A look at Windows 8.1
4th July 2013Last week, Microsoft released a preview of Windows 8.1 and some hailed the return of the Start button but the reality is not as simple as that. Being a Linux user, I am left wondering if ideas have been borrowed from GNOME Shell instead of putting back the Start Menu like it was in Windows 7. What we have got is a smoothing of the interface that is there for those who like to tweak settings and not available be default. GNOME Shell has been controversial too so borrowing from it is not an uncontentious move even if there are people like me who are at home in that kind of interface.
What you get now is more configuration options to go with the new Start button. Right clicking on the latter does get you a menu but this is no Start Menu like we had before. Instead, we get a settings menu with a “Shut down” entry. That’s better than before, which might be saying something about what was done in Windows 8, and it produces a sub-menu with options of shutting down or restarting your PC as well as putting it to sleep. Otherwise, it is place for accessing system configuration items and not your more usual software, not a bad thing but it’s best to be clear about these things. Holding down the Windows key and pressing X will pop up the same menu if you prefer keyboard shortcuts and I have a soft spot for them too.
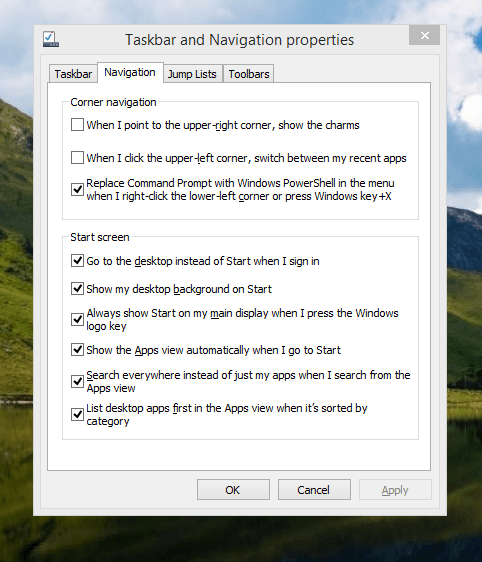
The real power is to be discovered when you right click on the task bar and select the Properties entry from the pop-up menu. Within the dialogue box box that appears, there is the Navigation tab that contains a whole plethora of interesting options. Corner navigation can be scaled back to remove the options of switching between applications at the upper left corner or getting the charms menu from the upper right corner. Things are interesting in the Start Screen section. This where you tell Windows to boot to the desktop instead of the Start Screen and adjust what the Start button gives you. For instance, you can make it use your desktop background and display the Start Screen Apps View. Both of these make the new Start interface less intrusive and make the Apps View feel not unlike the way GNOME Shell overlays your screen when you hit the Activities button or hover over the upper left corner of the desktop.
It all seems rather more like a series of little concessions and not the restoration that some (many?) would prefer. Classic Shell still works for all those seeking an actual Start Menu and even replaces the restored Microsoft Start button too. So, if the new improvements aren’t enough for you, you still can take matters into your own hands until you start to take advantage of what’s new in 8.1.
Apart from the refusal to give us back a Windows 7 style desktop experience, we now have a touchscreen keyboard button added to the taskbar.So far, it always appears there even when I try turning it off. For me, that’s a bug and it’s something that I’d like to see fixed before the final release.
All in all, Windows 8.1 feels more polished than Windows 8 was and will be a free update when the production version is released. My explorations have taken place within a separate VMware virtual machine because updating a Windows 8 installation to the 8.1 preview is forcing a complete re-installation on yourself later on. There are talks about Windows 9 now but I am left wondering if going for point releases like 8.2, 8.3, etc. might be a better strategy for Microsoft. It still looks as if Windows 8 could do with continual polishing before it gets more acceptable to users. 8.1 is a step forward and more like it may be needed yet.
Turning on autocompletion for the bash shell in terminal sessions
26th June 2013At some point, I managed to lose the ability to have tab key based autocompletion on terminal sessions on my Ubuntu GNOME machine. Wanting it back had me turn to the web for an answer and I found it on a Linux Mint forum; the bash shell is so pervasive in the UNIX and Linux worlds that you can look anywhere for a fix like this.
The problem centred around the .bashrc file in my home area. It does have quite a few handy custom aliases and I must have done a foolish spring clean on the file sometime. That is the only way that I can explain how the following lines got removed:
if [ -f /etc/bash_completion ]; then
. /etc/bash_completion
fi
What they do is look to see if /etc/bash_completion can be found on your system and to use it for tab-based autocompletion. With the lines not in .bashrc, it couldn’t happen. Others may replace bash_completion with bash.bashrc to got a fuller complement of features but I’ll stick with what I have for now.
A need to update graphics hardware
16th June 2013Not being a gaming enthusiast, having to upgrade graphics cards in PC’s is not something that I do very often or even rate as a priority. However, two PC’s in my possession have had that very piece of hardware upgraded on them and it’s not because anything was broken either. My backup machine has seen quite a few Linux distros on there since I built it nearly four years ago. The motherboard is an ASRock K10N78 that sourced from MicroDirect and it has onboard an NVIDIA graphics chip that has performed well if not spectacularly. One glitch that always existed was a less than optimal text rendering in web browsers but that never was enough to get me to add a graphics card to the machine.
More recently, I ran into trouble with Sabayon 13.04 with only the 2D variant of the Cinnamon desktop environment working on it and things getting totally non-functional when a full re-installation of the GNOME edition was attempted. Everything went fine until I added the latest updates to the system when a reboot revealed that it was impossible to boot into a desktop environment. Some will relish this as a challenge but I need to admit that I am not one of those. In fact, I tried out two Arch-based distros on the same PC and got the same results following a system update on each. So, my explorations of Antergos and Manjaro have to continue in virtual machines instead.
To get a working system, I gave Linux Mint 15 Cinnamon a go and that worked a treat. However, I couldn’t ignore that the cutting edge distros that I tried before it all took exception to the onboard NVIDIA graphics. systemd has been implemented in all of these and it seems reasonable to think that it is coming to Linux Mint at some stage in the future so I went about getting a graphics card to add into the machine. Having had good experiences with ATi’s Radeon in the past, I stuck with it even though it now is in the hands of AMD. Not being that fussed so long there was Linux driver support, I picked up a Radeon HD 6450 card from PC World. Adding it into the PC was a simpler of switching off the machine, slotting in the card, closing it up and powering it on again. Only later on did I set the BIOS to look for PCI Express graphics before anything else and I could have got away without doing that. Then, I made use of the Linux Mint Additional Driver applet in its setting panel to add in the proprietary driver before restarting the machine to see if there were any visual benefits. To sort out the web browser font rendering, I used the Fonts applet in the same settings panel and selected full RGBA hinting. The improvement was unmissable if not still like the appearance of fonts on my main machine. Overall, there had been an improvement and a spot of future proofing too.
That tinkering with the standby machine got me wondering about what I had on my main PC. As well as onboard Radeon graphics, it also gained a Radeon 4650 card for which 3D support wasn’t being made available by Ubuntu GNOME 12.10 or 13.04 to VMware Player and it wasn’t happy about this when a virtual machine was set to have 3D support. Adding the latest fglrx driver only ensured that I got a command line instead of a graphical interface. Issuing one of the following commands and rebooting was the only remedy:
sudo apt-get remove fglrx
sudo apt-get remove fglrx-updates
Looking at the AMD website revealed that they no longer support 2000, 3000 or 4000 series Radeon cards with their latest Catalyst driver the last version that did not install on my machine since it was built for version 3.4.x of the Linux kernel. A new graphics card then was in order if I wanted 3D graphics in VWware VM’s and both GNOME and Cinnamon appear to need this capability. Another ASUS card, a Radeon HD 6670, duly was acquired and installed in a manner similar to the Radeon HD 6450 on the standby PC. Apart from not needing to alter the font rendering (there is a Font tab on Gnome Tweak Tool where this can be set), the only real exception was to add the Jockey software to my main PC for installation of the proprietary Radeon driver. The following command does this:
sudo apt-get install jockey-kde
When that was done I issue the jockey-kde command and selected the first entry on the list. The machine worked as it should on restarting apart from an AMD message at the bottom right hand corner bemoaning unrecognised hardware. There had been two entries on that Jockey list with exactly the same name so it was time to select the second of these and see how it went. On restarting, the incompatibility message had gone and all was well. VMware even started virtual machines with 3D support without any messages so the upgrade did the needful there.
Hearing of someone doing two PC graphics card upgrades in a weekend may make you see them as an enthusiast but my disinterest in computer gaming belies this. Maybe it highlights that Linux operating systems need 3D more than might be expected. The Cinnamon desktop environment now issues messages if it is operating in 2D mode with software 3D rendering and GNOME always had the tendency to fall back to classic mode, as it had been doing when Sabayon was installed on my standby PC. However, there remain cases where Linux can rejuvenate older hardware and I installed Lubuntu onto a machine with 10 year old technology on there (an 1100 MHz Athlon CPU, 1GB of RAM and 60GB of hard drive space in case dating from 1998) and it works surprisingly well too.
It seems that having fancier desktop environments like GNOME Shell and Cinnamon means having the hardware on which it could run. For a while, I have been tempted by the possibility of a new PC since even my main machine is not far from four years old either. However, I also spied a CPU, motherboard and RAM bundle featuring an Intel Core i5-4670 CPU, 8GB of Corsair Vengence Pro Blue memory and a Gigabyte Z87-HD3 ATX motherboard included as part of a pre-built bundle (with a heatsink and fan for the CPU) for around £420. Even for someone who has used AMD CPU’s since 1998, that does look tempting but I’ll hold off before making any such upgrade decisions. Apart from exercising sensible spending restraint, waiting for Linux UEFI support to mature a little more may be no bad idea either.
Update 2013-06-23: The new graphics card in my main machine is working as it should and has reduced the number of system error report messages turning up too; maybe Ubuntu GNOME 13.04 didn’t fancy the old graphics card all that much. A rogue .fonts.conf file was found in my home area on the standby machine and removing it has improved how fonts are displayed on there immeasurably. If you find one on your system, it’s worth doing the same or renaming it to see if it helps. Otherwise, tinkering with the font rendering settings is another beneficial act and it even helps on Debian 6 too and that uses GNOME 2! Seeing what happens on Debian 7.1 could be something that I go testing sometime.
A little look at Debian 7.0
12th May 2013Having a virtual machine with Debian 6 on there, I was interested to hear that Debian 7.0 is out. In another VM, I decided to give it a go. Installing it on there using the Net Install CD image took a little while but proved fairly standard with my choice of the GUI-based option. GNOME was the desktop environment with which I went and all started up without any real fuss after the installation was complete; it even disconnnected the CD image from the VM before rebooting, a common failing in many Linux operating installations that lands into the installation cycle again unless you kill the virtual machine.
Though the GNOME desktop looked familiar, a certain amount of conservatism reigned too since the version was 3.4.2. That was no bad thing since raiding the GNOME Extension site for a set of mature extensions was made all the more easy. In fact, a certain number of these was included in the standard installation anyway and the omission of a power off entry on the user menu was corrected as a matter of course without needing any intervention from this user. Adding to what already was there made for a more friendly desktop experience in a short period of time.
Debian’s variant of Firefox , Iceweasel, is version 10 so a bit of tweaking is needed to get the latest version. LibreOffice is there now too and it’s version 3.5 rather than 4. Shotwell too is the older 0.12 and not the 0.14 that is found in the likes of Ubuntu 13.04. As it happens, GIMP is about the only software with a current version and that is 2.8; a slower release cycle may be the cause of that though. All in all, the general sense is that older versions of current software are being included for the sake of stability and that is sensible too so I am not complaining very much about this at all.
The reason for not complaining is that the very reason for having a virtual machine with Debian 6 on there is to have Zinio and Dropbox available too. Adobe’s curtailment of support for Linux means that any application needing Adobe Air may not work on a more current Linux distribution. That affects Zinio so I’ll be retaining a Debian 6 instance for a while yet unless a bout of testing reveals that a move to the newer version is possible. As for Dropbox, I am sure that I can recall why I moved it onto Debian but it’s working well on there so I am in no hurry to move it over either. There are times when slower software development cycles are better…
Getting an Epson Pefection 4490 Photo scanner going with Ubuntu GNOME Remix 12.10
7th March 2013My Epson Perfection 4490 Photo scanner has been in my possession for a while now and its impossible to justify any replacement given that it both works well and digital photography has taken over from its film predecessor for me. Every time I go installing an operating system afresh, I need to reinstate it again and last year’s installation of Ubuntu GNOME Remix 12.04 only saw me do the deed recently. When I did so, it was brought back to me that I’d never gone and documented on here how this was done. Given that I sometimes use this place as a repository of stuff to which I need to refer again in the future, it seemed remiss of me so here it is for you all.
Though I had XSane and SimpleScan already installed on the system, Sane wasn’t on there so I went and added it and a few other extras using the following command:
sudo apt-get install sane sane-utils libsane-extras
Then, it was onto the Epson website for their Perfection 4490 Photo Linux drivers since Sane’s support for this scanner seemingly remains incomplete even though it pre-dates my move to Linux in 2007. Three files were needed and the following commands install them (depending on when you do this, the file names may be different so just change them to whatever they are for you; it can be done with a single command too but there is not enough girth for that here):
sudo dpkg -i iscan-data_1.22.0-1_all.deb
sudo dpkg -i iscan_2.29.1-5~usb0.1.ltdl7_i386.deb
sudo dpkg -i iscan-plugin-gt-x750_2.1.2-1_i386.deb
With those in place, there was one other task that needed doing so that scanning could be done without resorting to running scanning software using sudo privileges. To free up the access to a normal user account, I needed a HAL device information file. These normally are in /usr/share/hal/fdi/ but they change every time an installation so any modifications that you may make are going to be lost. Therefore, there is no point modifying either /usr/share/hal/fdi/preprobe/10osvendor/20-libsane.fdi or /usr/share/hal/fdi/preprobe/10osvendor/20-libsane-extras.fdi where scanner information usually is to be found.
The first task in creating an fdi file was to issue the lsusb command and look for a line corresponding to my scanner. This is the one that I got:
Bus 001 Device 004: ID 04b8:0119 Seiko Epson Corp. Perfection 4490 Photo
From this, I gleaned the manufacturer ID and model ID as 04b8 and 0119, respectively. These are needed later on. Next I needed to create the hal/fdi/preprobe/ folder structure under /etc since it was there. Then, I created epson4490photo.fdi in the bottom folder of the tree (/etc/hal/fdi/preprobe/epson4490photo.fdi) as follows:
cd /etc/hal/fdi/preprobe/ && sudo touch epson4490photo.fdi
Then, I edited the new file using the following command:
gksu gedit epson4490photo.fdi &
When open, I added in the following text:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<deviceinfo version="0.2">
<device>
<match key="info.subsystem" string="usb">
<!-- Epson Perfection 4490 Photo -->
<match key="usb.vendor_id" int="0x04b8">
<match key="usb.product_id" int="0x0119">
<append key="info.capabilities" type="strlist">scanner</append>
<merge key="scanner.access_method" type="string">proprietary</merge>
</match>
</match>
</match>
</device>
</deviceinfo>
It’s all in XML so the place to look is immediately beneath the scanner name comment. The int attributes of the two match elements immediately following the comment line are populated using the information from the lsusb command output with 0x prefixing both the manufacturer and model identifiers. The element with a key attribute of usb.vendor_id is the former and that with a key attribute of usb.product_id is the latter. With epson4490photo.fdi saved, I rebooted the machine to restart HAL and all was as I wanted it to be apart maybe from XSane making complaints that seemed not to be of any actual consequence. With Epson’s Image Scan! and Simple Scan on the PC, there’s no need to be bothered with those messages. Choice is good when you have it, especially when you have expended some effort to get that far.
Installing the Cinnamon Desktop Environment on Sabayon Linux
26th January 2013During the week, I did an update on my Sabayon system and GNOME 3.6 came on board without to much of a bother. There was no system meltdown or need for an operating system re-installation. However, there was one matter that rankled: adding and updating extensions from extensions. gnome.org was impossible. The process would create a new folder in ~/.local/share/gnome-shell/extensions/ but not fill it with anything at all. Populating from another my Ubuntu GNOME Remix 12.10 machine didn’t seem to achieve the needful and I am left wondering if it is down to the version of GNOME Shell being 3.6.2. However, even adding an entry for the current version of GNOME Shell to metadata.json for one plugin didn’t appear to do what I wanted so resolving this issue needs further enquiry.
In the meantime, I added the Cinnamon desktop environment using the following command and will be using that from now on. If the GNOME Shell extension issue ever gets sorted I may move back but there is no rush. GNOME 3.8 sounds like it’s bringing an interesting option that makes use of the approach Linux Mint took for version 12 of that distribution and I can await that, especially if it avoids the need for adding extension on a personal basis like now.
sudo equo update && sudo equo install cinnamon
With the installation completed by the above command, it was a matter of logging out and choosing the Cinnamon entry (there is a 2D version too) from the session dropdown menu on the login screen to get it going. Then, it was a matter of tweaking Cinnamon to my heart’s content. Getting a two panel layout required logging out and in again as well as choosing the appropriate setting in the Cinnamon Panel options tab. Next, I decided to check on what themes are available at cinnamon.linuxmint.org before settling on Cinnamint 1.6. It all feels very comfortable apart from not having an automatically growing list of workspaces that are a default offering in GNOME Shell. That goes against the design principles of Cinnamon though so only hopes of someone making an extension that does that are left.
Adding Quicktime movie support to Firefox running on Linux
24th January 2013For whatever reason, my installation of Ubuntu GNOME Remix 12.10, didn’t have Quicktime support added to Firefox by default. To make a website work near enough as it was intended, this needed to be remedied. The solution was to issue a command to install the missing software:
sudo apt-get install mplayer gnome-mplayer gecko-mediaplayer
Mplayer is the main component here but running the above command adds all the required supporting packages too so that a Firefox restart was all that needed to get things going.
Sorting a kernel upgrade error in Linux Mint 13
30th November 2012Linux Mint 14 may be out now but I’ll be sticking with its predecessor for now. Being a user of GNOME Shell instead of Cinnamon or Mate, I’ll wait for extensions to get updated for 3.6 before making a move away from 3.4 where the ones that I use happily work. Given that Linux Mint 13 is set to get support until 2017, it’s not as if there is any rush either. Adding the back-ported packages repository to my list of software sources means that I will not miss out on the latest versions of MDM, Cinnamon and Mate anyway. With Ubuntu set to stick to GNOME 3.6 until after 13.04 is released, adding the GNOME 3 Team PPA will be needed if 3.8 arrives with interesting goodies; there are interesting noises that suggest the approach taken in Linux Mint 12 may be used to give more of a GNOME 2 desktop experience. Options abound and there are developments in the pipeline that I hope to explore too.
However, there is one issue that I have had to fix which stymies upgrades within the 3.2 kernel branch. A configuration file (/etc/grub.d/10_linux) points to /usr/share/grub/grub-mkconfig_lib instead of /usr/lib/grub/grub-mkconfig_lib so I have been amending it every time I needed to do a kernel update. However, it just reverts to the previous state so I thought of another solution: creating a symbolic link in the incorrect location that points to the correct one so that updates complete without manual intervention every time. The command that does the needful is below:
sudo ln -s /usr/lib/grub/grub-mkconfig_lib /usr/share/grub/grub-mkconfig_lib
Of course, figuring out what causes the reversion would be good too but the symbolic link fix works so well that there’s little point in exploring it further. Of course, if anyone can add how you’d do that, I’d welcome this advice too. New knowledge always is good.
A place for GNOME?
21st September 2012There has been a lot of doom and gloom spoken about the GNOME desktop environment and the project behind it. These days it seems to be the fashionable thing to go constantly criticising it, especially after what Linus Torvalds said. KDE went through the same sort of experience a few years ago and seems to have got far enough beyond it that some are choosing it in preference to GNOME. For a good while, it was the other way around.
Since its inception, the GNOME Shell has attracted a lot of adverse comment. However, since my first encounter, it has grown on me to the point that I add it to Ubuntu and Linux Mint and use it as my default desktop environment instead of Unity, Mate or Cinnamon. The first of these may not be so surprising because of the unique approach has been taken. The use of lenses and an application launch bar are items to which I could adapt but its the merging of application menus and title bars with the top panel of the desktop that really puts me off it. Application window buttons can be moved to the right everywhere but on this global menu so I tend to view things from afar instead of using it everyday. There just is something about the experience that won’t grow on me. Strangely, that also applies to my impressions of KDE albeit in a different; there just is something less slick about the appearance of the bottom panel, the plasmoids and other items like them.
Given that Mate and Cinnamon continue the GNOME 2 approach to things that dominated my home computing for much of the last five years since I turned to Ubuntu, my decision to use GNOME Shell in preference to either come as a surprise. It isn’t that the environments aren’t slick enough but that I have come to prefer the way that GNOME Shell handles workspaces, spawning them as you need them. If that could be an option in Cinnamon, then it might become my desktop of choice but that seems to go against the philosophy of the project even if someone adds and extension for it.
For a time, I played with going with LXDE rather than either Unity or GNOME Shell; as it happened, my first impressions of the latter weren’t so positive until I spent a day with the GNOME variant of Fedora 15. Being not dissimilar to GNOME 2 in the way that it worked was the main attraction of LXDE and my initial use of it was with Lubuntu running on a netbook; the LXDE version of Linux Mint 12 now runs on it so there hasn’t been so much change on that machine.
Sometimes, the only way to deal with change is to take a look at it to see what’s coming and to decide what you need to do about it. In the case to GNOME Shell, my day with Fedora 15 on a backup PC changed my impressions and Linux Mint 11’s GNOME 2 desktop looked a bit old-fashioned afterwards. In fact, I popped GNOME 3 on there and have been using it as my main desktop environment ever since.
In computing, there always are some who expect things to just work and be the way that they want them. The need for extra configuration is a criticism that still can be levelled at GNOME Shell. Before going with Mate and Cinnamon, Linux Mint went the same way and I wonder what be done with such an approach. Will someone else pick up that baton and do the handiwork so that users don’t have to do it? Not yet, it seems. Since no one is following the lead of Linux Mint 12, there is a need for user tweaking and I have found which ones work for me and it no longer takes so to do them either.
The first place to begin is GNOME’s Extensions website and I raid a few extensions from there every time I do an operating system installation. The Alternative Status Menu extension is among the first to get added so that I have the shutdown option again on the user menu, a common criticism of the default set up. Since I always install the GNOME Tweak Tool from the distro repositories, I add the Advanced Setting in User Menu extension to get an entry in the status menu that grants quick access. Frippery Bottom Panel comes next on the list because of its workspace switcher and application window list. Others like Frippery Move Clock, Monitor Status Indicator, Places Status Indicator, Removable Drive Menu, Remove Accessibility, Shell Restart User Menu Entry and User Themes follow in some order and make things feel more pleasing, at least to my mind.
You aren’t stuck with the default theme either and I have chosen Elementary Luna from deviantART. For adding your own themes, the above listed User Themes extension is needed. Because I want Frippery Bottom Panel to match the top panel, I tweak its stylesheet and that’s where the Restart User Menu Entry extension comes in handy, though some care is needed not to crash the desktop with constant shell restarts.
Doing the above makes GNOME Shell really amenable to me and I wouldn’t like to lose that freedom to customise. Saying that, the continued controversial changes aren’t stopping yet. Those made to the Nautilus file manager in GNOME 3.6 have caused the Linux Mint project to create Nemo, a fork of the software, and Ubuntu is sticking with the previous version for now. Taking some action yourself instead of just complaining loudly sounds a more positive approach and it too makes its own statement. Many want the GNOME project team to listen to users and the new Nautilus appears not to be what they needed to see. Could the project go on like this? Only time can answer that one.
While it appears that many have changed from GNOME to other desktop environments, I haven’t come across any numbers. A reducing user base could be one way of sending a message and it makes use of a great feature of free software: there is plenty of choice. If the next version of Nautilus isn’t to my taste, there are plenty of alternatives out there. After all, Cinnamon started on Linux Mint and has gone from there to being available for other distros too; Fedora is one example. Nemo could follow suit.
Now that GNOME’s constituent applications are seeing changes, it may be that GNOME Shell is left to mature. Computer interfaces are undergoing a lot of change at the moment and Microsoft Windows 8 is bringing its own big leap. Though controversial at the time, change can be a good thing too and us technical folk always like seeing new things come along (today saw the launch of iPhone 5 and many folk queueing up for it; Google’s Nexus 7 ran out of stock in its first weeks on the market; there are more). That could be what got me using GNOME 3 in the first place and my plan is to stick with it for a while yet.
Synchronising package selections between Linux Mint and Linux Mint Debian Edition
18th April 2012To generate the package list on the GNOME version of Linux Mint, I used the Backup Tool. It simply was a matter of using the Backup Software Selection button and telling it where to put the file that it generates. Alternatively, dpkg can be used from the command line like this:
sudo dpkg --get-selections > /backup/installed-software.txt
After transferring the file to the machine with Linux Mint Debian Edition, I tried using the Backup Tool on there too. However, using the Restore Software Selection button and loading the required only produced an irrecoverable error. Therefore, I set to looking around the web and found a command line approach that did the job for me.
The first step is to load the software selection using dpkg by issuing this command (it didn’t matter that the file wasn’t made using the dpkg command though I suspect that’s what the Linux Mint Backup Tool was doing that behind the scenes):
sudo dpkg --set-selections < /backup/installed-software.txt
Then, I started dselect and chose the installation option from the menu that appeared. First time around, it fell over but trying again was enough to complete the job. Packages available to the vanilla variant of Linux Mint but not found in the LMDE repositories were overlooked as I had hoped and installation of the extra packages had no impact on system stability either.
sudo dselect
Apparently, there is an alternative to using dselect that is based on the much used apt-get command but I didn’t make use of it so cannot say more:
sudo apt-get dselect-upgrade
All that I can say is that the dpkg/dselect combination did what I wanted so I’ll keep them in mind if ever need to synchronise software selections between two Debian-based distributions in the future again. The standard edition of Linux Mint may be based on Ubuntu rather than Debian but Ubuntu is itself based on Debian so the description holds here.