TOPIC: LINUX KERNEL
A pleasant surprise…
Yesterday, when taking the screen grab for my post on Quanta Plus, I did the Alt + Print Screen shuffle as usual. However, when I did so, I was greeted with a dialogue box asking me where I wanted to store the PNG file that was to be produced and what I wanted to call it. The operation was as swish as that. On Windows, the screenshot gets stuffed into the clipboard for you to extricate it with your graphics editor of choice, so this was an interesting surprise. It's the sort of thing that can make a good impression, and it is striking that Linux seems to be ahead of Windows on this one. Who said Linux was less than user-friendly?
Why I will be keeping Windows close to hand for a while to come after a switch to Linux
Even though I have moved to Linux, and it has been fulfilling nearly all of my home computing needs, I do and plan to continue to retain access to Windows courtesy of virtualisation technology. Thought keeping current with the world of the ever pervasive Windows is one motivation, there are others. In fact, now that Windows is more of a sideline, I may even get my hands on Vista at some point to take a further in-depth look at it, hopefully without having to suffer the consequences of my curiosity.
Talking of other reasons for hanging onto Windows, listening to music secured by DRM does come to mind. DRM is seen in a negative light by many in the open-source world, so Linux remains unencumbered by the beast. That isn't necessarily a bad thing, and the whole furore about Vista and DRM earlier this year had me wondering about a Linux future. However, I have been known to buy music from iTunes and would like to continue doing so. Though WINE might be one way to achieve this, retaining Windows seems a sounder option. That way, I am saved from having to convert my protected music files into either Ogg Vorbis or FLAC; the latter involves a lossless compression unlike the former, so the files are bigger with the additional quality that an audiophile would seek. MP3 is another option, yet there are those in the Linux world who frown upon anything patented. That makes getting MP3 support an additional task for those of us wanting it.
In my wisdom, I have succumbed to the delights of expensive web development tools like Altova's XMLSpy and Adobe's Dreamweaver. While I have found a way to get Quanta Plus to edit files on the web server directly and code hacking is my main way to improve my websites, I still will be having a bimble into Dreamweaver from time to time. I have yet to see XMLSpy's grid view replicated in the open-source world, so that should remain a key tool in my arsenal. While I haven't been looking too hard at open-source XML editors recently, there remains unexplored functionality in XMLSpy that I should really explore to see if it could be harnessed.
While I have included implicit references to this already, it needs saying that keeping Windows around also allows you to continue using familiar software. For some, this might be Microsoft Office, but OpenOffice and Evolution have usurped this in my case. Photoshop Elements is a better example for me. Digital transfers from scanners and DSLR's will stay in the world of Linux, while virtualisation allows me to process the images in whatever way I want. For now, I might just stick with the familiar before jumping ship to GIMP at some point in the future. With all that is written on Photoshop, having it there for learning new things seems a very sensible idea.
While open-source software can conceivably address every possible, there are bound to be niches that remain outside its reach. I use mapping software from Anquet when planning hillwalking excursions. It seems very much to be a Windows only offering and I have already downloaded a good amount of mapping, so Windows has to stay if I need to use this and the routes that I have plotted out before now. Another piece of software that finds its way into this bracket is my copy of SAS Learning Edition; there are times when a spot of learning at home goes a long way at work.
So, in summary, my reasons for keeping Windows around are as follows:
- Learning new things about the thing, since I am unlikely to escape its influence in the world of work
- Using iTunes to download new music and to continue to listen to what I have already
- Using and learning about industry standard web development tools like Dreamweaver and XMLSpy
- Easing the transition, by continuing to use Photoshop Elements, for example
- Using niche software like Anquet mapping
Though I suppose that many will relate to the above, Linux still has plenty to take over some of the above. In time, DRM may disappear from the music scene and not before time; accountants and shareholders may need to learn to trust customers. NVu and Quanta Plus could yet usurp Dreamweaver, and there may be an open-source alternative to XMLSpy like there is for so many other areas. The Photoshop versus GIMP choice will continue to prevent itself and all that is written about the former makes it seem silly to throw it away, however good the latter is. Even with changing over Linux equivalents of applications fulfilling standard needs, it still leaves niche applications like hillwalking mapping and that, together with the need to know what Windows might offer in the enterprise space, could be the enduring reasons for keeping it near to hand. That said, I can now go through whole days without firing up a Windows VM, a big change from how it was a few months ago. Still, I suppose that it's all too easy to stick with using one operating system at a time, which is Linux for me these days.
Do I still need serial numbers?
My spot of bad luck with Windows in August highlighted the importance of hanging on to serial numbers for software that I had purchased over the internet and downloaded. Though I could get at the ones that I needed, they were retained in a motley mix of text files and emails; one even was rediscovered by pottering back to the website of the purveyor. While the security of the installation files themselves was another matter of some concern, I was rather more organised in that regard. Both of these are things that need checking before Windows falls to pieces on you and needs to be reinstalled. Of course, human nature, being what it is, means that we often find ourselves picking up the pieces after a calamity has struck when a spot of planning would have made things that bit easier.
Linux does make life easier on this front: commercial applications are anything but the dominant force that they are in the world of Windows. That means that serial numbers are few and far between, and I only need the one for VMware Workstation. The mention of VMware brings me to my retention of Windows, so knowing where serial numbers are located remains a good idea. Even so, I cloned my Windows VM so that any Windows restoration following a destructive crash should be a quicker affair. Now that I am a Linux user, Windows crashes should not encroach as much on my home computing any more and Linux should be more stable anyway...
Setting up openSUSE in VMware Workstation
While it should have been as straightforward as following the instructions on the openSUSE website, a bug in VMware Tools derailed things for me. The usual procedure would have you starting by selecting Install VMware Tools from the VM menu before popping into the virtual machine to do the rest. Once binutils, gcc, gcc-c++, kernel-source and make are in place, the next steps should involve using YaST to install the RPM for you to run the vmware-config-tools.pl script from the terminal.
However, a bug in compat_slab.h puts a stop to any hopes of installing the vmhgfs component. That's needed if you like to enable the shared folders feature; looking in /mnt/hgfs then would get you to any shared folders. While everything else will be there, why miss out on one piece of functionality when it comes in useful?
Having found a useful thread on the subject, here's my way forward: it is as the expected procedure up to the point of installing the RPM. With VMware Tool installation on a Linux guest, you have two options: use RPM as described or use the compressed tarball. The latter seems the better course. Extract the contents into a folder and navigate to that folder. When there, go into vmware-tools-distrib/lib/modules/source and extract the file vmhgfs.tar. Proceed into the resulting vmhgfs-only contained wherever you put it and perform the following edit of compat_slab.h:
Change
#if LINUX_VERSION_CODE < KERNEL_VERSION(2, 6, 22) || defined(VMW_KMEMCR_HAS_DTOR)
to
#if LINUX_VERSION_CODE <= KERNEL_VERSION(2, 6, 22) || defined(VMW_KMEMCR_HAS_DTOR)
After that, recreate and replace vmhgfs.tar before issuing the following command in the terminal window while in the vmware-tools-distrib directory: ./vmware-config-tools.pl (anything prefixed with "./" picks up the file from the current working directory rather than where system binaries are stored). Though a kernel compilation will be involved, all the defaults should be sensible. Hopefully, all will work well after this.
Update: I am left with a number of outstanding issues that I need to resolve. Lack of internet access from the VM is one of them, and a constant forgetfulness regarding the nationality of my keyboard (it's British) might be another. In the interim, I have removed VMware tools until I can spend some time setting these to rights. That means internet access has returned, and the British keyboard layout is being interpreted correctly for now...
From real to virtual…
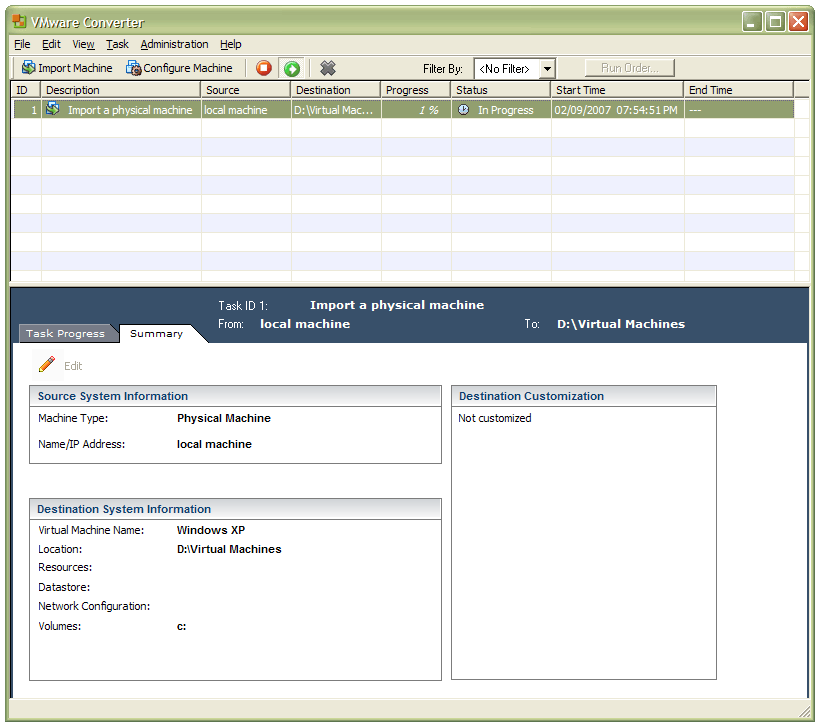
In a previous entry, I mused over a move from Windows to Linux, a suggestion being that Fedora Core Linux would be my base operating system with Windows installed in a Xen virtual machine. That, of course, led me to wonder how I would swap my current situation about: Linux in VM, Windows as host. Meantime, I discovered something that makes the whole process a little easier: VMware Convertor.
The Starter version can be downloaded free of charge, while the Enterprise edition comes with VirtualCenter Management Server for corporate use. What it does is to make a virtual version of a real computer, a process that takes drive imaging much, much further. I have given it a whirl and the conversion seems to go well; the only thing left is for me to fire it up in VMware Workstation - I believe that Player and Server will also run the VM that is created and, like Convertor Starter, they also can be downloaded free of charge; Workstation does everything for me, so I haven't looked beyond it, even though it did cost me money all those moons ago - and get through licence activation issues without leaving me with no authorised Windows installation.