Injection
This manipulates an LLM through crafty inputs, causing unintended actions by the LLM. Direct injections overwrite system prompts, while indirect ones manipulate inputs from external sources.
LLM02: Insecure Output Handling
This vulnerability occurs when an LLM output is accepted without scrutiny, exposing backend systems. Misuse may lead to severe consequences such as Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF), Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF), privilege escalation, or remote code execution.
LLM03: Training Data Poisoning
This occurs when LLM training data are tampered, introducing vulnerabilities or biases that compromise security, effectiveness, or ethical behaviour. Sources include Common Crawl, WebText, OpenWebText and books.
LLM04: Model Denial of Service
Attackers cause resource-heavy operations on LLMs, leading to service degradation or high costs. The vulnerability is magnified due to the resource-intensive nature of LLMs and the unpredictability of user inputs.
LLM05: Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
LLM application lifecycle can be compromised by vulnerable components or services, leading to security attacks. Using third-party datasets, pre-trained models, and plugins can add vulnerabilities.
LLM06: Sensitive Information Disclosure
LLMs may inadvertently reveal confidential data in its responses, leading to unauthorized data access, privacy violations, and security breaches. It’s crucial to implement data sanitization and strict user policies to mitigate this.
LLM07: Insecure Plugin Design
LLM plugins can have insecure inputs and insufficient access control. This lack of application control makes them easier to exploit and can result in consequences such as remote code execution.
LLM08: Excessive Agency
LLM-based systems may undertake actions leading to unintended consequences. The issue arises from excessive functionality, permissions, or autonomy granted to the LLM-based systems.
LLM09: Overreliance
Systems or people overly depending on LLMs without oversight may face misinformation, miscommunication, legal issues, and security vulnerabilities due to incorrect or inappropriate content generated by LLMs.
LLM10: Model Theft
This involves unauthorized access, copying, or exfiltration of proprietary LLM models. The impact includes economic losses, compromised competitive advantage, and potential access to sensitive information.