TOPIC: FIRMWARE
Setting up a WD My Book Live NAS on Ubuntu GNOME 13.10
1st December 2013The official line from Western Digital is this: they do not support the use of their My Book Live NAS drives with Linux or UNIX. However, what that means is that they only develop tools for accessing their products for Windows and maybe OS X. It still doesn't mean that you cannot access the drive's configuration settings by pointing your web browser at http://mybooklive.local/. In fact, not having those extra tools is no drawback at all since the drive can be accessed through your file manager of choice under the Network section and the default name is MyBookLive too, so you easily can find the thing once it is connected to a router, or switch anyway.
Once you are in the server's web configuration area, you can do things like changing its name, updating its firmware, finding out what network has been assigned to it, creating and deleting file shares, password protecting file shares and other things. These are the kinds of things that come in handy if you are going to have a more permanent connection to the NAS from a PC that runs Linux. The steps that I describe have worked on Ubuntu 12.04 and 13.10 with the GNOME desktop environment.
What I was surprised to discover that you cannot just set up a symbolic link that points to a file share. Instead, it needs to be mounted and this can be done from the command line using mount or at start-up with /etc/fstab. For this to happen, you need the Common Internet File System utilities and these are added as follows if you need them (check in the Software Centre or in Synaptic):
sudo apt-get install cifs-utils
Once these are added, you can add a line like the following to /etc/fstab:
//[NAS IP address]/[file share name] /[file system mount point] cifs
credentials=[full file location]/.creds,
iocharset=utf8,
sec=ntlm,
gid=1000,
uid=1000,
file_mode=0775,
dir_mode=0775
0 0
Though I have broken it over several lines above, this is one unwrapped line in /etc/fstab with all the fields in square brackets populated for your system and with no brackets around these. Though there are other ways to specify the server, using its IP address is what has given me the most success; this is found under Settings > Network on the web console. Next up is the actual file share name on the NAS; I have used a custom term instead of the default of Public. The NAS file share needs to be mounted to an actual directory in your file system like /media/nas or whatever you like; however, you will need to create this beforehand. After that, you have to specify the file system, and it is cifs instead of more conventional alternatives like ext4 or swap. After this and before the final two space delimited zeroes in the line comes the chunk that deals with the security of the mount point.
What I have done in my case is to have a password-protected file share and the user ID and password have been placed in a file in my home area with only the owner having read and write permissions for it (600 in chmod-speak). Preceding the filename with a "." also affords extra invisibility. That file then is populated with the user ID and password like the following. Of course, the bracketed values have to be replaced with what you have in your case.
username=[NAS file share user ID]
password=[NAS file share password]
With the credentials file created, its options have to be set. First, there is the character set of the file (usually UTF-8 and I got error code 79 when I mistyped this) and the security that is to be applied to the credentials (ntlm in this case). To save having no write access to the mounted file share, the uid and gid for your user needs specification, with 1000 being the values for the first non-root user created on a Linux system. After that, it does no harm to set the file and directory permissions because they only can be set at mount time; using chmod, chown and chgrp afterwards, has no effect whatsoever. Here, I have set permissions to read, write and execute for the owner and the user group while only allowing read and execute access for everyone else (that's 775 in the world of chmod).
All of what I have described here worked for me and had to be gleaned from disparate sources like Mount Windows Shares Permanently from the Ubuntu Wiki, another blog entry regarding the permissions settings for a CIFS mount point and an Ubuntu forum posting on mounting CIFS with UTF-8 support. Because of the scattering of information, I just felt that it needed to all together in one place for others to use, and I hope that fulfils someone else's needs similarly to mine.
iPod, identified
9th December 2007Plug in an iPod to a PC running Ubuntu, and it will recognise what it has got. That act mounts the player as a hard drive and fires up the Rhythmbox Music Player. The usual file transfer capabilities are available, and it does something that was thwarted partially by iTunes when I last tried it: transferring files from your iPod to your PC. Only music bought from the iTunes store can be copied from the player back to the PC. Unsurprisingly, you cannot update the iPod's firmware or anything like that. To do such things, you need the iTunes player and that means having either Windows or OS X. While I do wonder if it can't be that difficult to port the OS X version to Linux since they both share UNIX roots, it's over to the Windows VM for me on this one for now.
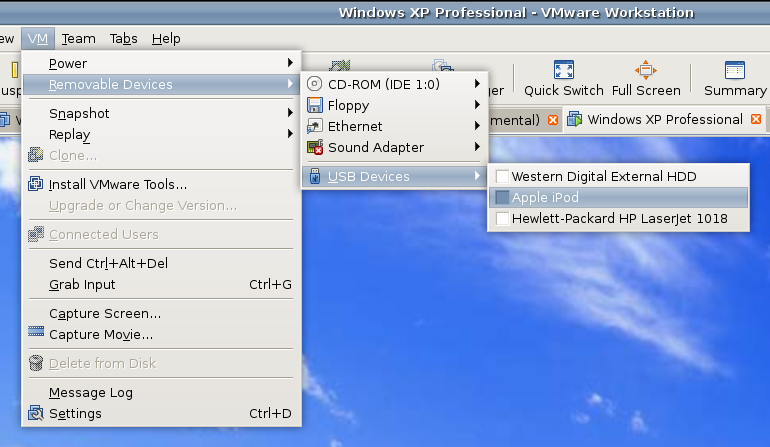
However, while VMware on Windows will happily pick up USB devices as they are connected so long as the VM is in focus, the behaviour on Linux seems to be different. As shown above, you have to go to the VM menu and potter down the chain (Removable Devices > USB Devices) to make the device of interest accessible. Dialogue boxes asking you if you wish to disconnect the device from the host operating system will appear, and the process may be unsubtle as you progress with it. In fact, Ubuntu was delivering warning messages about how its iPod connection got lost; it would have been wise to unmount the thing in the first place. Accessing USB devices like this opens up other possibilities: using Windows for scanning and for printing digital images.
Returning to the iPod story, Windows will see it once it has been made available and iTunes can access it accordingly. Then, you are free to update the gadget's firmware or manage the music stored on it if you prefer.