TOPIC: MYSQL WORKBENCH
Dealing with Error 1064 in MySQL queries
27th April 2023Recently, I was querying a MySQL database table and got a response like the following:
ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use
The cause was that one of the data column columns was named using the MySQL reserved word key. While best practice is not to use reserved words like this at all, this was not something that I could alter. Therefore, I enclosed the offending keyword in backticks (`) to make the query work.
There is more information in the MySQL documentation on Schema Object Names and on Keywords and Reserved Words for dealing with or avoiding this kind of situation. While I realise that things change over time and that every implementation of SQL is a little different, it does look as if not using established keywords should be a minimum expectation when any database tables get created.
Disabling the SSL connection requirement in MySQL Workbench
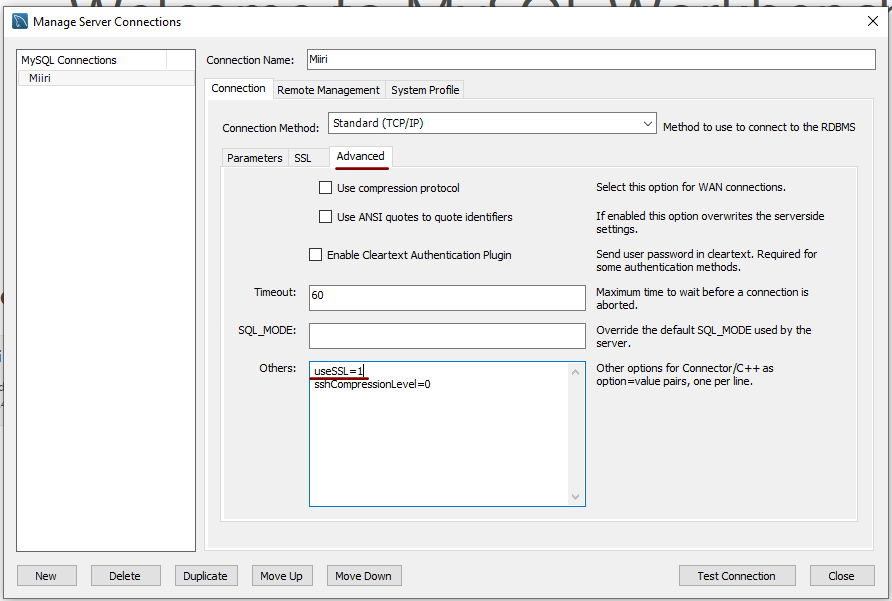
7th November 2022A while ago, I found that MySQL Workbench would only use SSL connections and that was stopping it from connecting to local databases. Thus, I looked for a way to override this: the cure was to go to Database > Manage Connections... in the menus for the application's home tab. In the dialogue box that appeared, I chose the connection of interest and went to the Advanced panel under Connection and removed the line useSSL=1 from the Others field. The screenshot below shows you what things looked like before the change was made. Naturally, the best practice would be to secure a remote database connection using SSL, so this approach is best reserved for remote non-production databases. While it may be that this does not happen now, I thought I would share this in case the problem persists for anyone.
Setting up MySQL on Sabayon Linux
27th September 2012For quite a while now, I have offline web servers for doing a spot of tweaking and tinkering away from the gaze of web users that visit what I have on there. Therefore, one of the tests that I apply to any prospective main Linux distro is the ability to set up a web server on there. This is more straightforward for some than for others. For Ubuntu and Linux Mint, it is a matter of installing the required software and doing a small bit of configuration. My experience with Sabayon is that it needs a little more effort than this, so I am sharing it here for the installation of MySQL.
The first step is to install the software using the commands that you find below. The first pops the software onto the system while the second completes the set-up. The --basedir option is need with the latter because it won't find things without it. It specifies the base location on the system, and it's /usr in my case.
sudo equo install dev-db/mysql
sudo /usr/bin/mysql_install_db --basedir=/usr
With the above complete, it's time to start the database server and set the password for the root user. That's what the two following commands achieve. Once your root password is set, you can go about creating databases and adding other users using the MySQL command line
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql start
mysqladmin -u root password 'password'
The last step is to set the database server to start every time you start your Sabayon system. The first command adds an entry for MySQL to the default run level so that this happens. The purpose of the second command is to check that this happened before restarting your computer to discover if it really happens. This procedure also is necessary for having an Apache web server behave in the same way, so the commands are worth having and even may have a use for other services on your system. ProFTP is another that comes to mind, for instance.
sudo rc-update add mysql default
sudo rc-update show | grep mysql
Further securing MySQL in Fedora
4th December 2009Ubuntu users must be spoilt because any MySQL installation asks you for a root password, an excellent thing in my opinion. With Fedora, it just pops the thing on there with you needing to set up a service and setting the root password yourself; if I recall correctly, I think that openSUSE does the same thing. For the service management, I needed to grab system-config-services from the repositories because my Live CD installation left off a lot of stuff, OpenOffice and GIMP even. The following command line recipe addressed the service manager omission:
su - # Change to root, entering password when asked
yum -y install system-config-services # Installs the thing without a yes/no prompt
exit # Return to normal user shell
Thereafter, the Services item from the menus at System > Administration was pressed into service and the MySQL service enabled and started. The next step was to lock down the root user, so the following sequence was used:
mysql # Enter MySQL prompt; no need for user or password because it still is unsecured!
UPDATE mysql.user SET Password=PASSWORD('MyNewPass') WHERE User='root';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
quit # Exit the mysql prompt, leaving the bare mysql command unusable
For those occasions when password problems keep you out of the MySQL shell, you'll find password resetting advice on the MySQL website, though I didn't need to go the whole hog here. MySQL Administrator might be another option for this type of thing. That thought never struck me while I was using it to set up less privileged users and allowing them access to the system. For a while, I was well stymied in my attempts to access the MySQL using any of those extra accounts until I got the idea of associating them with a host, another thing that is not needed on Ubuntu if my experience is any guide. All in all, Fedora may make you work a little extra to get things like thing done, yet I am not complaining if it makes you understand a little more about what is going on in the background, something that is never a disadvantage.
Running SQL scripts with MySQL
23rd September 2007Here's another of those little things that you forget if you aren't using them every day: running MySQL scripts using the Windows command line. Yes, you can also run SQL commands interactively, but there's a certain convenience about scripts. I am putting an example here so that it can be found again easily:
mysql -u username -p databasename < script.sql
Though I wouldn't be at all surprised if the same line worked under Linux and UNIX, I haven't needed to give it a try.