Creating a VirtualBox virtual disk image using the Linux command line
9th September 2019Much of the past weekend was spent getting a working Debian 10 installation up and running in a VirtualBox virtual machine. Because I chose the Cinnamon desktop environment, the process was not as smooth as I would have liked so a minimal installation was performed before I started to embellish as I liked. Along the way, I got to wondering if I could create virtual hard drives using the command line and I found that something like the following did what was needed:
VBoxManage createmedium disk --filename <full path including file name without extension> -size <size in MiB> --format VDI --variant Standard
Most of the options are self-explanatory part from the one named variant. This defines whether the VDI file expands to the maximum size specified using the size parameter or is reserved with the size defined in that parameter. Two VDI files were created in this way and I used these to replace their Debian 8 predecessors and even to save a bit of space too. If you want, you can find out more in the user documentation but this post hopefully gets you started anyway.
Installing Citrix Receiver 13.0 in Ubuntu GNOME 13.10 64-bit
28th November 2013Installing the latest version of Citrix Receiver (13.0 at the time of writing) on 64-bit Ubuntu should be as simple as downloading the required DEB package and double-clicking on the file so that Ubuntu Software Centre can work its magic. Unfortunately, the 64-bit DEB file is faulty so that means that the Ubuntu community how-to guide for Citrix still is needed. In fact, any user of Linux Mint or another distro that uses Ubuntu as its base would do well to have a look at that Ubuntu link.
For sake of completeness, I still am going to let you in on the process that worked for me. Once the DEB file has been downloaded, the first task is to creating a temporary folder where the DEB file’s contents can be extracted:
mkdir ica_temp
With that in place, it then is time to do the extraction and it needs two commands with the second of these need to extract the control file while the first extracts everything else.
sudo dpkg-deb -x icaclient- ica_temp
sudo dpkg-deb --control icaclient- ica_temp/DEBIAN
It is the control file that has been the cause of all the bother because it refers to unavailable dependencies that it really doesn’t need anyway. To open the file for editing, issue the following command:
sudo gedit ica_temp/DEBIAN/control
Then change line 7 (it should begin with Depends:) to: Depends: libc6-i386 (>= 2.7-1), lib32z1, nspluginwrapper. There are other software packages in there that Ubuntu no longer supports and they are not needed anyway. With the edit made and the file saved, the next step is to build a new DEB package with the corrected control file:
dpkg -b ica_temp icaclient-modified.deb
Once you have the package, the next step is to install it using the following command:
sudo dpkg -i icaclient-modified.deb
If it fails, then you have missing dependencies and the following command should sort these before a re-run of the above command again:
sudo apt-get install libmotif4:i386 nspluginwrapper lib32z1 libc6-i386
With Citrix Receiver installed, there is one more thing that is needed before you can use it freely. This is to put Thawte security certificate files into /opt/Citrix/ICAClient/keystore/cacerts. What I had not realised until recently was that many of these already are in /usr/share/ca-certificates/mozilla and linking to them with the following command makes them available to Citrix receiver:
sudo ln -s /usr/share/ca-certificates/mozilla/* /opt/Citrix/ICAClient/keystore/cacerts/
Another approach is to download the Thawte certificates and extract the archive to /tmp/. From there they can be copied to /opt/Citrix/ICAClient/keystore/cacerts and I copied the Thawte Personal Premium certificate as follows:
sudo cp /tmp/Thawte Root Certificates/Thawte Personal Premium CA/Thawte Personal Premium CA.cer /opt/Citrix/ICAClient/keystore/cacerts/
Until I found out about what was in the Mozilla folder, I simply picked out the certificate mentioned in the Citrix error message and copied it over like the above. Of course, all of this may seem like a lot of work to those who are non-tinkerers and I have added a repaired 64-bit DEB package that incorporates all of the above and should not need any further intervention aside from installing it using GDebi, Ubuntu’s Software Centre, dpkg or anything else that does what’s needed.
A look at Ubuntu GNOME 13.10
12th October 2013With its final release being near at hand, I decided to have a look at the beta release of Ubuntu GNOME 13.10 to get a sense of what might be coming. A misstep along the way had me inadvertently download and install the 64-bit edition of 13.04 into a VirtualBox virtual machine. The intention to update that to its soon to be released successor was scuppered by instability so I never did get to try out an in situ upgrade to 13.10. What I had in mind was to issue the following command:
gksu update-manager -d
However, I found another one when considering how Ubuntu Server might be upgraded without the GUI application that is the Update Manager. To update to a development version, the following command is what you need:
sudo do-release-upgrade -d
To upgrade to a final release of of a new version of Ubuntu, drop the -d switch from the above to use the following:
sudo do-release-upgrade
There is one further option that isn’t recommended for moving between Ubuntu versions but I use it to get updates such as new kernel subversions that are released:
sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
Rather than trying out the above, I downloaded the latest ISO image for the beta release of Ubuntu GNOME 13.10 and installed onto a VM that instead. Though it is the 32 bit version of the distro that is installed on my main home PC, it has been the 64 bit version that I have been trying. So far, that seems to be behaving itself even if it feels a little sluggish but that could be down to the four year old PC that hosts the virtual machine. For a while, I have been playing with the possibility of an upgrade involving an Intel Core i5 4670K CPU and 16 GB of RAM (useful for running multiple virtual machines at a time) along with any motherboard that supports those so looking at a 64 bit operating system has its uses.
The Linux kernel may be 3.11 but that is not my biggest concern. Neither is the fact that LibreOffice 4.1.2.3 was included and GIMP wasn’t, especially when that could be added easily anyway and it is version 2.8.6 that you get. The move to GNOME Shell 3.8 was what drew me to seeing what was coming because I have been depending on a number extensions. As with WordPress and plugins, GNOME Shell seems to have a tempestuous relationship with some of its extensions and I wanted to see which ones still worked. There also has been a change to the backstage application view in that you either get all installed applications displayed when you browse them or you have to start typing the name of the one you want to select it. Losing the categorical view that has been there until GNOME Shell 3.6 is a step backwards and I hope that version 3.10 has seen some sort of a reinstatement. There is a way to add these categories and the result is not as it once was either; also, it shouldn’t be necessary for anyone to dive into a systems innards to address things like this. With all the constant change, it is little wonder that Cinnamon has become a standalone entity with the release of its version 2.0 and that Debian’s toyed with not going with GNOME for its latest version (7.1 at the time of writing and it picked a good GNOME Shell version in 3.4).
Having had a look at other distribution that already have GNOME Shell 3.8, I knew that a few of my extensions worked with it. The list includes Frippery Bottom Panel, Frippery Move Clock, Places Status Indicator, Removable Drive Menu, Remove Rounded Corners (not really needed with the GNOME Shell theme that I use, Elementary Luna 3.4, but I retain it anyway), Show Desktop Button, User Themes and Ignore_Request_Hide_Titlebar. Because of the changes to the backstage view, I added Frippery Applications Menu in preference to Applications Menu because I have found that to be unstable. Useful new discoveries have included Curtains Up and GNOME Shell Open Terminal while Shell Restart User Menu Entry has made a return and found a use this time around too.
There have been some extensions that were not updated to work with GNOME Shell 3.8 that I have got working. In some cases, it was as simple as updating the metadata.json file for an extension with new version numbers of 3.8 and 3.84 to the list associated with the shell version property. All extensions are to be found in the .local/share/gnome-shell/extensions location in your home directory and each has a dedicated file containing the aforementioned file.
With others, it was a matter of looking in the Looking Glass (execute lg in the box that ALT + F2 brings up on your screen to access this) and seeing what error messages were to be found in there before attempting to correct these in either the extensions’ extension.js files or whatever JavaScript (*.js) file was causing the problem. With either or both of these remedies, I managed to port the four extensions below to GNOME Shell 3.8. In fact, you can download these zip files and install them yourself to see how you get on with them.
Advanced Settings in User Menu
There is a Remove Panel App Menu that works with GNOME Shell 3.8 but I found that it got rid of the Places menu instead of the panel’s App Menu so I tried porting the older extension to see if it behaved itself and it does. With these in place, I have bent Ubuntu GNOME 13.10 to my will ahead of its final release next week and that includes customising Nautilus too. Other than a new version of GNOME Shell, it looks as if it will come with less in the way of drama and a breather like that is no bad thing given that personal computing continues to remain in a state of flux these days.
A little look at Debian 7.0
12th May 2013Having a virtual machine with Debian 6 on there, I was interested to hear that Debian 7.0 is out. In another VM, I decided to give it a go. Installing it on there using the Net Install CD image took a little while but proved fairly standard with my choice of the GUI-based option. GNOME was the desktop environment with which I went and all started up without any real fuss after the installation was complete; it even disconnnected the CD image from the VM before rebooting, a common failing in many Linux operating installations that lands into the installation cycle again unless you kill the virtual machine.
Though the GNOME desktop looked familiar, a certain amount of conservatism reigned too since the version was 3.4.2. That was no bad thing since raiding the GNOME Extension site for a set of mature extensions was made all the more easy. In fact, a certain number of these was included in the standard installation anyway and the omission of a power off entry on the user menu was corrected as a matter of course without needing any intervention from this user. Adding to what already was there made for a more friendly desktop experience in a short period of time.
Debian’s variant of Firefox , Iceweasel, is version 10 so a bit of tweaking is needed to get the latest version. LibreOffice is there now too and it’s version 3.5 rather than 4. Shotwell too is the older 0.12 and not the 0.14 that is found in the likes of Ubuntu 13.04. As it happens, GIMP is about the only software with a current version and that is 2.8; a slower release cycle may be the cause of that though. All in all, the general sense is that older versions of current software are being included for the sake of stability and that is sensible too so I am not complaining very much about this at all.
The reason for not complaining is that the very reason for having a virtual machine with Debian 6 on there is to have Zinio and Dropbox available too. Adobe’s curtailment of support for Linux means that any application needing Adobe Air may not work on a more current Linux distribution. That affects Zinio so I’ll be retaining a Debian 6 instance for a while yet unless a bout of testing reveals that a move to the newer version is possible. As for Dropbox, I am sure that I can recall why I moved it onto Debian but it’s working well on there so I am in no hurry to move it over either. There are times when slower software development cycles are better…
Using a variant of Debian’s Iceweasel that keeps pace with Firefox
5th February 2013Left to its own devices, Debian will leave you with an ever ageing re-branded version of Firefox that was installed at the same time as the rest of the operating system. From what I have found, the main cause of this was that Mozilla’s wanting to retain control of its branding and trademarks in a manner not in keeping with Debian’s Free Software rules. This didn’t affect just Firefox but also Thunderbird, Sunbird and Seamonkey with Debian’s equivalents for these being IceDove, IceOwl and IceApe, respectively.
While you can download a tarball of Firefox from the web and use that, it’d be nice to get a variant that updated through Debian’s normal apt-get channels. In fact, IceWeasel does get updated whenever there is a new release of Firefox even if these updates never find their way into the usual repositories. While I have been know to take advantage of the more frozen state of Debian compared with other Linux distributions, I don’t mind getting IceWeasel updated so it isn’t a security worry.
The first step in so doing is to add the following lines to /etc/apt/sources.list using root access (using sudo, gksu or su to assume root privileges) since the file normally cannot be edited by normal users:
deb http://backports.debian.org/debian-backports squeeze-backports main
deb http://mozilla.debian.net/ squeeze-backports iceweasel-release
With the file updated and saved, the next step is to update the repositories on your machine using the following command:
sudo apt-get update
With the above complete, it is time to overwrite the existing IceWeasel installation with the latest one using an apt-get command that specifies the squeeze-backports repository as its source using the -t switch. While IceWeasel is installed from the iceweasel-release squeeze-backports repository, there dependencies that need to be satisfied and these come from the main squeeze-backports one. The actual command used is below:
sudo apt-get install -t squeeze-backports iceweasel
While that was all that I needed to do to get IceWeasel 18.0.1 in place, some may need the pkg-mozilla-archive-keyring package installed too. For those needing more information that what’s here, there’s always the Debian Mozilla team.
Synchronising package selections between Linux Mint and Linux Mint Debian Edition
18th April 2012To generate the package list on the GNOME version of Linux Mint, I used the Backup Tool. It simply was a matter of using the Backup Software Selection button and telling it where to put the file that it generates. Alternatively, dpkg can be used from the command line like this:
sudo dpkg --get-selections > /backup/installed-software.txt
After transferring the file to the machine with Linux Mint Debian Edition, I tried using the Backup Tool on there too. However, using the Restore Software Selection button and loading the required only produced an irrecoverable error. Therefore, I set to looking around the web and found a command line approach that did the job for me.
The first step is to load the software selection using dpkg by issuing this command (it didn’t matter that the file wasn’t made using the dpkg command though I suspect that’s what the Linux Mint Backup Tool was doing that behind the scenes):
sudo dpkg --set-selections < /backup/installed-software.txt
Then, I started dselect and chose the installation option from the menu that appeared. First time around, it fell over but trying again was enough to complete the job. Packages available to the vanilla variant of Linux Mint but not found in the LMDE repositories were overlooked as I had hoped and installation of the extra packages had no impact on system stability either.
sudo dselect
Apparently, there is an alternative to using dselect that is based on the much used apt-get command but I didn’t make use of it so cannot say more:
sudo apt-get dselect-upgrade
All that I can say is that the dpkg/dselect combination did what I wanted so I’ll keep them in mind if ever need to synchronise software selections between two Debian-based distributions in the future again. The standard edition of Linux Mint may be based on Ubuntu rather than Debian but Ubuntu is itself based on Debian so the description holds here.
Ubuntu 10.10 and Citrix
15th January 2011Many of us with the opportunity to work from home will have met up with logging via a Citrix server. With that in mind, I set to getting an ICA client going on my main Ubuntu box at home. There is information scattered about the web in the form of question on the Ubuntu forum and a step-by-step guide by Liberian Geek. To summarise the process that I followed here, you have to download a copy of the Citrix Receiver installer for Linux from the company’s website. There, you’ll see DEB and RPM packages along with a tarball for other systems. The latter needs a bit more work so I got the x86 DEB package and installed that in the usual way using Ubuntu’s Software Centre to do the installation following the download. Needing to start the Citrix connection via a browser session meant that a browser restart was needed too. That wasn’t the end of the leg work because Thawte certificate errors were to stop me in my tracks until I downloaded their root certificates from their website. Once the zip file was on my PC, I extracted it and copied the required certificate (Thawte Server CA.cer from the thawte Server CA directory) to /usr/lib/ICAClient/keystore/cacerts on my system; it helped that the error message had told me which was the one I needed from the collection in the zip file. With that matter addressed, the connection happened without a glitch and I was able to get to working without recourse to a Windows virtual machine. For once, Linux wasn’t to be excluded from one of the ways of using computers that has been getting more prevalent these days.
Update 2012-04-14: On an equivalent installation on Linux Mint Debian Edition, I found that the installation location for the certificate had moved to /opt/Citrix/ICAClient/keystore/cacerts. This was for the 64-bit edition.
Update 2012-12-17: The above applied to an installation of version 12.10 on 32-bit Ubuntu GNOME Remix too.
You always can install things yourself…
26th November 2009With Linux distributions offering you everything on a plate, there is a temptation to stick with what they offer rather than taking things into your own hands. For example, Debian’s infrequent stable releases and the fact that they don’t seem to change software versions throughout the lifetime of such a release means that things such as browser versions are fixed for the purposes of stability; Lenny has stuck with Firefox 3.06 and called it Iceweasel for some unknown reason. However, I soon got to grabbing a tarball for 3.5 and popped its contents into /opt where the self-contained package worked without a hitch. The same modus operandii was used to get in Eclipse PDT and that applied to Ubuntu too until buttons stopped working, forcing a jumping of ship to Netbeans. Of course, you could make a mess when veering away from what is in a distribution but that should be good enough reason not to get carried away with software additions. With the availability of DEB packages for things like Adobe Reader, RealPlayer, VirtualBox, Google Chrome and Opera, keeping things clean isn’t so hard. Your mileage may vary when it comes to how well things work out for you but I have only ever had the occasional problem anyway.
What reminded me of this was a recent irritation with the OpenOffice package included in Ubuntu 9.10 whereby spell checking wasn’t working. While there were thoughts about is situ fixes like additional dictionary installations, I ended up plumping for what could be called the lazy option: grabbing a tarball full of DEB packages from the OpenOffice website and extracting its contents into /tmp and, once the URE package was in place, installing from there using the command:
dpkg -i o*
To get application shortcuts added to the main menu, it was a matter of diving into the appropriate subfolder and installing from the GNOME desktop extension package. Of course, Ubuntu’s OpenOffice variant was removed as part of all this but, if you wanted to live a little more dangerously, the external installation goes into /opt so there shouldn’t be too much of a conflict anyway. In any case, the DIY route got me the spell checking in OpenOffice Writer that I needed so all was well and another Ubuntu rough edge eradicated from my life, for now anyway.
Adding Microsoft core fonts to Debian
18th June 2009When setting up Ubuntu, I usually add in Microsoft’s core fonts by installing the msttcorefonts package using either Synaptic or apt-get. I am not sure why I didn’t try doing the same thing for Debian until now but it’s equally as feasible. Just pop over to System > Administration > Software Sources and ensure that the check-boxes for the contrib and non-free categories are checked like you see below.
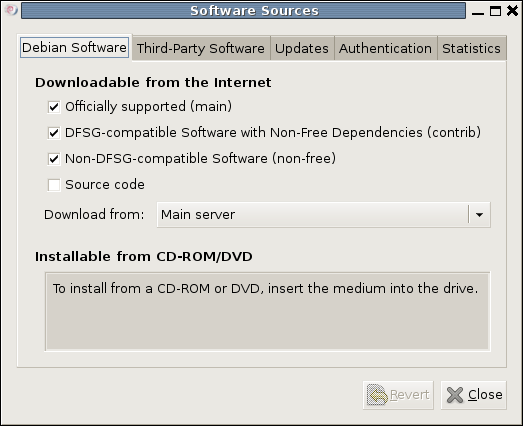
You could also achieve the same end by editing /etc/apt/sources.list and adding the non-free and contrib keywords to make lines look like these before issuing the command apt-get update as root:
deb http://ftp.debian.org/debian/ lenny main non-free contrib
deb-src http://ftp.debian.org/debian/ lenny main non-free contrib
All that you are doing with the manual editing route is performing the same operations that the more friendly front end would do for you anyway. After that, it’s a case of going with the installation method of your choice and restarting Firefox or Iceweasel to see the results.
A quick way to do an update
8th August 2008Here’s a quick way to get the latest updates on your PC using the command line if you are using Ubuntu or Debian:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade
Of course, you can split these commands up if you prefer to look before you leap. At the very least least, it’s so much slicker than the GUI route.