TOPIC: COMPARISON OF X WINDOW SYSTEM DESKTOP ENVIRONMENTS
Making GNOME Shell work through extensions and customisation
21st September 2012There has been a lot of doom and gloom spoken about the GNOME desktop environment and the project behind it. These days, it seems to be the fashionable thing to go constantly criticising it, especially after what Linus Torvalds said. KDE went through the same sort of experience a few years ago and seems to have got far enough beyond it that some are choosing it instead of GNOME. For a good while, it was the other way around.
Since its inception, the GNOME Shell has attracted a lot of adverse comment. However, since my first encounter, it has grown on me to the point that I added it to Ubuntu and Linux Mint and use it as my default desktop environment instead of Unity, Mate or Cinnamon. The first of these may not be so surprising because of the unique approach that has been taken. The use of lenses and an application launch bar are items to which I could adapt, but it is the merging of application menus and title bars with the top panel of the desktop that really puts me off it. Application window buttons can be moved to the right everywhere but on this global menu, so I tend to view things from afar instead of using it every day. There just is something about the experience that won't grow on me. Strangely, that also applies to my impressions of KDE, albeit differently; there just is something less slick about the appearance of the bottom panel, the plasmoids and other items like them.
Given that Mate and Cinnamon continue the GNOME 2 approach to things that dominated my home computing for much of the last five years since I turned to Ubuntu, my decision to use GNOME Shell instead of either come as a surprise. It isn't that the environments aren't slick enough, just that I have come to prefer the way that GNOME Shell handles workspaces, spawning them as you need them. If that could be an option in Cinnamon, then it might become my desktop of choice. However, that seems to go against the philosophy of the project, even if someone adds and extension for it.
For a time, I played with going with LXDE rather than either Unity or GNOME Shell; as it happened, my first impressions of the latter weren't so positive until I spent a day with the GNOME variant of Fedora 15. Being not dissimilar to GNOME 2 in the way that it worked was the main attraction of LXDE and my initial use of it was with Lubuntu running on a netbook; the LXDE version of Linux Mint 12 now runs on it so there hasn't been so much change on that machine.
Sometimes, the only way to deal with change is to have a look at it to see what's coming and to decide what you need to do about it. In the case of GNOME Shell, my day with Fedora 15 on a backup PC changed my impressions, and Linux Mint 11's GNOME 2 desktop looked a bit old-fashioned afterwards. In fact, I popped GNOME 3 on there and have been using it as my main desktop environment ever since.
With computing, there always are some who expect things to just work and be the way that they want them. The need for extra configuration is a criticism that still can be levelled at GNOME Shell. Before going with Mate and Cinnamon, Linux Mint went the same way for a while, leaving me to wonder what can be done with such an approach. Will someone else pick up that baton and do the handiwork so that users don't have to do it? Not yet, it seems. Since no one is following the lead of Linux Mint 12, the need for user tweaking remains, even if I have found which ones work for me.
The first place to begin is GNOME's Extensions website, from where I raid a few extensions every time I do an operating system installation. The Alternative Status Menu extension is among the first to get added so that I have the shutdown option again on the user menu, a common criticism of the default set up. Since I always install the GNOME Tweak Tool from the distro repositories, I add the Advanced Setting in User Menu extension to get an entry in the status menu that grants quick access. Frippery Bottom Panel comes next on the list because of its workspace switcher and application window list. Others like Frippery Move Clock, Monitor Status Indicator, Places Status Indicator, Removable Drive Menu, Remove Accessibility, Shell Restart User Menu Entry and User Themes follow in some order and make things feel more pleasing, at least to my mind.
You aren't stuck with the default theme, either, and I have chosen Elementary Luna from deviantART. For adding your own themes, the above listed User Themes extension is needed. Because I want the Frippery Bottom Panel to match the top panel, I tweaked its stylesheet and that's where the Restart User Menu Entry extension is useful, though some care is needed not to crash the desktop with constant shell restarts.
Doing the above makes GNOME Shell really amenable to me, and I wouldn't like to lose that freedom to customise. Saying that, the continued controversial changes aren't stopping yet. Those made to the Nautilus file manager in GNOME 3.6 have caused the Linux Mint project to create Nemo, a fork of the software, and Ubuntu is sticking with the previous version for now. Taking some action yourself instead of just complaining loudly sounds like a more positive approach, which makes its own statement. However, at a time when many want the GNOME project team to listen to users, the new Nautilus appears and is not to be what they needed to see. Could the project go on like this? Only time can answer that one.
While it appears that many have changed from GNOME to other desktop environments, I haven't come across any numbers. A reducing user base could be a way of sending a message about any discontent, one that makes use of a great feature of free software: there is plenty of choice. If the next version of Nautilus isn't to my taste, there are plenty of alternatives out there. After all, Cinnamon started on Linux Mint and has gone from there to being available for other distros too; Fedora is one example. Nemo could follow suit.
Now that GNOME's constituent applications are seeing changes, GNOME Shell may be left to mature. Computer interfaces are undergoing a lot of change right now, and Microsoft Windows 8 is bringing its own big leap. Though controversial at the time, change can be a good thing too and us technical folk always like seeing new things come along (today saw the launch of the iPhone 5 and many folk queueing up for it; Google's Nexus 7 ran out of stock in its first weeks on the market; there are more). That could be what got me using GNOME 3 in the first place, even if my plan is to stick with it for a while yet.
How the Cinnamon desktop environment offers a conventional alternative to the experimental approaches of others
28th January 2012The computer on which I am writing these words is running Linux Mint with the Cinnamon desktop environment, a fork of GNOME Shell. This looks as if it will be the default face of GNOME 3 in the next version of Linux Mint, with the MGSE dressing up of GNOME Shell looking more and more like an interim measure until something more consistent was available. While some complained that what was delivered in version 12 of the distribution was a sort of greatest hits selection, I reckon that bets were being hedged by the project team.
Impressions of what's coming
By default, you get a single panel at the bottom of your screen with everything you need in there. However, it is possible to change the layout so that the panel is at the top or there are two panels, one at the top and the other at the bottom. So far, there is no means of configuring which panel applet goes where, as was the case in Linux Mint 11 and its predecessors. However, the default placements are very sensible, so I have no cause for complaint at this point.
Just because you cannot place applets doesn't mean that there is no configurability, though. Since Cinnamon is extensible, you can change the way that time is displayed in the clock, as well as enabling additional applets. It is also possible to control visual effects, such as the way new application windows pop up on a screen.
GNOME 3 is there underneath all of this, though there's no sign of the application dashboard of GNOME Shell. The continually expanding number of slots in the workspace launcher is one sign, as is the enabling of a hotspot at the top right hand corner by default. This brings up an overview screen showing what application windows are open in a workspace. The new Mint menu even gets the ability to search through installed applications, together with the ability to browse through what's available.
In summary, Cinnamon already looks good, though a little polish and extra configuration options wouldn't go amiss. An example of the former is the placement of desktop numbers in the workspace switcher, and I already have discussed the latter. It does appear that the Linux Mint approach to desktop environments is taking shape with a far more conventional feel than the likes of Unity or GNOME Shell. Just as Cinnamon has become available in openSUSE, I can see it gracing LMDE too whenever Debian gets to moving over to GNOME 3 as must be inevitable now unless they take another approach such as MATE.
In comparison with a revolution
While Linux Mint are choosing convention and streamlining GNOME to their own designs, it appears that Ubuntu's Unity is getting ever more experimental as the time when Ubuntu simply evolved from one release to the next becomes an increasingly more distant memory. The latest development is the announcement that application menus could get replaced by a heads-up display (HUD) instead. That would be yet another change made by what increasingly looks like a top-down leadership, reminiscent of what exists at Apple. While it is good to have innovation, you have to ask where users fit in all of this when Linux Mint already has gained from what has been done so far and may gain more again. Still, seeing what happens to Ubuntu sounds like an interesting pastime, though I'm not sure that I'd be depending on the default spin of this distro as my sole operating system right now. Also, changing the interface every few months wouldn't work in a corporate environment at all, so you have to wonder where Mark Shuttleworth is driving all this, though Microsoft is engaging in a bit of experimentation of its own. We are living in interesting times for the computer desktop, so it's just as well that there are safe havens like Linux Mint, too. Watching from afar sounds safer.
Making Nautilus work like it does in Ubuntu for any other GNOME-using distro
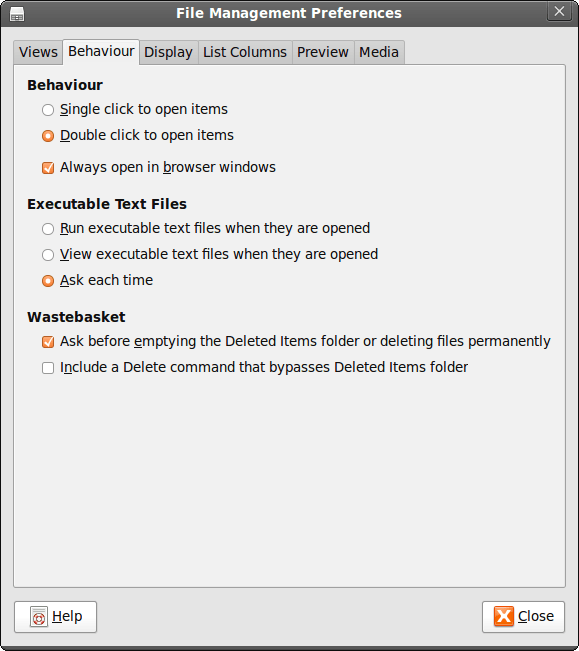
26th July 2009While It's a personal preference, I like the way that Nautilus (GNOME's default file manager if you need to know) is set to work on Ubuntu by default. For some tastes, it might look too similar to Windows Explorer, but having all the action happening in the same window is a convenience that users of other GNOME using distributions may not realise is there at all. By default, Debian and Fedora use what is called spatial mode, with each double-clicking action on a folder icon firing up a new window. Personally, I think that clutters the desktop without good cause, yet it's easy to change. All that's needed is to go to Edit>Preferences in a Nautilus window, proceed to the Behaviour tab and toggle the Always open in browser windows tick box as shown below. Quite why this is not the default in all GNOME using distributions is beyond me, but others may prefer what I dislike and Linux is all about choice, after all. Well, you can decide to use Gnome Commander instead and there are times when I do the same along with being a command line user too.
Choices, choices…
10th November 2007While choice is a great thing, too much of it can be confusing, and the world of Linux is a one very full of decisions. The first of these centres around the distro to use when taking the plunge; you quickly find that there can be quite a lot to it. In fact, it is a little like buying your first SLR/DSLR or your first car: you only really know what you are doing after your first one. Putting it another way, you only know how to get a house built after you have done just that.
With that in mind, it is probably best to play a little on the fringes of the Linux world before committing yourself. It used to be that you had two main choices for your dabbling:
- using a spare PC
- dual booting with Windows by either partitioning a hard drive or dedicating one for your Linux needs.
In these times, innovations such as Live CD distributions and virtualisation technology keep you away from such measures. In fact, I would suggest starting with the former and progressing to the latter for more detailed perusal; it's always easy to wipe and restore virtual machines anyway, so you can evaluate several distros at the same time if you have the hard drive space. It also a great way to decide which desktop environment you like. Otherwise, terms like KDE, GNOME, XFCE, etc. might not mean much.
The mention of desktop environments brings me to software choices because they do drive what software is available to you. For instance, the Outlook lookalike that is Evolution is more likely to appear where GNOME is installed than where you have KDE. The opposite applies to the music player Amarok. Nevertheless, you do find certain stalwarts making a regular appearance; Firefox, OpenOffice and the GIMP all fall into this category.
The nice thing about Linux is that distros more often than not contain all the software that you are likely to need. However, that doesn't mean that it is all on the disk and that you have to select what you need during the installation. Though there might have been a time when it might have felt like that, my recent experience has been that a minimum installation is set in place that does all the basics for you to easily add the extras later on an as needed basis. I have also found that online updates are a strong feature too.
Picking up what you need when you need it has major advantages, the big one being that Linux grows with you. You can add items like Apache, PHP and MySQL when you know what they are and why you need them. It's a long way from picking applications of which you know very little at installation time and with the suspicion that any future installation might land you in dependency hell while performing compilation of application source code; the temptation to install everything that you saw was a strong one. The "learn before you use" approach favoured by how things are done nowadays is an excellent one.
Even if life is easier in the Linux camp these days, there is no harm in sketching out your software needs. Any distribution should be able to fulfil most if not all of them. As it happened, the only third party application that I have needed to install on Ubuntu without recourse to Synaptic was VMware Workstation, and that procedure thankfully turned out to be pretty painless.